|
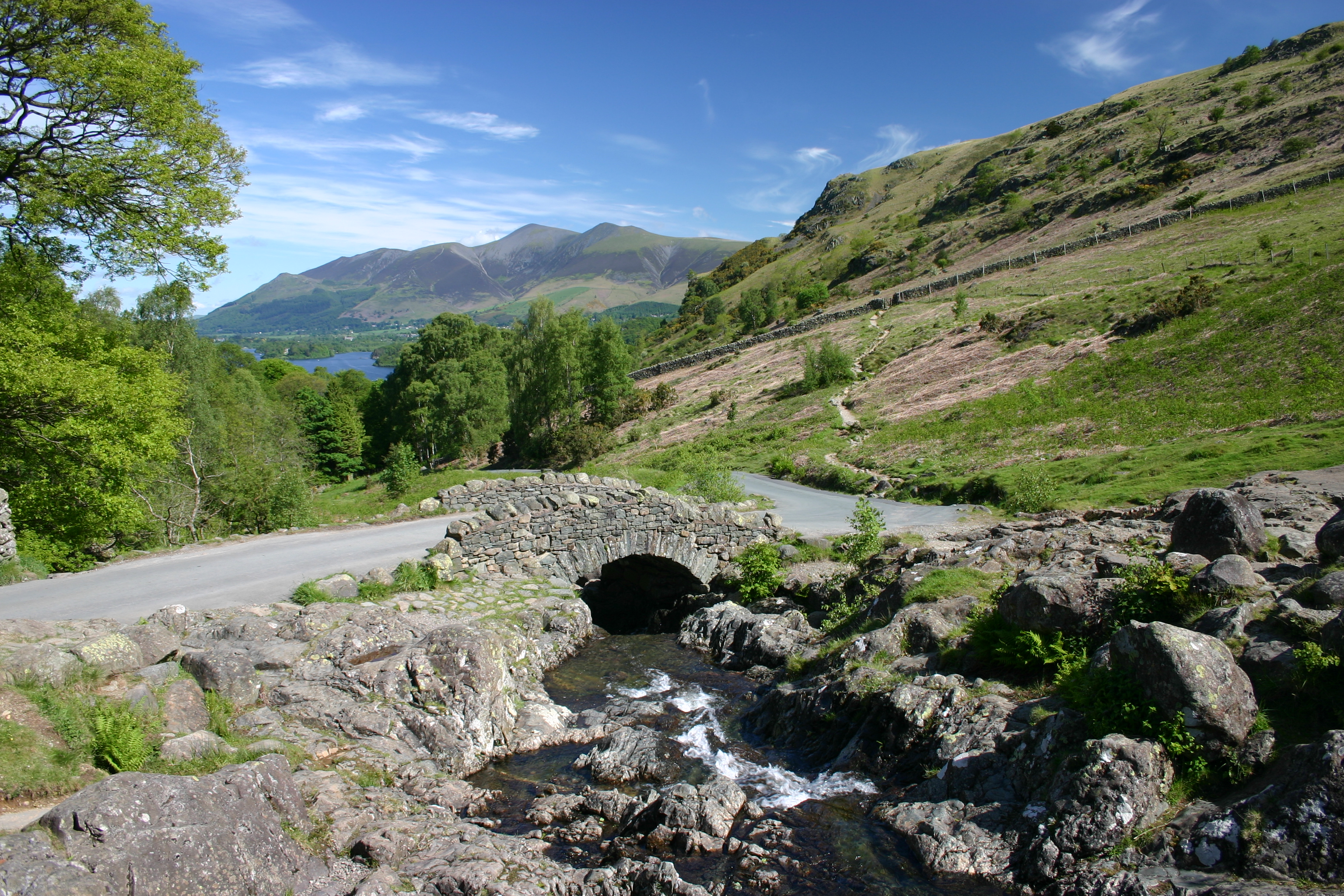
Slater's Bridge
Slater's Bridge is a traditional packhorse bridge in Little Langdale in the English Lake District, standing at National Grid Reference . History and construction The bridge dates back to the 17th century, and became a listed building in 1967. Built of slate, it consists of a segmental arch and a flatter span built of slabs, and incorporates a natural boulder in midstream. The bridge is thought to have been created by miners working in the nearby Tilberthwaite Fells. Already in the 19th century, Alexander Craig Gibson called it "an exquisite and unique specimen of a style of bridge all but extinct"; a century later, Alfred Wainwright called it "the most picturesque footbridge in Lakeland, a slender arch constructed of slate from the quarries and built to give the quarrymen a shorter access from their homes". Literary associations The bridge was acclaimed in a 20th-century poem as "...this/exercise in hanging circularity, toppling stress./The rough slate wedges carry their own ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Brathay
The Brathay is a river of north-west England. Its name comes from Old Norse and means ''broad river''. It rises at a point 1289 feet (393 m) above sea level near the Three Shire Stone at the highest point of Wrynose Pass () in the Lake District. Its catchment area includes the northern flanks of Wetherlam, Great Carrs and others of the Furness Fells, as well as a substantial area of the Langdale Fells. The small stream at the top of Wrynose quickly gathers pace as it descends some 930 feet (283 m) in a distance of about two miles (3.2 km), running roughly parallel to, and south of, the Wrynose Pass road. Before flowing into Little Langdale Tarn it subsumes Bleamoss Beck, the outflow from Blea Tarn. Little Langdale Tarn is also replenished by the Greenburn Beck. The Brathay drains Little Langdale Tarn at its eastern side. It continues in an easterly direction, over Colwith Force where it falls 40 feet (12 m), before turning north and flowing into the tarn of Elter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Little Langdale
Little Langdale is a valley in the Lake District, England, containing Little Langdale Tarn and a hamlet also called Little Langdale. A second tarn, Blea Tarn, is in a hanging valley between Little Langdale and the larger Great Langdale to the north. Little Langdale is flanked on the south and southwest by Wetherlam and Swirl How, and to the north and northwest by Lingmoor Fell and Pike of Blisco. The valley descends to join with Great Langdale above Elter Water. Description Langdale was previously known as ''Langdene'' meaning 'far away wooded valley' and referring to its distance along the flint route from Whitley Bay. Historically Little Langdale was at the intersection of packhorse routes leading to Ravenglass, Whitehaven, Keswick, Penrith & Carlisle, Ambleside, Hawkshead, and Coniston, Ulverston, Broughton-in-Furness and Barrow in Furness. Slater's Bridge which crosses the River Brathay in 3 spans supported by a large mid-stream boulder and stone causeways is a 16th-c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cumbria
Cumbria ( ) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in North West England, bordering Scotland. The county and Cumbria County Council, its local government, came into existence in 1974 after the passage of the Local Government Act 1972. Cumbria's county town is Carlisle, in the north of the county. Other major settlements include Barrow-in-Furness, Kendal, Whitehaven and Workington. The administrative county of Cumbria consists of six districts (Allerdale, Barrow-in-Furness, Carlisle, Copeland, Eden and South Lakeland) and, in 2019, had a population of 500,012. Cumbria is one of the most sparsely populated counties in England, with 73.4 people per km2 (190/sq mi). On 1 April 2023, the administrative county of Cumbria will be abolished and replaced with two new unitary authorities: Westmorland and Furness (Barrow-in-Furness, Eden, South Lakeland) and Cumberland (Allerdale, Carlisle, Copeland). Cumbria is the third largest ceremonial county in England by area. It is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Packhorse Bridge
A packhorse bridge is a bridge intended to carry packhorses ( horses loaded with sidebags or panniers) across a river or stream. Typically a packhorse bridge consists of one or more narrow (one horse wide) masonry arches, and has low parapets so as not to interfere with the panniers borne by the horses. Multi-arched examples sometimes have triangular cutwaters that are extended upward to form pedestrian refuges. Packhorse bridges were often built on the trade routes (often called packhorse routes) that formed major transport arteries across Europe and Great Britain until the coming of the turnpike roads and canals in the 18th century. Before the road-building efforts of Napoleon, all crossings of the Alps were on packhorse trails. Travellers' carriages were dismantled and transported over the mountain passes by ponies and mule trains. Definition In the British Isles at least, the definition of a packhorse bridge is somewhat nebulous. Ernest Hinchliffe discusses the diffi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake District
The Lake District, also known as the Lakes or Lakeland, is a mountainous region in North West England. A popular holiday destination, it is famous for its lakes, forests, and mountains (or '' fells''), and its associations with William Wordsworth and other Lake Poets and also with Beatrix Potter and John Ruskin. The Lake District National Park was established in 1951 and covers an area of . It was designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2017. The Lake District is today completely within Cumbria, a county and administrative unit created in 1974 by the Local Government Act 1972. However, it was historically divided between three English counties (Cumberland, Westmorland and Lancashire), sometimes referred to as the Lakes Counties. The three counties met at the Three Shire Stone on Wrynose Pass in the southern fells west of Ambleside. All the land in England higher than above sea level lies within the National Park, including Scafell Pike, the highest mountain in E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slate
Slate is a fine-grained, foliated, homogeneous metamorphic rock derived from an original shale-type sedimentary rock composed of clay or volcanic ash through low-grade regional metamorphism. It is the finest grained foliated metamorphic rock. Foliation may not correspond to the original sedimentary layering, but instead is in planes perpendicular to the direction of metamorphic compression. The foliation in slate is called " slaty cleavage". It is caused by strong compression causing fine grained clay flakes to regrow in planes perpendicular to the compression. When expertly "cut" by striking parallel to the foliation, with a specialized tool in the quarry, many slates will display a property called fissility, forming smooth flat sheets of stone which have long been used for roofing, floor tiles, and other purposes. Slate is frequently grey in color, especially when seen, en masse, covering roofs. However, slate occurs in a variety of colors even from a single locality; f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
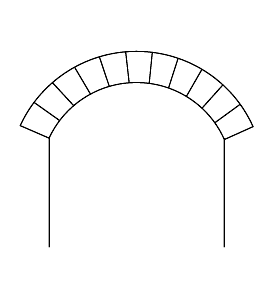
Segmental Arch
A segmental arch is a type of arch with a circular arc of less than 180 degrees. It is sometimes also called a scheme arch. The segmental arch is one of the strongest arches because it is able to resist thrust. To prevent failure, a segmental arch must have a rise that is equal to at least one-eighth the width of the span. Segmental arches with a rise that is less than one-eighth of the span width must have a permanent support or frame beneath the arch to prevent failure. As far as is known, the ancient Romans were the first to develop the segmental arch. The closed-spandrel Pont-Saint-Martin bridge in the Aosta Valley in Italy dates to 25 BC. The first open-spandrel segmental arch bridge is the Anji Bridge over the Xiao River in Hebei Province Hebei or , (; alternately Hopeh) is a northern province of China. Hebei is China's sixth most populous province, with over 75 million people. Shijiazhuang is the capital city. The province is 96% Han Chinese, 3% Manchu, 0.8% ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wetherlam
Wetherlam (763 m) is a mountain in the English Lake District. It is the most northerly of the Coniston Fells, the range of fells to the north-west of Coniston village; its north-east slopes descend to Little Langdale. Topography Wetherlam stands apart from the main north-south spine of the Coniston Fells, the connection being via the long east ridge of Swirl How. Midway along this ridge is Black Sails, an intermediate top usually considered to be part of Wetherlam,Richards, Mark: ''Southern Fells'': Collins (2003): Alfred Wainwright: ''A Pictorial Guide to the Lakeland Fells'', Book 4: and listed as a Hewitt in its own right. From Swirl How the east ridge drops steeply down Prison Band to Swirl Hawse, before rising again to the summit of Black Sails. Black Sails has a descending southern spur which steps down over High and Low Wether Crags. Between this and the main Coniston range is the valley of Swirl Hawse Beck and Levers Water. This tarn has been raised by dam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Craig Gibson
Alexander Craig Gibson (1813–1874) was an English surgeon, folklorist and antiquarian. Life Born at Harrington, Cumberland, on 17 March 1813, he was the eldest son of Joseph Gibson by his wife Mary Stuart Craig, from Moffat, Dumfriesshire. He had medical training in Whitehaven, and studied at the University of Edinburgh. Gibson started in practice at Branthwaite and Ullock in Allerdale, in west Cumberland, for about two years. He moved to Coniston in 1843. In 1849 he removed to Hawkshead, as surgeon to the Coniston copper mines. In 1857, finding the work heavy, he settled at Bebington in Cheshire, where he remained in practice until poor health compelled him to retire, in 1872. Gibson was a Fellow of the Society of Antiquaries of London; his medical qualifications were M.R.C.S. Engl. 1846, L.S.A. 1855, and L.M. Edinb. (Univ. Edinb.). He died at Bebington on 12 June 1874. Works Gibson wrote two books: *''The Old Man, or Ravings and Ramblings round Coniston'' (Kendal, 1849, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred Wainwright
Alfred Wainwright MBE (17 January 1907 – 20 January 1991), who preferred to be known as A. Wainwright or A.W., was a British fellwalker, guidebook author and illustrator. His seven-volume ''Pictorial Guide to the Lakeland Fells'', published between 1955 and 1966 and consisting entirely of reproductions of his manuscript, has become the standard reference work to 214 of the fells of the English Lake District. Among his 40-odd other books is the first guide to the Coast to Coast Walk, a 182-mile long-distance footpath devised by Wainwright which remains popular today. Life Alfred Wainwright was born in Blackburn, Lancashire, into a family which was relatively poor, mostly because of his stonemason father's alcoholism. He did very well at school (first in nearly every subject) although he left at the age of 13. While most of his classmates were obliged to find employment in the local mills, Wainwright started work as an office boy in Blackburn Borough Engineer's Department. He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashness Bridge
Ashness Bridge is a traditional stone-built bridge on the single-track road from the Borrowdale road (B5289) to Watendlath, in the English Lake District, Cumbria. The brisge is at grid reference , and is known for being a fine viewpoint across Borrowdale towards Skiddaw, including views of Derwent Water nearby. It or its predecessor may have been a packhorse bridge conveying packhorse traffic from Watendlath to Keswick. Near the bridge is a small cairn to Bob Graham, who ran a round of 42 Lakeland peaks in 1932 (in under 24 hours), a record which was not equalled for 28 years. The area is owned by the National Trust. See also *Birks Bridge *Listed buildings in Borrowdale *Slater's Bridge Slater's Bridge is a traditional packhorse bridge in Little Langdale in the English Lake District, standing at National Grid Reference . History and construction The bridge dates back to the 17th century, and became a listed building in 1967. ... References Bridges in Cumbria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birks Bridge
Birks Bridge is a traditional stone-built bridge over the River Duddon in the English Lake District, in Dunnerdale-with-Seathwaite, Cumbria, standing at Grid Reference . History and construction The bridge was built around the 18th century, with voussoirs and inbuilt drainage, and became a listed building in 1990. Aspect Birks Bridge is a packhorse bridge of outstanding beauty, even for Lakeland. Hunter Davies described how "the hump-back stone bridge seems itself to be a work of nature, blending and melding so well with the rocks either side". Wainwright considered this a tribute to the artistry of craftsmen of former times. See also *Listed buildings in Dunnerdale-with-Seathwaite *Ashness Bridge *Harter Fell (Eskdale) *Slater's Bridge Slater's Bridge is a traditional packhorse bridge in Little Langdale in the English Lake District, standing at National Grid Reference . History and construction The bridge dates back to the 17th century, and became a listed buildin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |