|
Silanization
Silanization is the attachment of an organosilyl group to some chemical species. Almost always, silanization is the conversion of a silanol-terminated surface to a alkylsiloxy-terminated surface. This conversion confers hydrophobicity to a previously hydrophilic surface. This process is often used to modify the surface properties of glass, silicon, alumina, quartz, and metal oxide substrates, which all have an abundance of hydroxyl groups. Silanization differs from silylation, which usually refers to attachment of organosilicon groups to molecular substrates. Mechanism Silanization mechanisms vary with substrate and with silanization reagent. In the usual circumstance, surface MOH groups react as nucleophiles with silyl chlorides or silyl alkoxides. The stoichiometry for these reactions are shown: : : M is typically Si, but could be many other elements. The process is assumed to follow the pathways that apply to silylation of molecular substrates, such as alcohols. Properti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silylation
Silylation is the introduction of one or more (usually) substituted silyl groups (R3Si) to a molecule. Silylations are core methods for production of organosilicon chemistry. Silanization, while similar to silylation, usually refers to attachment of silyl groups to solids. Silyl groups are commonly used for: alcohol protection, enolate trapping, gas chromatography, electron-impact mass spectrometry (EI-MS), and coordinating with metal complexes. Protection Chemistry Protection Silylation is often used to protect alcohols, as well as amines, carboxylic acids, and terminal alkynes. The products after silylation, namely silyl ethers and silyl amines, are resilient toward basic conditions. Protection is typically done by reacting the functional group with a silyl halide by an SN2 reaction mechanism, typically in the presence of base. The protection mechanism begins with the base deprotonating the alcohol group. Next, the deprotonated alcohol group attacks the silyl atom of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
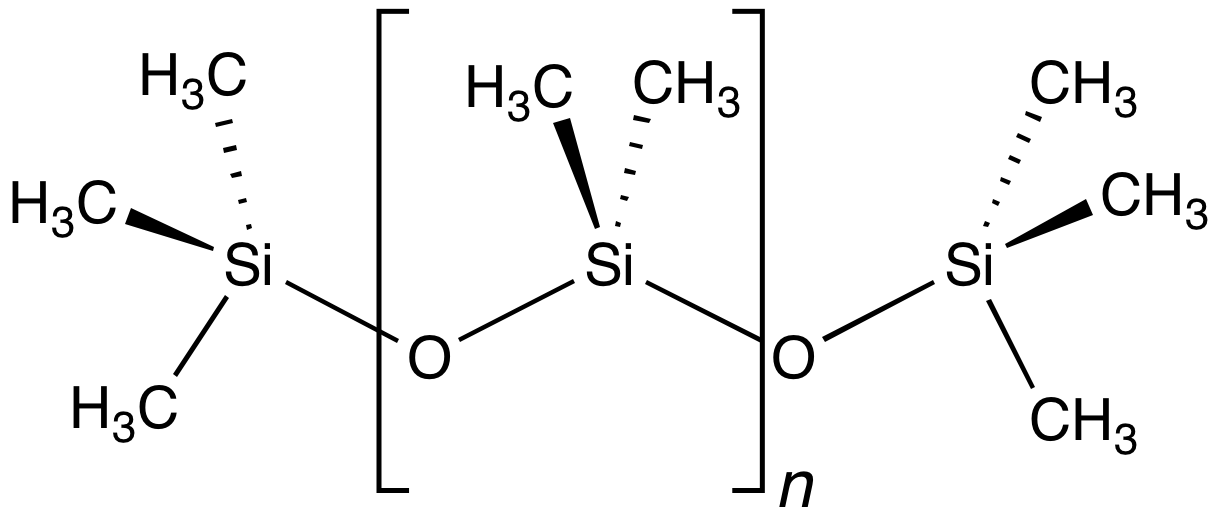
Organosilicon Compound
Organosilicon chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds containing carbon–silicon bonds, to which they are called organosilicon compounds. Most organosilicon compounds are similar to the ordinary organic compounds, being colourless, flammable, hydrophobic, and stable to air. Silicon carbide is an ''inorganic'' compound. History In 1863, Charles Friedel and James Crafts made the first organochlorosilane compound. The same year, they also described a "polysilicic acid ether" in the preparation of ethyl- and methyl-o-silicic acid. Extensive research in the field of organosilicon compounds was pioneered in the beginning of 20th century by Frederic S. Kipping. He also had coined the term "silicone" (resembling ''ketones'', though this is erroneous) in relation to these materials in 1904. In recognition of Kipping's achievements, the Dow Chemical Company had established an award in the 1960s that is given for significant contributions to the field of silicon chemistry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcohol (chemistry)
In chemistry, an alcohol (), is a type of organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl () functional group bound to a Saturated and unsaturated compounds, saturated carbon atom. Alcohols range from the simple, like methanol and ethanol, to complex, like sugar alcohols and cholesterol. The presence of an OH group strongly modifies the properties of Hydrocarbon, hydrocarbons, conferring Hydrophile, hydrophilic (water-loving) properties. The OH group provides a site at which many reactions can occur. History The flammable nature of the exhalations of wine was already known to ancient natural philosophers such as Aristotle (384–322 BCE), Theophrastus (–287 BCE), and Pliny the Elder (23/24–79 CE). However, this did not immediately lead to the isolation of alcohol, even despite the development of more advanced distillation techniques in second- and third-century Roman Egypt. An important recognition, first found in one of the writings attributed to Jabir ibn Hayyan, J� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octadecyltrichlorosilane
Octadecyltrichlorosilane (ODTS or ''n''-octadecyltrichlorosilane) is an organosilicon compound with the formula . A colorless liquid, it is used as a silanization agent to prepare hydrophobic Stationary phase (chemistry), stationary phase, for reversed-phase chromatography. It is also evaluated for forming self-assembled monolayers on silicon dioxide substrates. Its structural chemical formula is CH3(CH2)17SiCl3. It is flammable and hydrolyzes readily with release of hydrogen chloride. Dodecyltrichlorosilane, an ODTS analog with shorter alkyl chain, is used for the same purpose. ODTS-poly-4-vinylphenol, PVP films are used in organic-substrate LCD displays. References {{reflist Organochlorosilanes Thin films ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functional Group
In organic chemistry, a functional group is any substituent or moiety (chemistry), moiety in a molecule that causes the molecule's characteristic chemical reactions. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reactions regardless of the rest of the molecule's composition. This enables systematic prediction of chemical reactions and behavior of chemical compounds and the design of chemical synthesis. The Reactivity (chemistry), reactivity of a functional group can be modified by other functional groups nearby. Functional group interconversion can be used in retrosynthetic analysis to plan organic synthesis. A functional group is a group of atoms in a molecule with distinctive Chemical property, chemical properties, regardless of the other atoms in the molecule. The atoms in a functional group are linked to each other and to the rest of the molecule by covalent bonds. For repeating units of polymers, functional groups attach to their Chemical polarity, nonp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stationary Phase (chemistry)
In chemical analysis, chromatography is a laboratory technique for the separation of a mixture into its components. The mixture is dissolved in a fluid solvent (gas or liquid) called the ''mobile phase'', which carries it through a system (a column, a capillary tube, a plate, or a sheet) on which a material called the ''stationary phase'' is fixed. Because the different constituents of the mixture tend to have different affinities for the stationary phase and are retained for different lengths of time depending on their interactions with its surface sites, the constituents travel at different apparent velocities in the mobile fluid, causing them to separate. The separation is based on the differential partitioning between the mobile and the stationary phases. Subtle differences in a compound's partition coefficient result in differential retention on the stationary phase and thus affect the separation. Chromatography may be ''preparative'' or ''analytical''. The purpose of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleic Acid
Nucleic acids are large biomolecules that are crucial in all cells and viruses. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomer components: a pentose, 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main classes of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). If the sugar is ribose, the polymer is RNA; if the sugar is deoxyribose, a variant of ribose, the polymer is DNA. Nucleic acids are chemical compounds that are found in nature. They carry information in cells and make up genetic material. These acids are very common in all living things, where they create, encode, and store information in every living cell of every outline of life forms, life-form on Earth. In turn, they send and express that information inside and outside the cell nucleus. From the inner workings of the cell to the young of a living thing, they contain and provide information via the nucleic acid sequence. This gives the RNA and DNA their unmistakable 'la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |