|
Sigeberht Of East Anglia
Sigeberht of East Anglia (also known as Saint Sigebert), (Old English: ''Sigebryht'') was a saint and a king of East Anglia, the Anglo-Saxon kingdom which today includes the English counties of Norfolk and Suffolk. He was the first English king to receive a Christian baptism and education before his succession and the first to abdicate in order to enter the monastic life. The principal source for Sigeberht is Bede's ''Ecclesiastical History of the English People'', which was completed in the 730s. Sigeberht was probably either a younger son of Rædwald of East Anglia, or his step-son from Rædwald's marriage to a pagan princess from the kingdom of Essex. Nothing is known of his life before he was exiled to Gaul, which was possibly done in order to ensure that Rædwald's own descendants ruled the kingdom. After his step-brother Eorpwald's assassination in about 627, Sigeberht returned to East Anglia and (perhaps in the aftermath of a military campaign) became king, ruling joint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mercia
Mercia (, was one of the principal kingdoms founded at the end of Sub-Roman Britain; the area was settled by Anglo-Saxons in an era called the Heptarchy. It was centred on the River Trent and its tributaries, in a region now known as the Midlands of England. The royal court moved around the kingdom without a fixed capital city. Early in its existence Repton seems to have been the location of an important royal estate. According to the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'', it was from Repton in 873–874 that the Great Heathen Army deposed the King of Mercia. Slightly earlier, Offa of Mercia, King Offa seems to have favoured Tamworth, Staffordshire, Tamworth. It was there where he was crowned and spent many a Christmas. For the three centuries between 600 and 900, known as Mercian Supremacy or the "Golden Age of Mercia", having annexed or gained submissions from five of the other six kingdoms of the Heptarchy (Kingdom of East Anglia, East Anglia, Kingdom of Essex, Essex, Kingdom of Kent, K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
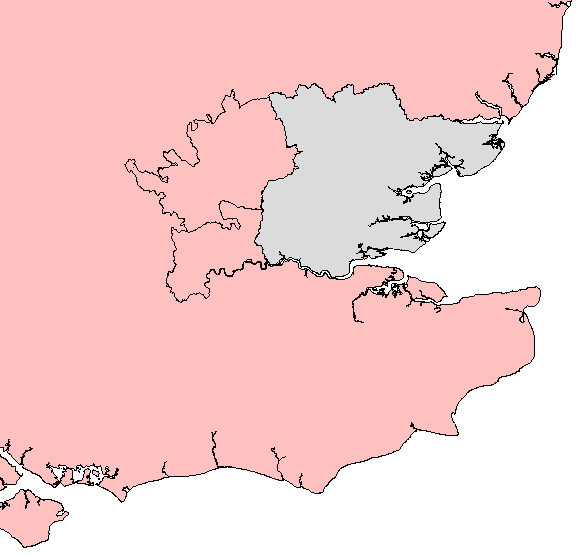
Norfolk
Norfolk ( ) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in England, located in East Anglia and officially part of the East of England region. It borders Lincolnshire and The Wash to the north-west, the North Sea to the north and east, Cambridgeshire to the west, and Suffolk to the south. The largest settlement is the city of Norwich. The county has an area of and a population of 859,400. It is largely rural with few large towns: after Norwich (147,895), the largest settlements are King's Lynn (42,800) in the north-west, Great Yarmouth (38,693) in the east, and Thetford (24,340) in the south. For local government purposes Norfolk is a non-metropolitan county with seven districts. The centre of Norfolk is gently undulating lowland. To the east are the Broads, a network of rivers and lakes which extend into Suffolk and which are protected by the Broads Authority, which give them a similar status to a National parks of England and Wales, national park. To the west the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Saint Fursey
Saint Fursey (also known as Fursa, Fursy, Forseus, and Furseus: died 650) was an Irish monk who did much to establish Christianity throughout the British Isles and particularly in East Anglia. He reportedly experienced angelic visions of the afterlife. Fursey is one of the Four Comely Saints. Early life He was born in the region of modern-day Connacht supposedly the son of Fintan and grandson of Finlog, pagan king of the area. His mother was Gelges, the Christian daughter of Aed-Finn, king of Connacht. He was born probably amongst the Hy-Bruin, and was baptised by St Brendan the Traveller, his father's uncle, who then ruled a monastery in the Island of Oirbsen, now called Inisquin in Lough Corrib. He was educated by St Brendan's monks, and when he became of the proper age he was inducted into the monastery at Inisquin (near Galway), under the Abbot St Meldan, his "soul-friend" (''anam-chura''), where he devoted himself to religious life. His great sanctity was early discer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area around Rome, Italy. Through the expansion of the Roman Republic, it became the dominant language in the Italian Peninsula and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. It has greatly influenced many languages, Latin influence in English, including English, having contributed List of Latin words with English derivatives, many words to the English lexicon, particularly after the Christianity in Anglo-Saxon England, Christianization of the Anglo-Saxons and the Norman Conquest. Latin Root (linguistics), roots appear frequently in the technical vocabulary used by fields such as theology, List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names, the sciences, List of medical roots, suffixes and prefixes, medicine, and List of Latin legal terms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dommoc
''Dommoc'' (or ''Domnoc''), a place not certainly identified but probably within the modern county of Suffolk, was the original seat of the Anglo-Saxon bishops of the Kingdom of East Anglia. It was established by Sigeberht of East Anglia for Saint Felix in . It remained the bishopric of all East Anglia until , when Theodore of Tarsus, Archbishop of Canterbury, divided the see and created a second bishopric, the See of Elmham associated with both North Elmham, Norfolk and South Elmham, Suffolk. The see of ''Dommoc'' continued to exist until the time of the Viking Wars of the 860s, after which it lapsed. Foundation The primary authority for the foundation of the see of ''Dommoc'' is Bede's '' Historia ecclesiastica'' which stipulates Felix's mission in relation to Sigeberht's rule. Following the assassination of Eorpwald of East Anglia by Ricberht in the kingdom fell back into "error" for three years, before Sigeberht, brother or half-brother of Eorpwald, took possession of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Episcopal See
An episcopal see is the area of a bishop's ecclesiastical jurisdiction. Phrases concerning actions occurring within or outside an episcopal see are indicative of the geographical significance of the term, making it synonymous with ''diocese''. The word ''see'' is derived from Latin , which in its original or proper sense denotes the seat or chair that, in the case of a bishop, is the earliest symbol of the bishop's authority. This symbolic chair is also known as the bishop's . The church in which it is placed is for that reason called the bishop's cathedral, from Latin , meaning the 'church of the '. The word ''throne'' is also used, especially in the Eastern Orthodox Church, both for the chair and for the area of ecclesiastical jurisdiction. The term ''see'' is also used of the town where the cathedral or the bishop's residence is located. Catholic Church Within Catholicism, each diocese is considered to be a see unto itself with a certain allegiance to the See of Rome. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Felix Of Burgundy
Felix of Burgundy (died 8 March 647 or 648), also known as Felix of Dunwich, was the first bishop of the kingdom of the East Angles. He is widely credited as the man who introduced Christianity to the kingdom. Almost all that is known about him comes from the ''Ecclesiastical History of the English People'', completed by the English historian Bede in about 731, and the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle''. Bede wrote that Felix freed "the whole of this kingdom from long-standing evil and unhappiness". Felix came from the Francia, Frankish kingdom of Kingdom of Burgundy, Burgundy, and may have been a priest at one of the monasteries in Francia founded by the Irish missionary Columbanus—he may have been Bishop of Châlons, before being forced to seek refuge elsewhere. Felix travelled from Burgundy to Canterbury, before being sent by Archbishop Honorius of Canterbury to Sigeberht of East Anglia's kingdom in about 630 (travelling by sea to Babingley in Norfolk, according to local legend). U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kingdom Of Northumbria
Northumbria () was an early medieval Heptarchy, kingdom in what is now Northern England and Scottish Lowlands, South Scotland. The name derives from the Old English meaning "the people or province north of the Humber", as opposed to the Southumbria, people south of the Humber, Humber Estuary. What was to become Northumbria started as two kingdoms, Deira in the south and Bernicia in the north. Conflict in the first half of the seventh century ended with the murder of the last king of Deira in 651, and Northumbria was thereafter unified under Bernician kings. At its height, the kingdom extended from the Humber, Peak District and the River Mersey on the south to the Firth of Forth on the north. Northumbria ceased to be an independent kingdom in the mid-tenth century when Deira was conquered by the Danelaw, Danes and formed into the Kingdom of York. The rump Earl of Northumbria, Earldom of Bamburgh maintained control of Bernicia for a period of time; however, the area north of R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kingdom Of Kent
The Kingdom of the Kentish (; ), today referred to as the Kingdom of Kent, was an Early Middle Ages, early medieval kingdom in what is now South East England. It existed from either the fifth or the sixth century AD until it was fully absorbed into the Kingdom of Wessex in the mid-9th century and later into the Kingdom of England in the early 10th century. Under the preceding Roman Britain, Romano-British administration the area of Kent faced repeated attacks from seafaring raiders during the fourth century AD. It is likely that Germanic-speaking ''foederati'' were invited to settle in the area as mercenaries. Following the end of Roman administration in 410, further linguistically Germanic tribal groups moved into the area, as testified by both archaeological evidence and Late Anglo-Saxon textual sources. The primary ethnic group to settle in the area appears to have been the Jutes: they established their Kingdom in East Kent and may initially have been under the dominion of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Eorpwald Of East Anglia
Eorpwald; also Erpenwald or Earpwald, (reigned from 624, assassinated c. 627 or 632), succeeded his father Rædwald as King of the East Angles. Eorpwald was a member of the East Anglian dynasty known as the Wuffingas, named after the semi-historical king Wuffa. Little is known of Eorpwald's life or of his short reign, as little documentary evidence about the East Anglian kingdom has survived. The primary source for Eorpwald is the ''Ecclesiastical History of the English People'', written by Bede in the 8th century. Soon after becoming king, Eorpwald received Christian teaching and was baptised in 627 or 632. Soon after his conversion he was killed by Ricberht, a pagan noble, who may have succeeded him and ruled for three years. The motive for Eorpwald's assassination was probably political as well as religious. He was the first early English king to suffer death as a consequence of his Christian faith and was subsequently venerated by the Church as a saint and martyr. In 1939, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gaul
Gaul () was a region of Western Europe first clearly described by the Roman people, Romans, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, and parts of Switzerland, the Netherlands, Germany, and Northern Italy. It covered an area of . According to Julius Caesar, who took control of the region on behalf of the Roman Republic, Gaul was divided into three parts: Gallia Celtica, Gallia Belgica, Belgica, and Gallia Aquitania, Aquitania. Archaeologically, the Gauls were bearers of the La Tène culture during the 5th to 1st centuries BC. This material culture was found throughout Gaul and as far east as modern-day southern Poland, Slovakia, and Hungary. Warbands led by the Gaul Brennus (leader of the Senones), Brennos Battle of the Allia, sacked Rome in 387 BC, becoming the only time Rome was conquered by a foreign enemy in 800 years. However, Gallia Cisalpina was conquered by the Romans in 204 BC and Gallia Narbonensis in 123 BC. Gaul was invaded after 120 BC by the Cimbri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kingdom Of Essex
The Kingdom of the East Saxons (; ), referred to as the Kingdom of Essex , was one of the seven traditional kingdoms of the Anglo-Saxon Heptarchy. It was founded in the 6th century and covered the territory later occupied by the counties of Essex, Middlesex, much of Hertfordshire and (for a short while) west Kent. The last king of Essex was Sigered of Essex, who in 825 ceded the kingdom to Ecgberht, King of Wessex. Extent The Kingdom of Essex was bounded to the north by the River Stour and the Kingdom of East Anglia, to the south by the River Thames and Kent, to the east lay the North Sea and to the west Mercia. The territory included the remains of two provincial Roman capitals, Colchester and London. The kingdom included the Middle Saxon Province, which included the area of the later County of Middlesex and most, if not all, of Hertfordshire Although the province is ever recorded only as part of the East Saxon Kingdom, charter evidence shows that it was not part of its co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |