|
Skin Grafting
Skin grafting, a type of graft surgery, involves the transplantation of skin without a defined circulation. The transplanted tissue is called a skin graft. Surgeons may use skin grafting to treat: * extensive wounding or trauma * burns * areas of extensive skin loss due to infection such as necrotizing fasciitis or purpura fulminans * specific surgeries that may require skin grafts for healing to occur – most commonly removal of skin cancers Skin grafting often takes place after serious injuries when some of the body's skin is damaged. Surgical removal (excision or debridement) of the damaged skin is followed by skin grafting. The grafting serves two purposes: reducing the course of treatment needed (and time in the hospital), and improving the function and appearance of the area of the body which receives the skin graft. There are two types of skin grafts: * Partial-thickness: The more common type involves removing a thin layer of skin from a healthy part of the bod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skin Graft On Ankle After Third Degree Burns
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation. Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different developmental origin, structure and chemical composition. The adjective cutaneous means "of the skin" (from Latin ''cutis'' 'skin'). In mammals, the skin is an organ of the integumentary system made up of multiple layers of ectodermal tissue and guards the underlying muscles, bones, ligaments, and internal organs. Skin of a different nature exists in amphibians, reptiles, and birds. Skin (including cutaneous and subcutaneous tissues) plays crucial roles in formation, structure, and function of extraskeletal apparatus such as horns of bovids (e.g., cattle) and rhinos, cervids' antlers, giraffids' ossicones, armadillos' osteoderm, and os penis/os clitoris. All mammals have some hair on their skin, even marine mammals like whales, dolphins, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
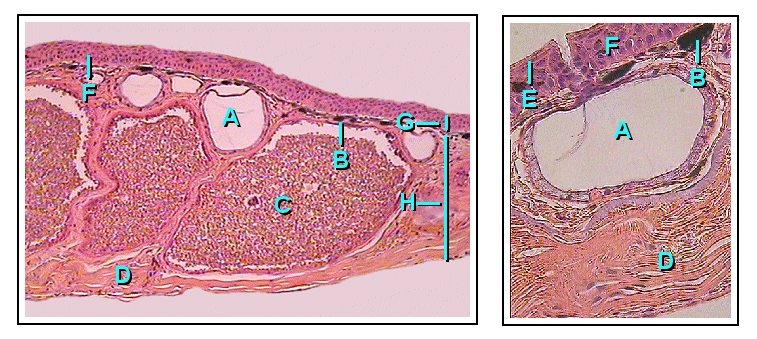
Epidermis (skin)
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and hypodermis. The epidermal layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the amount of water released from the body into the atmosphere through transepidermal water loss. The epidermis is composed of multiple layers of flattened cells that overlie a base layer ( stratum basale) composed of columnar cells arranged perpendicularly. The layers of cells develop from stem cells in the basal layer. The thickness of the epidermis varies from 31.2μm for the penis to 596.6μm for the sole of the foot with most being roughly 90μm. Thickness does not vary between the sexes but becomes thinner with age. The human epidermis is an example of epithelium, particularly a stratified squamous epithelium. The word epidermis is derived through Latin , itself and . Something related to or part of the epidermis is termed epidermal. Structure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Plasma
Blood plasma is a light Amber (color), amber-colored liquid component of blood in which blood cells are absent, but which contains Blood protein, proteins and other constituents of whole blood in Suspension (chemistry), suspension. It makes up about 55% of the body's total blood volume. It is the Intravascular compartment, intravascular part of extracellular fluid (all body fluid outside cells). It is mostly water (up to 95% by volume), and contains important dissolved proteins (6–8%; e.g., serum albumins, globulins, and fibrinogen), glucose, clotting factors, electrolytes (, , , , , etc.), hormones, carbon dioxide (plasma being the main medium for excretory product transportation), and oxygen. It plays a vital role in an intravascular osmotic effect that keeps electrolyte concentration balanced and protects the body from infection and other blood-related disorders. Blood plasma can be separated from whole blood through blood fractionation, by adding an anticoagulant to a tube ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neovascularization
Neovascularization is the natural formation of new blood vessels ('' neo-'' + ''vascular'' + '' -ization''), usually in the form of functional microvascular networks, capable of perfusion by red blood cells, that form to serve as collateral circulation in response to local poor perfusion or ischemia. Growth factors that inhibit neovascularization include those that affect endothelial cell division and differentiation. These growth factors often act in a paracrine or autocrine fashion; they include fibroblast growth factor, placental growth factor, insulin-like growth factor, hepatocyte growth factor, and platelet-derived endothelial growth factor. There are three different pathways that comprise neovascularization: (1) vasculogenesis, (2) angiogenesis, and (3) arteriogenesis. Three pathways of neovascularization Vasculogenesis Vasculogenesis is the de novo formation of blood vessels. This primarily occurs in the developing embryo with the development of the first primitive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inosculation
Inosculation is a natural phenomenon in which trunks, branches or roots of two trees grow together in a manner biologically similar to the artificial process of grafting. The term is derived from the Latin roots ''in'' + '' ōsculārī'', "to kiss into/inward/against" or etymologically and more illustratively "to make a small mouth inward/into/against"; trees having undergone the process are referred to in forestry as gemels, from the Latin word meaning "a pair". It is most common for branches of two trees of the same species to grow together, though inosculation may be noted across related species. The branches first grow separately in proximity to each other until they touch. At this point, the bark on the touching surfaces is gradually abraded away as the trees move in the wind. Once the cambium of two trees touches, they sometimes self-graft and grow together as they expand in diameter. Inosculation customarily results when tree limbs are braided or pleached. The term ''i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surgical Staple
Surgical staples are specialized Staple (fastener), staples used in surgery in place of surgical suture, sutures to close skin wounds or to resection (surgery), resect and/or anastomosis, connect parts of an Organ (biology), organ (e.g. bowels, stomach or lungs). The use of staples over sutures reduces the local inflammatory response, width of the wound, and time it takes to close a defect. A more recent development, from the 1990s, uses clips instead of staples for some applications; this does not require the staple to penetrate. History The technique was pioneered by "father of surgical stapling", Hungarian surgeon Hümér Hültl. Hultl's prototype stapler of 1908 weighed , and required two hours to assemble and load. The technology was refined in the 1950s in the Soviet Union, allowing for the first commercially produced re-usable stapling devices for creation of bowel and Surgical anastomosis, anastomoses. Mark M. Ravitch brought a sample of stapling device after attendin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
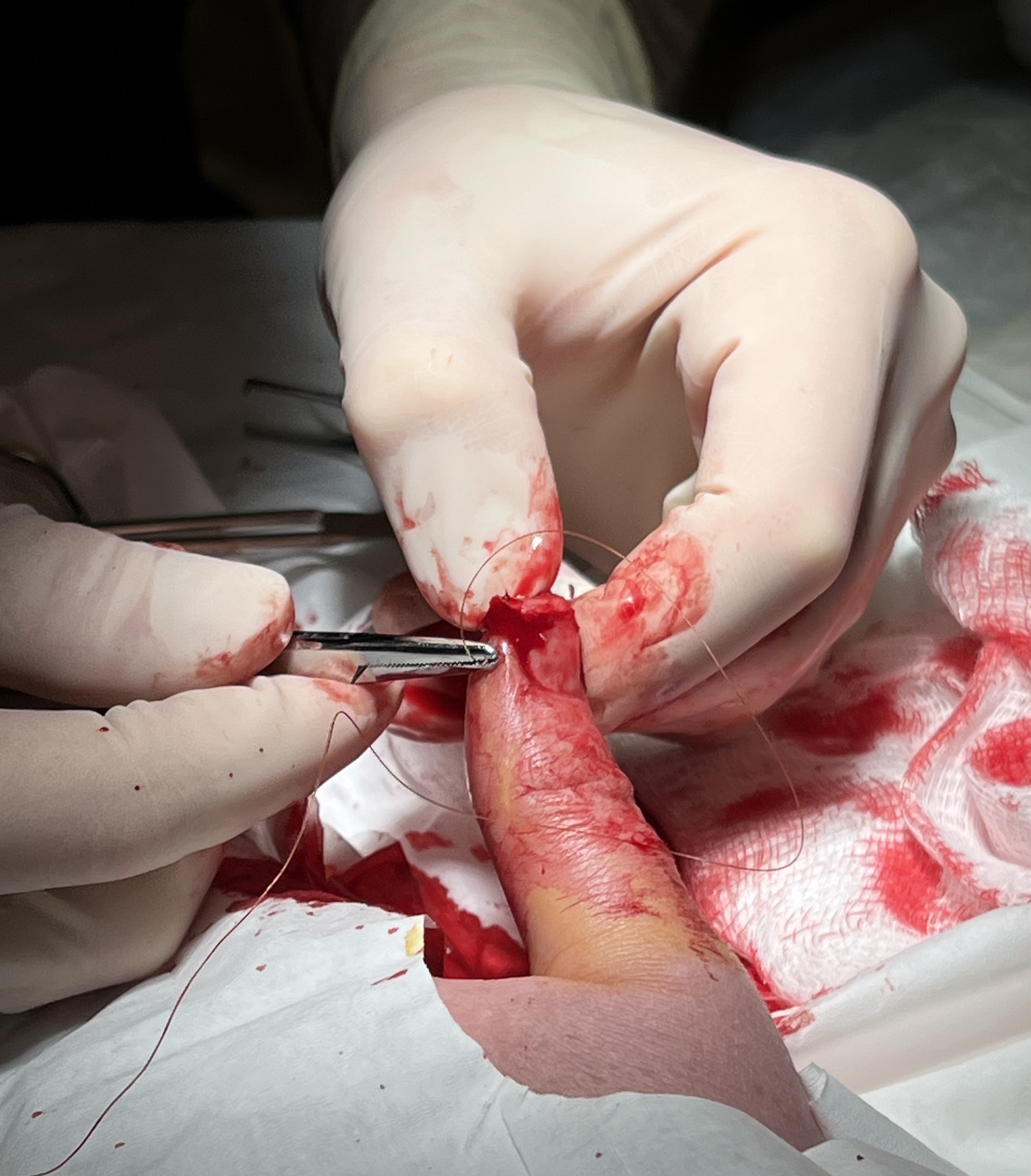
Surgical Suture
A surgical suture, also known as a stitch or stitches, is a medical device used to hold Tissue (biology), body tissues together and approximate wound edges after an injury or surgery. Application generally involves using a Sewing needle, needle with an attached length of thread (yarn), thread. There are numerous types of suture which differ by needle shape and size as well as thread material and characteristics. Selection of surgical suture should be determined by the characteristics and location of the wound or the specific body tissues being approximated. In selecting the needle, thread, and suturing technique to use for a specific patient, a medical care provider must consider the tensile strength of the specific suture thread needed to efficiently hold the tissues together depending on the mechanical and shear forces acting on the wound as well as the thickness of the tissue being approximated. One must also consider the elasticity of the thread and ability to adapt to differe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
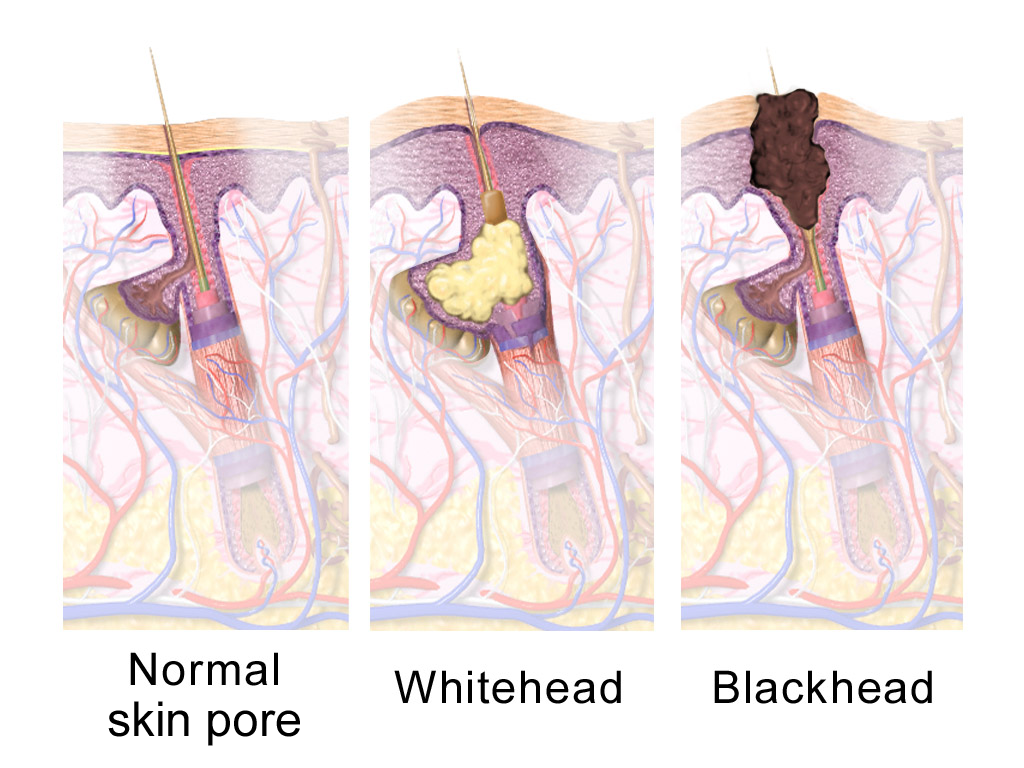
Sebaceous Gland
A sebaceous gland or oil gland is a microscopic exocrine gland in the skin that opens into a hair follicle to secrete an oily or waxy matter, called sebum, which lubricates the hair and skin of mammals. In humans, sebaceous glands occur in the greatest number on the face and scalp, but also on all parts of the skin except the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. In the eyelids, meibomian glands, also called tarsal glands, are a type of sebaceous gland that secrete a special type of sebum into tears. Surrounding the female nipples, areolar glands are specialized sebaceous glands for lubricating the nipples. Fordyce spots are benign, visible, sebaceous glands found usually on the lips, gums and inner cheeks, and genitals. Structure Location In humans, sebaceous glands are found throughout all areas of the skin, except the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. There are two types of sebaceous glands: those connected to hair follicles and those that ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hair Follicle
The hair follicle is an organ found in mammalian skin. It resides in the dermal layer of the skin and is made up of 20 different cell types, each with distinct functions. The hair follicle regulates hair growth via a complex interaction between hormones, neuropeptides, and immune cells. This complex interaction induces the hair follicle to produce different types of hair as seen on different parts of the body. For example, terminal hairs grow on the scalp and lanugo hairs are seen covering the bodies of fetuses in the uterus and in some newborn babies. The process of hair growth occurs in distinct sequential stages: ''anagen'' is the active growth phase, ''catagen'' is the regression of the hair follicle phase, ''telogen'' is the resting stage, ''exogen'' is the active shedding of hair phase and ''kenogen'' is the phase between the empty hair follicle and the growth of new hair. The function of hair in humans has long been a subject of interest and continues to be an impor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermatome (instrument)
A dermatome is a surgical instrument for producing thin slices of skin from a donor area, for use in skin grafts. One of its main applications is for reconstituting skin areas damaged by third degree burn (injury), burns or Physical trauma, trauma. Dermatomes can be operated either manually or electrically. The first drum dermatomes, developed in the 1930s, were manually operated. Afterwards, dermatomes which were operated by air pressure, such as the Brown dermatome, achieved higher speed and precision. Electrical dermatomes are better for cutting out thinner and longer strips of skin with a more homogeneous thickness. Free-hand knives Those are manual dermatomes and the term ''knife'' or ''scalpel'' is used to describe them. Their disadvantages are harvesting of grafts with irregular edges and grafts of variable thickness. Their operator has to be experienced in their use for optimal results. Types There are several types of dermatomes, usually named after their inventor. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skin Graft Donor Site
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation. Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different developmental origin, structure and chemical composition. The adjective cutaneous means "of the skin" (from Latin ''cutis'' 'skin'). In mammals, the skin is an organ of the integumentary system made up of multiple layers of ectodermal tissue and guards the underlying muscles, bones, ligaments, and internal organs. Skin of a different nature exists in amphibians, reptiles, and birds. Skin (including cutaneous and subcutaneous tissues) plays crucial roles in formation, structure, and function of extraskeletal apparatus such as horns of bovids (e.g., cattle) and rhinos, cervids' antlers, giraffids' ossicones, armadillos' osteoderm, and os penis/os clitoris. All mammals have some hair on their skin, even marine mammals like whales, dolphins, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |