|
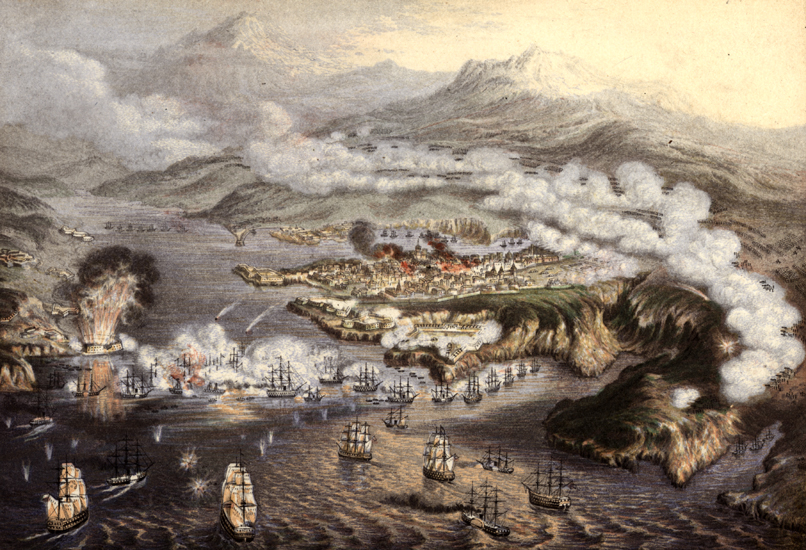
Siege Of Sevastopol (1854–1855)
The siege of Sevastopol (at the time called in English the siege of Sebastopol) lasted from October 1854 until September 1855, during the Crimean War. The allies ( French, Sardinian, Ottoman, and British) landed at Eupatoria on 14 September 1854, intending to make a triumphal march to Sevastopol, the capital of the Crimea, with 50,000 men. Major battles along the way were Alma (September 1854), Balaklava (October 1854), Inkerman (November 1854), Tchernaya (August 1855), Redan (September 1855), and, finally, Malakoff (September 1855). During the siege, the allied navy undertook six bombardments of the capital, on 17 October 1854; and on 9 April, 6 June, 17 June, 17 August, and 5 September 1855. The siege of Sevastopol is one of the last classic sieges in history. The city of Sevastopol was the home of the tsar's Black Sea Fleet, which threatened the Mediterranean. The Russian field army withdrew before the allies could encircle it. The siege was the culminating struggle for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crimean War
The Crimean War was fought between the Russian Empire and an alliance of the Ottoman Empire, the Second French Empire, the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, and the Kingdom of Sardinia (1720–1861), Kingdom of Sardinia-Piedmont from October 1853 to February 1856. Geopolitical causes of the war included the "Eastern question" (Decline and modernization of the Ottoman Empire, the decline of the Ottoman Empire, the "sick man of Europe"), expansion of Imperial Russia in the preceding Russo-Turkish wars, and the British and French preference to preserve the Ottoman Empire to maintain the European balance of power, balance of power in the Concert of Europe. The flashpoint was a dispute between France and Russia over the rights of Catholic Church, Catholic and Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox minorities in Palestine (region), Palestine. After the Sublime Porte refused Nicholas I of Russia, Tsar Nicholas I's demand that the Empire's Orthodox subjects were to be placed unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir Henry William Barnard
Sir Henry William Barnard (1799 – 5 July 1857) was an officer of the British Army. He served during the First Anglo-Afghan War and the Crimean War, rising to the rank of lieutenant-general. Family and early life Barnard, the son of the Reverend William Henry Barnard of Water Stratford, Buckinghamshire, and great-grandson of William Barnard, bishop of Derry, was born at Westbury, Buckinghamshire, in 1799. He was educated at Westminster School and Sandhurst, and obtained a commission in the Grenadier Guards in 1814. He served on the staff of his uncle, Sir Andrew Francis Barnard during the occupation of Paris, and afterwards on that of Sir John Keane in Jamaica. Later he was with his battalion in Canada, and filled various staff appointments at home. Crimean War A newly made major-general on the outbreak of the Crimean War, Barnard landed in the Crimea in 1854, in command of a brigade of the 3rd, or Sir Richard England's, division of the army, with which he was present ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
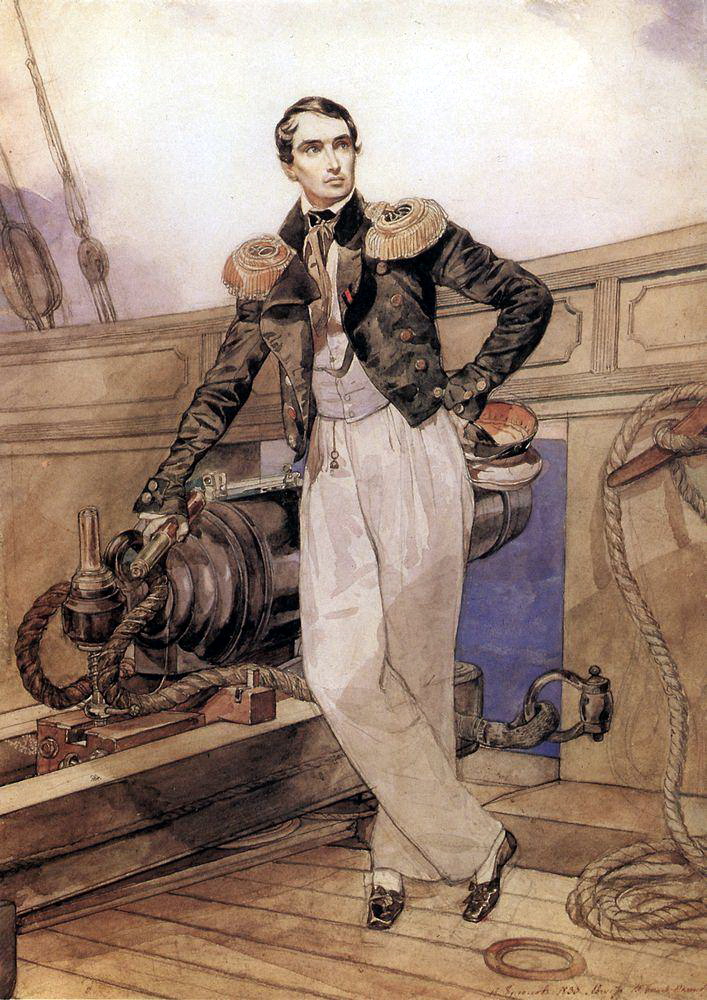
Vladimir Istomin
Vladimir Ivanovich Istomin (; – ) was a Russian rear admiral (1853) and hero of the Siege of Sevastopol. Biography In 1827, Vladimir Istomin graduated from the Naval College. That same year, he then took part in the Battle of Navarino and later in the blockade of the Dardanelles (1828-1829). In 1836, Istomin was transferred from the Baltic Fleet to the Black Sea Fleet. In 1850, he was appointed commander of the ship of the line '' Parizh'' (Париж), which would participate in the Battle of Sinop in 1853. During the Siege of Sevastopol, Vladimir Istomin was in charge of the defense of the Malakhov Mound (Малахов курган) and nearby redoubts, setting an example of bravery and tenacity. He was killed by a cannonball A round shot (also called solid shot or simply ball) is a solid spherical projectile without explosive charge, launched from a gun. Its diameter is slightly less than the bore of the barrel from which it is shot. A round shot fired from a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pavel Nakhimov
Pavel Stepanovich Nakhimov (, ; – ) was a Russian admiral in the Imperial Russian Navy known for his victory in the Battle of Sinop and his leadership in the Siege of Sevastopol (1854–1855) during the Crimean War. He joined the Imperial Russian Navy and moved up the ranks, serving in the Greek War of Independence and the Russo-Turkish War (1828–29). At the beginning of the Crimean War, he delivered a significant victory at the Battle of Sinop against the Ottoman Empire. Afterward, he was a leader in the defense of Sevastopol against British, French, and Ottoman forces, during which a sniper wounded him. He died a few days later. After his death, he became a hero in Russia, with medals and ships named after him, especially during Soviet times, starting with Stalin. Also, a Soviet Film called '' Admiral Nakhimov'' was made in 1947 about his life. Early life Nakhimov was born in the village of Gorodok in the Vyazma district of the Smolensk Governorate into a nobl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladimir Alexeyevich Kornilov
Vice Admiral Vladimir Alexeyevich Kornilov (; 13 February 1806 – 17 October 1854) was a Russian naval officer who took part in the Crimean War and is known for his battle against the Pervaz-ı Bahrî in what is considered the first battle between steam ships. Biography Early life and career Kornilov was born on his family estate in Staritsky District, Tver Governorate in 1806. His father was governor of Irkutsk. Kornilov entered the naval service in 1823, and in 1827 he fought in the Battle of Navarino as a midshipman aboard the fleet's flagship . In 1841 he became the first captain of the battleship ''Twelve Apostles'', he disciplined the crew and participated with it in the Black Sea Fleet Review (held every seven years) before Grand Duke Konstantin Nikolayevich. He sailed to London in 1847 to buy a new steam frigate. In 1849 he became chief of staff Black Sea Fleet. Crimean War Battle against the ''Pervaz-ı Bahrî'' The Russian Black Fleet was split int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Sergeyevich Menshikov
Prince Alexander Sergeyevich Menshikov (; 26 August 17872 May 1869) was a Russian nobleman, military commander and statesman. He was made adjutant general in 1817 and admiral in 1833. A great-grandson of Alexander Danilovich Menshikov, Duke of Ingria, and a cognatic descendant of the Princely House of Golitsyn (another of his great-grandfathers was Prince Mikhail Golitsyn, the military governor of Åbo (Turku) during the Russian occupation in the Great Northern War). Menshikov entered the Russian service as attaché to the embassy at Vienna in 1809. He became close to Tsar Alexander I and accompanied him throughout his campaigns against Napoleon. In 1817 Menshikov was appointed acting Quartermaster general of the General Staff. In 1823, he was transferred to the ministry of foreign affairs. Menshikov retired from army service in 1824. During the initiation of the Russo-Persian War of 1826–28 and the success of Abbas Mirza's initiative in Tehran, Menshikov was placed u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mikhail Dmitrievich Gorchakov
Prince Mikhail Dmitrievich Gorchakov (, ; – , Warsaw) was a Russian General of the Artillery from the Gorchakov family, who commanded the Russian forces in the latter stages of the Crimean War and later served as a Namestnik of Kingdom of Poland from 1856 until his death. His military career included remarkable successes, such as the Battle of the Great Redan, as well as significant setbacks, such as the Battle of the Chernaya. Life and career Mikhail and his brother Pyotr Gorchakov were the children of a notable writer Prince Dmitri Petrovich Gorchakov and his wife Natalie Boborykina. Mikhail entered the Russian army in 1807 as a cadet of the Leub Guard Artillery battalion. In 1809 in the rank of lieutenant he took part in the campaigns against Persia. During the Napoleonic Wars he distinguished himself at Borodino (received the Order of St. Vladimir of 4th degree) and at Bautzen (received the Order of St. Anna of 2nd degree, the Prussian Order Pour le Mérite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eduard Totleben
Franz Eduard Graf von Tottleben (, tr. ; – ), better known as Eduard Totleben in English, was a Baltic German military engineer and Imperial Russian Army general. He was in charge of fortification and sapping work during a number of important Russian military campaigns. Early life Totleben was born at Mitau in Courland (now Jelgava, Latvia). His parents were of Thuringian descent and originated in Tottleben, belonging to the Baltic German noble Tottleben family (also spelled ''Totleben'' or ''Todleben''), but had since become merchants. Eduard himself was intended for commerce, but instead sought a career as a military engineer. He entered the school of engineers at Saint Petersburg (now the Military Engineering-Technical University). Military career Early military career Totleben joined the Imperial Russian Army in 1836. He saw active service as captain of engineers in the campaigns against Imam Shamil in the Caucasus, beginning in 1848 for two years. Crimean War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander II Of Russia
Alexander II ( rus, Алекса́ндр II Никола́евич, Aleksándr II Nikoláyevich, p=ɐlʲɪˈksandr ftɐˈroj nʲɪkɐˈlajɪvʲɪtɕ; 29 April 181813 March 1881) was Emperor of Russia, Congress Poland, King of Poland and Grand Duke of Finland from 2 March 1855 until Assassination of Alexander II of Russia, his assassination in 1881. Alexander's most significant reform as emperor was the emancipation reform of 1861, emancipation of Serfdom in Russia, Russia's serfs in 1861, for which he is known as Alexander the Liberator ( rus, Алекса́ндр Освободи́тель, r=Aleksándr Osvobodítel, p=ɐlʲɪˈksandr ɐsvəbɐˈdʲitʲɪlʲ). The tsar was responsible for other Liberalism, liberal reforms, including reorganizing the judicial system, setting up elected local judges, abolishing corporal punishment, promoting local self-government through the ''zemstvo'' system, imposing universal military service, ending some privileges of the nobility, and promot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicholas I Of Russia
Nicholas I, group=pron (Russian language, Russian: Николай I Павлович; – ) was Emperor of Russia, List of rulers of Partitioned Poland#Kings of the Kingdom of Poland, King of Congress Poland, and Grand Duke of Finland from 1825 to 1855. He was the third son of Paul I of Russia, Paul I and younger brother of his predecessor, Alexander I of Russia, Alexander I. Nicholas's thirty-year reign began with the failed Decembrist revolt. He is mainly remembered as a reactionary whose controversial reign was marked by geographical expansion, centralisation of administrative policies, and repression of dissent both in Imperial Russia, Russia and among its neighbors. Nicholas had a happy marriage that produced a large family, with all of their seven children surviving childhood. Nicholas's biographer Nicholas V. Riasanovsky said that he displayed determination, singleness of purpose, and an iron will, along with a powerful sense of duty and a dedication to very hard work. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selim Fathi Pasha
Lieutenant general Selim Fathi Pasha ({{langx, arz, سليم فتحي باشا) (Probably born in the early 19th century and killed in the Crimean War on February 17, 1855) was an Egyptians, Egyptian military commander, who led the Egyptian Army, Egyptian ground forces in the Crimean War.Prince Omar Toussoun, ''الجيش المصري في الحرب الروسية المعروفة بحرب القرم (1853-1855). سلسلة "صفحات من تاريخ مصر"'', second edition, Madbouly Library, Cairo, 1996. Military career Prince Omar Toussoun described Selim Pasha as the best student of Soliman Pasha al-Faransawi, to whom Muhammad Ali of Egypt, Mahammad Ali Pasha entrusted the establishment of the Egyptian army and was its chief of staff. Selim Fathi Pasha participated in the wars of Ibrahim Pasha of Egypt, Ibrahim Pasha in the Levant and Anatolia, and was one of their heroes. During the reign of Mahammad Ali Pasha, he became head of the School of Staff of War, then in 1848 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Cannon (Behram Pasha)
Robert Cannon may refer to: * Robert Cannon (Behram Pasha) (1811–1882), British lieutenant general * Robert Cannon (triple jumper) (born 1958), American Olympic athlete * Robert C. Cannon (1917–2008), American judge, Milwaukee Brewers executive * Robert Milchrist Cannon (1901–1976), United States Army Lieutenant General {{human name disambiguation, Cannon, Robert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |