|
Sigeberht The Little
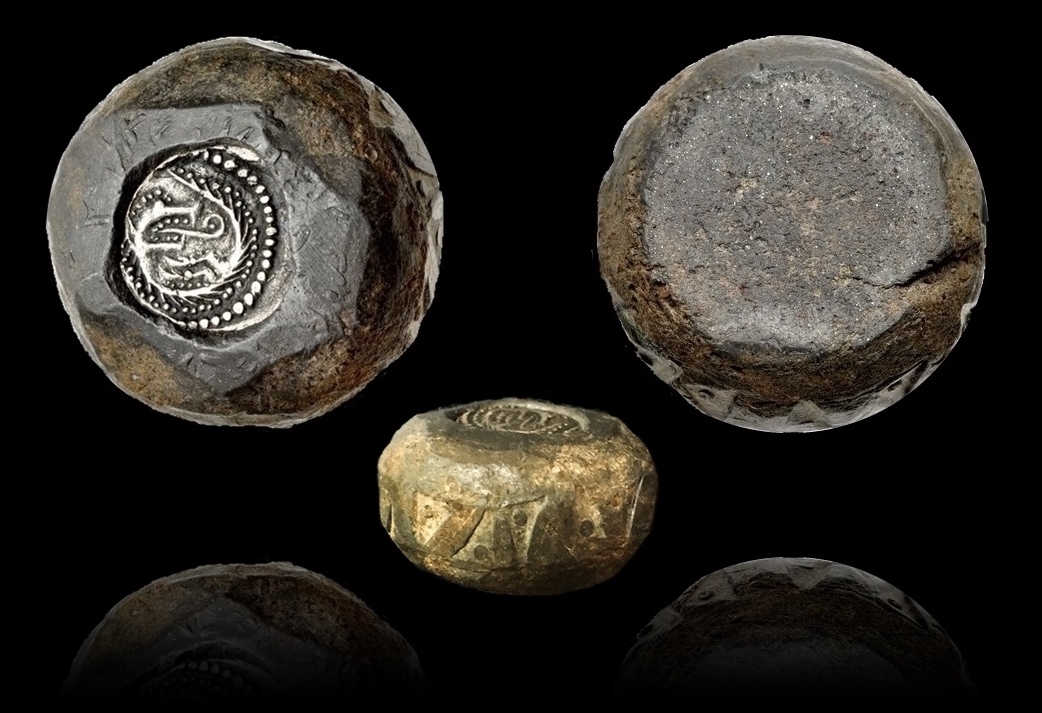
Sigeberht the Little was king of Kingdom of Essex, Essex from 623? to 653. A Sigeberht was the son of Sæward of Essex, Sæward, who was slain in battle against forces from Wessex in 623(?), and father of later king Sighere of Essex, Sighere, but Yorke thought it more likely this was his successor, Sigeberht II of Essex, Sigeberht the Good. Sigeberht the Little was considered a Anglo-Saxon paganism, pagan and most likely allied with Penda of Mercia in 635, who was also a pagan. After his death, he was succeeded by his relative, Sigeberht the Good. References External links * 653 deaths Anglo-Saxon warriors Anglo-Saxon pagans East Saxon monarchs, Sigeberht I of Essex 7th-century English monarchs Year of birth unknown {{England-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
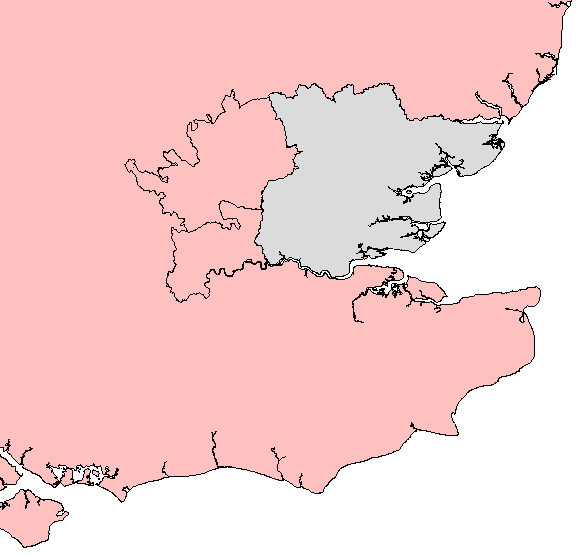
Kingdom Of Essex
The Kingdom of the East Saxons (; ), referred to as the Kingdom of Essex , was one of the seven traditional kingdoms of the Anglo-Saxon Heptarchy. It was founded in the 6th century and covered the territory later occupied by the counties of Essex, Middlesex, much of Hertfordshire and (for a short while) west Kent. The last king of Essex was Sigered of Essex, who in 825 ceded the kingdom to Ecgberht, King of Wessex. Extent The Kingdom of Essex was bounded to the north by the River Stour and the Kingdom of East Anglia, to the south by the River Thames and Kent, to the east lay the North Sea and to the west Mercia. The territory included the remains of two provincial Roman capitals, Colchester and London. The kingdom included the Middle Saxon Province, which included the area of the later County of Middlesex and most, if not all, of Hertfordshire Although the province is ever recorded only as part of the East Saxon Kingdom, charter evidence shows that it was not part of its co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wessex
The Kingdom of the West Saxons, also known as the Kingdom of Wessex, was an Anglo-Saxon Heptarchy, kingdom in the south of Great Britain, from around 519 until Alfred the Great declared himself as King of the Anglo-Saxons in 886. The Anglo-Saxons believed that Wessex was founded by Cerdic and Cynric of the Gewisse, though this is considered by some to be a legend. The two main sources for the history of Wessex are the West Saxon Genealogical Regnal List and the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' (the latter of which drew on and adapted an early version of the List), which sometimes conflict. Wessex became a Christianity, Christian kingdom after Cenwalh () was baptised and was expanded under his rule. Cædwalla later conquered Kingdom of Sussex, Sussex, Kingdom of Kent, Kent and the Isle of Wight. His successor, Ine of Wessex, Ine (), issued one of the oldest surviving English law codes and established a second West Saxon bishopric. The throne subsequently passed to a series of kings wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sighere Of Essex
Sighere was the joint king of the Kingdom of Essex along with his cousin Sæbbi from 663 or 664 until about 688. He was son of Sigeberht Sæwarding, probably Saint Sigeberht, but perhaps Sigeberht the Little. He was outlived by Sæbbi, who became the sole ruler of Essex after his death. Sighere and Sæbbi were cousins of their predecessor Swithelm. While Sighere returned to paganism, Sæbbi remained Christian. They soon developed a rivalry. Sighere found an ally in Wessex, and Sæbbi with Mercia. As a result of their rivalry, King Wulfhere of Mercia established himself as overlord of Essex, and induced Sighere to marry Wulfhere's niece Osgyth, daughter of Frithuwold, sub-king of Mercia in Surrey. Jaruman, the bishop of Mercia, was assigned to reconvert the people of Essex to Christianity. In 673, Sighere separated from Osgyth, who then fled to the protection of Bishop Beaduwine of North Elmham North Elmham is a village and civil parish in the English county of No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigeberht II Of Essex
Sigeberht II, nicknamed the Good (''Bonus'') or the Blessed (''Sanctus''), was King of the East Saxons (r. ''c''. 653 to ? 660 x 661), in succession to his relative Sigeberht I the Little. Although a bishopric in Essex had been created under Mellitus, the kingdom had lapsed to paganism and it was in Sigeberht's reign that a systematic (re-)conversion of the East Saxons took root. Bede's ''Historia Ecclesiastica'', Book III, chapter 22, is virtually the sole source for his career. Family Apart from referring to the odd kinsman, Bede offers little that is of help in determining Sigeberht's family connections. Additional evidence is provided by genealogies for Offa, Swithred and Sigered in a 9th-century West-Saxon manuscript and in two post-Conquest sources: William of Malmesbury's ''Gesta regum'' and John of Worcester's ''Chronicon ex Chronicis'', the latter including a memorandum (''Chronicon'' A) and a genealogical list (''Chronicon'' B). Their testimony is at times confused a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Saxon Paganism
Anglo-Saxon paganism, sometimes termed Anglo-Saxon heathenism, Anglo-Saxon pre-Christian religion, Anglo-Saxon traditional religion, or Anglo-Saxon polytheism refers to the religious beliefs and practices followed by the Anglo-Saxons between the 5th and 8th centuries AD, during the initial period of Anglo-Saxon England, Early Medieval England. A variant of Germanic paganism found across much of north-western Europe, it encompassed a heterogeneous variety of beliefs and cultic practices, with much regional variation. Developing from the earlier Iron Age religion of continental northern Europe, it was introduced to Britain following the Anglo-Saxon invasion of Britain, Anglo-Saxon migration in the mid 5th century, and remained the dominant belief system in England until the Christianisation of Anglo-Saxon England, Christianisation of its kingdoms between the 7th and 8th centuries, with some aspects gradually blending into English folklore, folklore. The pejorative terms ''paganis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penda Of Mercia
Penda (died 15 November 655)Manuscript A of the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' gives the year as 655. Bede also gives the year as 655 and specifies a date, 15 November. R. L. Poole (''Studies in Chronology and History'', 1934) put forward the theory that Bede began his year in September, and consequently November 655 would actually fall in 654; Frank Stenton also dated events accordingly in his ''Anglo-Saxon England'' (1943). 1 Others have accepted Bede's given dates as meaning what they appear to mean, considering Bede's year to have begun on 25 December or 1 January (see S. Wood, 1983: "Bede's Northumbrian dates again"). The historian D. P. Kirby suggested the year 656 as a possibility, alongside 655, in case the dates given by Bede are off by one year (see Kirby's "Bede and Northumbrian Chronology", 1963). The '' Annales Cambriae'' gives the year as 657Annales Cambriae at Fordham University/ref> was a 7th-century king of Mercia, the Anglo-Saxon kingdom in what is today the Midla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigeberht The Good
Sigeberht II, nicknamed the Good (''Bonus'') or the Blessed (''Sanctus''), was King of the East Saxons (r. ''c''. 653 to ? 660 x 661), in succession to his relative Sigeberht I the Little. Although a bishopric in Essex had been created under Mellitus, the kingdom had lapsed to paganism and it was in Sigeberht's reign that a systematic (re-)conversion of the East Saxons took root. Bede's ''Historia Ecclesiastica'', Book III, chapter 22, is virtually the sole source for his career. Family Apart from referring to the odd kinsman, Bede offers little that is of help in determining Sigeberht's family connections. Additional evidence is provided by genealogies for Offa, Swithred and Sigered in a 9th-century West-Saxon manuscript and in two post-Conquest sources: William of Malmesbury's ''Gesta regum'' and John of Worcester's ''Chronicon ex Chronicis'', the latter including a memorandum (''Chronicon'' A) and a genealogical list (''Chronicon'' B). Their testimony is at times confused a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
653 Deaths
__NOTOC__ Year 653 ( DCLIII) was a common year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 653 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Byzantine Empire * Emperor Constans II voluntarily surrenders Armenia to the Arabs, following a truce with Muawiyah, governor of Syria. Muawiyah grants the Armenians virtual autonomy, and appoints the ''nakharar'' Theodor Rshtuni as ruler of Armenia. * Muawiyah leads a raid against Rhodes, taking the scattered pieces of the Colossus of Rhodes (one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World) and shipping it back to Syria, where he destroys the bronze scrap to make coins. Europe * King Rodoald is murdered after a six-month reign, and is succeeded by Aripert I, who is elected as king of the Lombards. He spreads Catholicism over the Lombard realm and builds many new churches through the kingdom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Saxon Warriors
The Anglo-Saxons, in some contexts simply called Saxons or the English, were a cultural group who spoke Old English and inhabited much of what is now England and south-eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. They traced their origins to Germanic settlers who became one of the most important cultural groups in Britain by the 5th century. The Anglo-Saxon period in Britain is considered to have started by about 450 and ended in 1066, with the Norman Conquest. Although the details of their early settlement and political development are not clear, by the 8th century an Anglo-Saxon cultural identity which was generally called had developed out of the interaction of these settlers with the existing Romano-British culture. By 1066, most of the people of what is now England spoke Old English, and were considered English. Viking and Norman invasions changed the politics and culture of England significantly, but the overarching Anglo-Saxon identity evolved and remained dominant even ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |