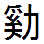|
Shōgi Zushiki
The ''Shōgi Zushiki'' (象戯図式), ''Sho Shōgi Zushiki'' (諸象戯図式), and ''Shōgi Rokushu no Zushiki'' (象棋六種之図式) are Edo period The , also known as the , is the period between 1600 or 1603 and 1868 in the history of Japan, when the country was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and some 300 regional ''daimyo'', or feudal lords. Emerging from the chaos of the Sengok ... publications describing various shogi variant, variants of Japanese chess, otherwise known as ''shōgi''. The ''Shōgi Zushiki'' covers the setup and moves of standard ''shogi, shōgi, chu shogi, chū shōgi, dai shogi, dai shōgi, tenjiku shogi, tenjiku shōgi, dai dai shogi, dai dai shōgi, maka dai dai shogi, maka dai dai shōgi,'' and ''tai shogi, tai shōgi.'' It also mentions ''wa shogi, wa shōgi, Tang shōgi'' (which is Game of the Seven Kingdoms, seven-person Chinese chess), ''ko shogi, kō shōgi,'' and ''taikyoku shogi, taikyoku shōgi.'' The ''Sho Shōgi Zushiki'' (p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
:Category:Japanese Words And Phrases ...
{{Commons Words and phrases by language Words Words Words A word is a basic element of language that carries meaning, can be used on its own, and is uninterruptible. Despite the fact that language speakers often have an intuitive grasp of what a word is, there is no consensus among linguists on its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Works About Shogi
Works may refer to: People * Caddy Works (1896–1982), American college sports coach * John D. Works (1847–1928), California senator and judge * Samuel Works (c. 1781–1868), New York politician Albums * ''Works'' (Pink Floyd album), a Pink Floyd album from 1983 * ''Works'', a Gary Burton album from 1972 * ''Works'', a Status Quo album from 1983 * ''Works'', a John Abercrombie album from 1991 * ''Works'', a Pat Metheny album from 1994 * ''Works'', an Alan Parson Project album from 2002 * ''Works Volume 1'', a 1977 Emerson, Lake & Palmer album * ''Works Volume 2'', a 1977 Emerson, Lake & Palmer album * '' The Works'', a 1984 Queen album Other uses *Good works, a topic in Christian theology * Microsoft Works, a collection of office productivity programs created by Microsoft * IBM Works, an office suite for the IBM OS/2 operating system * Mount Works, Victoria Land, Antarctica See also * The Works (other) * Work (other) Work may refer to: * Work ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shogi Variants
A shogi variant is a game related to or derived from shogi (Japanese chess). Many shogi variants have been developed over the centuries, ranging from some of the largest chess-type games ever played to some of the smallest. A few of these variants are still regularly played, though none are as popular as shogi itself. The drop rule, often considered the most notable feature of shogi, is absent from most shogi variants, which therefore play more like other forms of chess, with the board becoming less crowded as pieces are exchanged. This is especially true for variants larger than shogi itself. In fact, the largest well-known variant that features the drop rule is the 11×11 game wa shogi. Predecessors of modern shogi Some form of chess had almost certainly reached Japan by the 9th century, if not earlier, but the earliest surviving Japanese description of the rules of chess dates from the early 12th century, during the Heian period. Unfortunately, this description does not gi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ko Shogi
Kō shōgi (広将棋 or 廣象棋 'broad chess') is a large-board variant of shogi, or Japanese chess. The game dates back to the turn of the 18th century and is based on xiangqi and go as well as shogi. Credit for its invention has been given to Confucian scholar Ogyū Sorai (1666–1728), who had also described the rules of the game in his book, Kōshōgifu (廣象棋譜). Rules of the game Unlike standard shogi, pieces may not be dropped back into play after being captured. Promotion rules are complex, and the fates of several pieces are interdependent. Objective The objective is to capture the opponent's commanding pieces: The general, plus, if present, the governor; otherwise, the banner ''or'' middle army. Game equipment Two players, Black and White, play on a go board ruled into a grid of 19 ''ranks'' (rows) by 19 ''files'' (columns) with a total of 361 intersections. Each player has a set of 90 pieces of 34 different types. The pieces are round and flatt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Game Of The Seven Kingdoms
Game of the Seven Kingdoms ( Chinese: , p ''qī-guó-xiàng-qí'' ;) is a seven-player variant of the game xiangqi ("Chinese chess"). It is traditionally ascribed to Sima Guang, although he died well before the 13th century, to which this game is traditionally dated. The rules of the game can be found in his book, ''古局象棋圖''. There is skepticism regarding the game's 13th-century formulation."The imbalance in the array must reflect on the play (assuming that the game was ever played), and can perhaps be attributed to the fact that a weiqi board rather than a bespoke board was used. The existence of pieces moving as Q and B at least two centuries before their introduction into orthochess is a phenomenon few will credit. (Leventhal, ''Chess of China'')" ut note that the queen and bishop are already present in Japan in the game of chu shogi, which is recorded by the 14th century and was the most commonly played version of chess in 15th-century Japan. They are also pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wa Shogi
Wa shogi (和将棋, ''wa shōgi'', harmony chess) is a large board Shogi variant, variant of shogi (Japanese chess) in which all of the pieces are named for animals. It is played either with or without drops. Because of the terse and often incomplete wording of the historical sources for the large shogi variants, except for chu shogi and to a lesser extent dai shogi (which were at some points of time the most prestigious forms of shogi being played), the historical rules of wa shogi are not clear. Different sources differ significantly in the moves attributed to the pieces. Presented here are the piece movements that are somewhat standard among modern players of wa shogi, among which the game is played with drops. Rules of the game Objective The objective of the game is to capture your opponent's crane king. Game equipment Two players, Black and White (or 先手 ''sente'' and 後手 ''gote''), play on a board ruled into a grid of 11 ''ranks'' (rows) by 11 ''files'' (col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maka Dai Dai Shogi
Maka dai dai shōgi (摩訶大大将棋 or 摩𩹄大大象戯 'ultra-huge chess') is a large board Shogi variant, variant of shogi (Japanese chess). The game dates back to the 15th century and is based on dai dai shogi and the earlier dai shogi. The three Edo-era sources are not congruent in their descriptions of the pieces not found in smaller games. Apart from its size and number of pieces, the major difference from these smaller games is the "promotion by capture" rule. A more compact modern proposal for the game is called #Hishigata shogi, hishigata shogi. Because of the terse and often incomplete wording of the historical sources for the large shogi variants, except for chu shogi and to a lesser extent dai shogi (which were at some points of time the most prestigious forms of shogi being played), the historical rules of maka dai dai shogi are not clear. Different sources often differ significantly in the moves attributed to the pieces, and the degree of contradiction (summar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edo Period
The , also known as the , is the period between 1600 or 1603 and 1868 in the history of Japan, when the country was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and some 300 regional ''daimyo'', or feudal lords. Emerging from the chaos of the Sengoku period, the Edo period was characterized by prolonged peace and stability, urbanization and economic growth, strict social order, Isolationism, isolationist foreign policies, and popular enjoyment of Japanese art, arts and Culture of Japan, culture. In 1600, Tokugawa Ieyasu prevailed at the Battle of Sekigahara and established hegemony over most of Japan, and in 1603 was given the title ''shogun'' by Emperor Go-Yōzei. Ieyasu resigned two years later in favor of his son Tokugawa Hidetada, Hidetada, but maintained power, and defeated the primary rival to his authority, Toyotomi Hideyori, at the Siege of Osaka in 1615 before his death the next year. Peace generally prevailed from this point on, making samurai largely redundant. Tokugawa sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dai Dai Shogi
Dai dai shōgi (大大将棋 'huge chess') is a large board variant of shogi (Japanese chess). The game dates back to the 15th century and is based on the earlier dai shogi. Apart from its size, the major difference is in the range of the pieces and the "promotion by capture" rule. It is the smallest board variant to use this rule. Because of the terse and often incomplete wording of the historical sources for the large shogi variants, except for chu shogi and to a lesser extent dai shogi (which were at some points of time the most prestigious forms of shogi being played), the historical rules of dai dai shogi are not clear. Different sources often differ significantly in the moves attributed to the pieces, and the degree of contradiction (summarised below with the listing of most known alternative moves) is such that it is likely impossible to reconstruct the "true historical rules" with any degree of certainty, if there ever was such a thing. It is not clear if the game was ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tenjiku Shogi
Tenjiku shogi (天竺将棋 ''tenjiku shōgi,'' "Indian chess" or 天竺大将棋 ''tenjiku dai shōgi'' "great Indian chess") is a large-board Shogi variant, variant of shogi (Japanese chess). The game dates back to the 15th or 16th century and was based on the earlier chu shogi, which itself was based on dai shogi. Because of the terse and often incomplete wording of the historical sources for the large shogi variants, except for chu shogi and to a lesser extent dai shogi (which were at some points of time the most prestigious forms of shogi being played), the historical rules of Tianzhu (India), tenjiku shogi are not clear. Different sources often differ significantly in the moves attributed to the pieces. The descriptions listed here are a likely reconstruction based on chu shogi, the primary basis of tenjiku shogi, but not all contemporary players follow these historically-based rules. It is not clear if the game was ever played much historically, as there is no record of sets ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |