|
Signs And Symptoms Of Parkinson's Disease
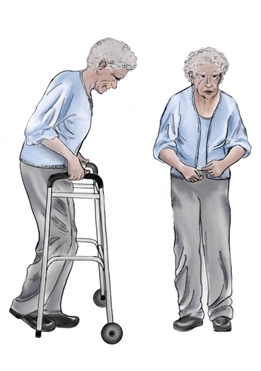
Signs and symptoms of Parkinson's disease are varied. Parkinson's disease affects movement, producing motor symptoms. Non-motor symptoms, which include dysautonomia, cognitive and neurobehavioral problems, and sensory and sleep difficulties, are also common. When other diseases mimic Parkinson's disease, they are categorized as parkinsonism. Motor Four motor symptoms are considered cardinal signs in PD: slowness of movement (bradykinesia), tremor, rigidity, and postural instability. Typical for PD is an initial asymmetric distribution of these symptoms, where in the course of the disease, a gradual progression to bilateral symptoms develops, although some asymmetry usually persists. Other motor symptoms include gait and posture disturbances such as decreased arm swing, a forward-flexed posture, and the use of small steps when walking; speech and swallowing disturbances; and other symptoms such as a mask-like facial expression or small handwriting are examples of the range of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffuse Malignant PD
Diffusion is the net movement of anything (for example, atoms, ions, molecules, energy) generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion is driven by a gradient in Gibbs free energy or chemical potential. It is possible to diffuse "uphill" from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration, as in spinodal decomposition. Diffusion is a stochastic process due to the inherent randomness of the diffusing entity and can be used to model many real-life stochastic scenarios. Therefore, diffusion and the corresponding mathematical models are used in several fields beyond physics, such as statistics, probability theory, information theory, neural networks, finance, and marketing. The concept of diffusion is widely used in many fields, including physics ( particle diffusion), chemistry, biology, sociology, economics, statistics, data science, and finance (diffusion of people, ideas, data and price values). The central ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supination
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative to the anatomical position of the body parts involved. Anatomists and others use a unified set of terms to describe most of the movements, although other, more specialized terms are necessary for describing unique movements such as those of the hands, feet, and eyes. In general, motion is classified according to the anatomical plane it occurs in. ''Flexion'' and ''extension'' are examples of ''angular'' motions, in which two axes of a joint are brought closer together or moved further apart. ''Rotational'' motion may occur at other joints, for example the shoulder, and are described as ''internal'' or ''external''. Other terms, such as ''elevation'' and ''depression'', describe movement above or below the horizontal plane. Many anatomic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perception
Perception () is the organization, identification, and interpretation of sensory information in order to represent and understand the presented information or environment. All perception involves signals that go through the nervous system, which in turn result from physical or chemical stimulation of the sensory system.Goldstein (2009) pp. 5–7 Vision involves light striking the retina of the eye; smell is mediated by odor molecules; and hearing involves pressure waves. Perception is not only the passive receipt of these signals, but it is also shaped by the recipient's learning, memory, expectation, and attention. Gregory, Richard. "Perception" in Gregory, Zangwill (1987) pp. 598–601. Sensory input is a process that transforms this low-level information to higher-level information (e.g., extracts shapes for object recognition). The following process connects a person's concepts and expectations (or knowledge) with restorative and selective mechanisms, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognition
Cognition is the "mental action or process of acquiring knowledge and understanding through thought, experience, and the senses". It encompasses all aspects of intellectual functions and processes such as: perception, attention, thought, imagination, intelligence, the formation of knowledge, memory and working memory, judgment and evaluation, reasoning and computation, problem-solving and decision-making, comprehension and production of language. Cognitive processes use existing knowledge to discover new knowledge. Cognitive processes are analyzed from very different perspectives within different contexts, notably in the fields of linguistics, musicology, anesthesia, neuroscience, psychiatry, psychology, education, philosophy, anthropology, biology, systemics, logic, and computer science. These and other approaches to the analysis of cognition (such as embodied cognition) are synthesized in the developing field of cognitive science, a progressively autonomou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthostatic Hypotension
Orthostatic hypotension, also known as postural hypotension, is a medical condition wherein a person's blood pressure drops when they are standing up ( orthostasis) or sitting down. Primary orthostatic hypotension is also often referred to as neurogenic orthostatic hypotension. The drop in blood pressure may be sudden ( vasovagal orthostatic hypotension), within 3 minutes (classic orthostatic hypotension) or gradual (delayed orthostatic hypotension). It is defined as a fall in systolic blood pressure of at least 20 mmHg or diastolic blood pressure of at least 10 mmHg after 3 minutes of standing. It occurs predominantly by delayed (or absent) constriction of the lower body blood vessels, which is normally required to maintain adequate blood pressure when changing the position to standing. As a result, blood pools in the blood vessels of the legs for a longer period, and less is returned to the heart, thereby leading to a reduced cardiac output and inadequate blood flo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reflexes
In biology, a reflex, or reflex action, is an involuntary, unplanned sequence or action and nearly instantaneous response to a Stimulus (physiology), stimulus. Reflexes are found with varying levels of complexity in organisms with a nervous system. A reflex occurs via neural pathways in the nervous system called reflex arcs. A stimulus initiates a neural signal, which is carried to a synapse. The signal is then transferred across the synapse to a motor neuron, which evokes a target response. These neural signals do not always travel to the brain, so many reflexes are an automatic response to a stimulus that does not receive or need conscious thought. Many reflexes are fine-tuned to increase organism survival and self-defense. This is observed in reflexes such as the Startle response, startle reflex, which provides an automatic response to an unexpected stimulus, and the Cat righting reflex, feline righting reflex, which reorients a cat's body when falling to ensure safe landin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balance Disorder
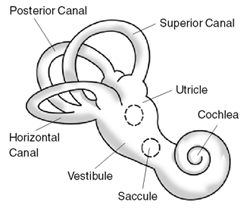
A balance disorder is a disturbance that causes an individual to feel unsteady, for example when standing or walking. It may be accompanied by feelings of giddiness, or wooziness, or having a sensation of movement, spinning, or floating. Equilibrioception, Balance is the result of several body systems working together: the visual system (eyes), vestibular system (ears) and proprioception (the body's sense of where it is in space). Degeneration or loss of function in any of these systems can lead to balance deficits. Signs and symptoms Cognitive dysfunction (disorientation) may occur with vestibular disorders. Cognitive deficits are not just spatial in nature, but also include non-spatial functions such as object recognition memory. Vestibular dysfunction has been shown to adversely affect processes of attention and increased demands of attention can worsen the postural sway associated with vestibular disorders. Recent MRI studies also show that humans with bilateral vestibular da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akinesia
Hypokinesia is one of the classifications of movement disorders, and refers to decreased bodily movement. Hypokinesia is characterized by a partial or complete loss of muscle movement due to a disruption in the basal ganglia. Hypokinesia is a symptom of Parkinson's disease shown as muscle rigidity and an inability to produce movement. It is also associated with mental health disorders and prolonged inactivity due to illness, amongst other diseases. The other category of movement disorder is hyperkinesia that features an exaggeration of unwanted movement, such as twitching or writhing in Huntington's disease or Tourette syndrome. Spectrum of disorders Hypokinesia describes a variety of more specific disorders: Causes The most common cause of hypokinesia is Parkinson's disease, and conditions related to Parkinson's disease. Other conditions may also cause slowness of movements. These include hypothyroidism and severe depression. These conditions need to be ruled out before a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bradykinesia
Hypokinesia is one of the classifications of movement disorders, and refers to decreased bodily movement. Hypokinesia is characterized by a partial or complete loss of muscle movement due to a disruption in the basal ganglia. Hypokinesia is a symptom of Parkinson's disease shown as muscle rigidity and an inability to produce movement. It is also associated with mental health disorders and prolonged inactivity due to illness, amongst other diseases. The other category of movement disorder is hyperkinesia that features an exaggeration of unwanted movement, such as twitching or writhing in Huntington's disease or Tourette syndrome. Spectrum of disorders Hypokinesia describes a variety of more specific disorders: Causes The most common cause of hypokinesia is Parkinson's disease, and conditions related to Parkinson's disease. Other conditions may also cause slowness of movements. These include hypothyroidism and severe depression. These conditions need to be ruled out before ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ratchet (device)
A ratchet (occasionally spelled rachet) is a mechanical device that allows continuous linear or rotary motion in only one direction while preventing motion in the opposite direction. Ratchets are widely used in machinery and tools. The word ''ratchet'' is also used informally to refer to a ratcheting socket wrench. __TOC__ Theory of operation A ratchet consists of a round gear or a linear rack with teeth, and a pivoting, spring-loaded finger called a '' pawl'' (or ''click'', in clocks and watches) that engages the teeth. The teeth are uniform but are usually asymmetrical, with each tooth having a moderate slope on one edge and a much steeper slope on the other edge. When the teeth are moving in the unrestricted (i.e. forward) direction, the pawl easily slides up and over the gently sloped edges of the teeth, with a spring forcing it (often with an audible 'click') into the depression between the teeth as it passes the tip of each tooth. When the teeth move in the oppo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cogwheel
A gear or gearwheel is a rotating machine part typically used to transmit rotational motion and/or torque by means of a series of teeth that engage with compatible teeth of another gear or other part. The teeth can be integral saliences or cavities machined on the part, or separate pegs inserted into it. In the latter case, the gear is usually called a cogwheel. A cog may be one of those pegsDefinition of "cog" in the ''Oxford Learner's Dictionary'' online. Accessed on 2024-07-29.Definition of "cog" in the ''Merriam-Webster Dictionary'' online. Accessed on 2024-07-29. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |