|
Sigma Approximation
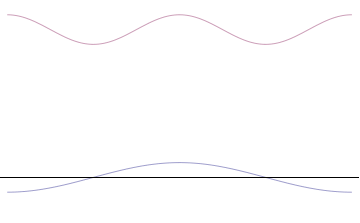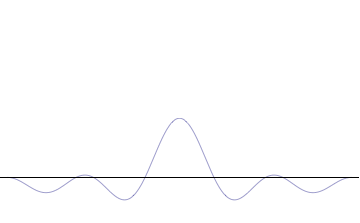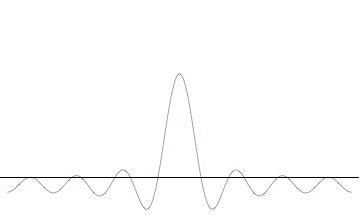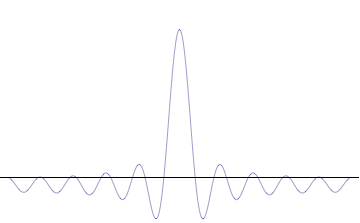
In mathematics, σ-approximation adjusts a Fourier summation to greatly reduce the Gibbs phenomenon, which would otherwise occur at discontinuities. An ''m-1''-term, σ-approximated summation for a series of period ''T'' can be written as follows: s(\theta) = \frac a_0 + \sum_^ \left(\operatorname \frac\right)^ \cdot \left _ \cos \left( \frac \theta \right) + b_k \sin \left( \frac \theta \right) \right in terms of the normalized sinc function: \operatorname x = \frac. a_ and b_ are the typical Fourier Series coefficients, and ''p'', a non negative parameter, determines the amount of smoothening applied, where higher values of ''p'' further reduce the Gibbs phenomenon but can overly smoothen the representation of the function. The term \left(\operatorname \frac\right)^ is the Lanczos σ factor, which is responsible for eliminating most of the Gibbs phenomenon. This is sampling the right side of the main lobe of the \operatorname function to rolloff the higher frequency Fouri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many areas of mathematics, which include number theory (the study of numbers), algebra (the study of formulas and related structures), geometry (the study of shapes and spaces that contain them), Mathematical analysis, analysis (the study of continuous changes), and set theory (presently used as a foundation for all mathematics). Mathematics involves the description and manipulation of mathematical object, abstract objects that consist of either abstraction (mathematics), abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicspurely abstract entities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. Mathematics uses pure reason to proof (mathematics), prove properties of objects, a ''proof'' consisting of a succession of applications of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fourier Series
A Fourier series () is an Series expansion, expansion of a periodic function into a sum of trigonometric functions. The Fourier series is an example of a trigonometric series. By expressing a function as a sum of sines and cosines, many problems involving the function become easier to analyze because trigonometric functions are well understood. For example, Fourier series were first used by Joseph Fourier to find solutions to the heat equation. This application is possible because the derivatives of trigonometric functions fall into simple patterns. Fourier series cannot be used to approximate arbitrary functions, because most functions have infinitely many terms in their Fourier series, and the series do not always Convergent series, converge. Well-behaved functions, for example Smoothness, smooth functions, have Fourier series that converge to the original function. The coefficients of the Fourier series are determined by integrals of the function multiplied by trigonometric func ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gibbs Phenomenon
In mathematics, the Gibbs phenomenon is the oscillatory behavior of the Fourier series of a piecewise continuously differentiable periodic function around a jump discontinuity. The Nth partial Fourier series of the function (formed by summing the N lowest constituent sinusoids of the Fourier series of the function) produces large peaks around the jump which overshoot and undershoot the function values. As more sinusoids are used, this approximation error approaches a limit of about 9% of the jump, though the infinite Fourier series sum does eventually converge almost everywhere. The Gibbs phenomenon was observed by experimental physicists and was believed to be due to imperfections in the measuring apparatus, but it is in fact a mathematical result. It is one cause of ringing artifacts in signal processing. It is named after Josiah Willard Gibbs. Description The Gibbs phenomenon is a behavior of the Fourier series of a function with a jump discontinuity and is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discontinuity (mathematics)
Continuous functions are of utmost importance in mathematics, functions and applications. However, not all Function (mathematics), functions are continuous. If a function is not continuous at a limit point (also called "accumulation point" or "cluster point") of its Domain of a function, domain, one says that it has a discontinuity there. The Set theory, set of all points of discontinuity of a function may be a discrete set, a dense set, or even the entire domain of the function. The Oscillation (mathematics), oscillation of a function at a point quantifies these discontinuities as follows: * in a removable discontinuity, the distance that the value of the function is off by is the oscillation; * in a jump discontinuity, the size of the jump is the oscillation (assuming that the value ''at'' the point lies between these limits of the two sides); * in an essential discontinuity (a.k.a. infinite discontinuity), oscillation measures the failure of a Limit of a function, limit to exist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinc Function
In mathematics, physics and engineering, the sinc function ( ), denoted by , has two forms, normalized and unnormalized.. In mathematics, the historical unnormalized sinc function is defined for by \operatorname(x) = \frac. Alternatively, the unnormalized sinc function is often called the sampling function, indicated as Sa(''x''). In digital signal processing and information theory, the normalized sinc function is commonly defined for by \operatorname(x) = \frac. In either case, the value at is defined to be the limiting value \operatorname(0) := \lim_\frac = 1 for all real (the limit can be proven using the squeeze theorem). The normalization causes the definite integral of the function over the real numbers to equal 1 (whereas the same integral of the unnormalized sinc function has a value of ). As a further useful property, the zeros of the normalized sinc function are the nonzero integer values of . The normalized sinc function is the Fourier transform of the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uncertainty Principle
The uncertainty principle, also known as Heisenberg's indeterminacy principle, is a fundamental concept in quantum mechanics. It states that there is a limit to the precision with which certain pairs of physical properties, such as position and momentum, can be simultaneously known. In other words, the more accurately one property is measured, the less accurately the other property can be known. More formally, the uncertainty principle is any of a variety of mathematical inequalities asserting a fundamental limit to the product of the accuracy of certain related pairs of measurements on a quantum system, such as position, ''x'', and momentum, ''p''. Such paired-variables are known as complementary variables or canonically conjugate variables. First introduced in 1927 by German physicist Werner Heisenberg, the formal inequality relating the standard deviation of position ''σx'' and the standard deviation of momentum ''σp'' was derived by Earle Hesse Kennard later that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Window Function
In signal processing and statistics, a window function (also known as an apodization function or tapering function) is a mathematical function that is zero-valued outside of some chosen interval. Typically, window functions are symmetric around the middle of the interval, approach a maximum in the middle, and taper away from the middle. Mathematically, when another function or waveform/data-sequence is "multiplied" by a window function, the product is also zero-valued outside the interval: all that is left is the part where they overlap, the "view through the window". Equivalently, and in actual practice, the segment of data within the window is first isolated, and then only that data is multiplied by the window function values. Thus, tapering, not segmentation, is the main purpose of window functions. The reasons for examining segments of a longer function include detection of transient events and time-averaging of frequency spectra. The duration of the segments is determine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lanczos Resampling
Lanczos filtering and Lanczos resampling are two applications of a certain mathematical formula. It can be used as a low-pass filter or used to smoothly interpolate the value of a digital signal between its samples. In the latter case, it maps each sample of the given signal to a translated and scaled copy of the Lanczos kernel, which is a sinc function windowed by the central lobe of a second, longer, sinc function. The sum of these translated and scaled kernels is then evaluated at the desired points. Lanczos resampling is typically used to increase the sampling rate of a digital signal, or to shift it by a fraction of the sampling interval. It is often used also for multivariate interpolation, for example to resize or rotate a digital image. It has been considered the "best compromise" among several simple filters for this purpose. The filter was invented by Claude Duchon, who named it after Cornelius Lanczos due to Duchon's use of the sigma approximation in const ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |