|
Shvetsov Ash-62
The Shvetsov ASh-62 (Russian: АШ-62, designated M-62 before 1941) is a nine-cylinder, air-cooled, radial aircraft engine produced in the Soviet Union. A version of this engine is produced in Poland as the ASz-62 and the People's Republic of China as the HS-5. Design and development The ASh-62 was a development of the Wright R-1820 Cyclone that had been built in Russia under licence as the Shvetsov M-25, the main improvements including a two-speed supercharger and a more efficient induction system. Power was increased from the Cyclone's 775 hp to 1,000 hp. First run in 1937, licensed versions are still in production by WSK "PZL-Kalisz" in Poland (as of 2017).Gruszczyński, Jerzy. ''W pierwszej lidze dostawców'', "Lotnictwo Aviation International" Nr. 9/2017, p. 34-37 (in Polish) The Ash-62 was also produced in China. It is estimated that 40,361 were produced in the USSR. Polish-built ASz-62IR engines (Polish transcription of Russian name), by WSK "PZL-Kalisz" in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is an affinity group for contributors with shared goals within the Wikimedia movement. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within Wikimedia project, sibling projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by ''Smithsonian Magazine, Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outsi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalisz
Kalisz () is a city in central Poland, and the second-largest city in the Greater Poland Voivodeship, with 97,905 residents (December 2021). It is the capital city of the Kalisz Region. Situated on the Prosna river in the southeastern part of Greater Poland, the city forms a conurbation with the nearby towns of Ostrów Wielkopolski and Nowe Skalmierzyce. Kalisz is one of the oldest cities in Poland and one of the two traditional capitals of Greater Poland (alongside Poznań). It has served as an important regional center in Poland since the Middle Ages as a provincial capital and notable royal city. It is one of the historical burial sites of medieval Polish monarchs and dukes of the Piast dynasty and the site of a number of significant events in Polish history as well as several battles. Since the 19th century it has been the center of an industrial district. It is the cultural, scientific, educational and administrative center of the eastern and southern Greater Poland regio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overhead Valve
An overhead valve engine, abbreviated (OHV) and sometimes called a pushrod engine, is a piston engine whose valves are located in the cylinder head above the combustion chamber. This contrasts with flathead (or "sidevalve") engines, where the valves were located below the combustion chamber in the engine block. Although an overhead camshaft (OHC) engine also has overhead valves, the common usage of the term "overhead valve engine" is limited to engines where the camshaft is located in the engine block. In these traditional OHV engines, the motion of the camshaft is transferred using pushrods (hence the term "pushrod engine") and rocker arms to operate the valves at the top of the engine. However, some designs have the camshaft in the cylinder head but still sit below or alongside the valves (the Ford CVH and Opel CIH are good examples), so they can essentially be considered overhead valve designs. Some early intake-over-exhaust engines used a hybrid design combining elemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VL Myrsky
The VL Myrsky ("Storm") is a Finnish World War II fighter aircraft originally developed by Valtion lentokonetehdas for the Finnish Air Force. The models of the aircraft were Myrsky I, Myrsky II, and Myrsky III. It was designed by Edward Wegelius, Martti Vainio and Torsti Verkkola who worked at Valtion lentokonetehdas. Development The decision to start developing a new fighter for the Finnish Air Force was based on experience gained before the Winter War: in the "arms race" leading up to a war, smaller nations can have difficulty purchasing top-of-the-line fighters without a significant political cost. The Finnish Air Force requested preliminary proposals for a domestic fighter from State Aircraft Factory (Valtion Lentokonetehdas) in early 1939, before the Winter War. State Aircraft Factory prepared five alternative proposals by May 1939. After that, The Ministry of Defence ordered the fighter design from State Aircraft Factory in June 1939. The preliminary design was made b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sukhoi Su-12
The Sukhoi Su-12 (Aircraft RK) was a prototype Soviet Union, Soviet reconnaissance and artillery spotter aircraft developed during World War II. Development In November 1943, the Sukhoi OKB designed an artillery spotter aircraft based on the German Focke-Wulf Fw 189. As designed, the aircraft had a crew of three and was powered by a pair of Shvetsov M-62 engines. The aircraft was initially denied funding but was eventually approved thanks to an intervention by the Soviet Chief Marshal of Artillery Nikolai Voronov, N.N. Voronov. As a result of evolving specifications, the crew was increased to four and the engines were changed to more powerful Shvetsov ASh-82M with 1,640 kW (2,200 hp). The Su-12 prototype flew on 26 August 1947 with N.D. Fikson at the controls. The test flight program was completed by 30 October. Due to problems with the ASh-82M engines, the powerplant was changed to ASh-82FN making 1,380 kW (1,850 hp), but while reliable, the less-powerful en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sukhoi Su-2
The Sukhoi Su-2 () is a Soviet reconnaissance and light bomber aircraft used in the early stages of World War II. It was the first airplane designed by Pavel Sukhoi. The basic design received an engine and armament upgrade (Su-4) and was modified for the ground-attack role (ShB). Development In 1936, Joseph Stalin released a requirement for a multipurpose combat aircraft. Codenamed Ivanov, the airplane had to be capable of performing reconnaissance and then attacking the targets it located. P. O. Sukhoi was working in the Tupolev OKB at the time and designed the "Ivanov" aircraft under the tutelage of Andrei Tupolev. The resulting ANT-51 flew on 25 August 1937 with M. M. Gromov at the controls. Powered by a 610 kW (820 hp) Shvetsov M-62 air-cooled radial engine, the ANT-51 reached 403 km/h (220 kn, 250 mph) at 4,700 m (15,420 ft). This was considered insufficient but since the basic design was sound, it was decided to re-test it with a m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PZL M-24 Dromader Super
The PZL M-24 Dromader Super ( Super Dromedary) is a single engine agricultural aircraft, developed in the 1980s by the WSK-Mielec (later PZL-Mielec) from the PZL-Mielec M-18 Dromader. It did not progress beyond the prototyping stage. Development The plane was developed as a bigger and more capable variant of the successful agricultural plane PZL-Mielec M-18 Dromader. Some components of the M-18 were used it its construction, but it is generally bigger and stronger, with a more powerful engine. The wings were fitted with a new central section of a larger span. The first prototype of the M-24 flew on July 20, 1987, and was powered with a Shvetsov ASh-62IR radial engine. The second prototype, designated M-24B, was powered by the Polish-designed PZL-Kalisz K-9AA radial engine and first flew in 1988. The third prototype, M-24T, was powered by the Pratt & Whitney PT6A-45AG turboprop engine. Four prototypes were built, but the type did not enter production. The experience with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PZL-Mielec M-18 Dromader
The PZL-Mielec M-18 ''Dromader'' ( English: "Dromedary") is a single engine agricultural aircraft that is manufactured by PZL-Mielec in Poland. The aircraft is used mainly as a cropduster or firefighting machine. Development PZL-Mielec, then known as WSK-Mielec, began to design the Dromader in the mid 1970s, with help of United States aircraft manufacturer Rockwell International. PZL-Mielec asked for Rockwell's help because of the political situation at the time: operating in an Eastern Bloc country, PZL wanted the aircraft to sell well worldwide, and the company realized that certification by the United States Federal Aviation Administration would be important in reaching that goal. Rockwell on the other hand wanted to fit Polish high-power radial engines into its agricultural planes. As a result of this cooperation the Rockwell Thrush Commander aircraft was fitted with the PZL-3 engine, and the Polish designers created the higher payload M-18 Dromader by introducing the more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PZL-106 Kruk
The PZL-106 Kruk () is a Polish agricultural aircraft designed and built by Państwowe Zakłady Lotnicze, WSK PZL Warszawa-Okęcie (later PZL "Warszawa-Okęcie" and now EADS-PZL). Design and development The PZL-106 was developed as a modern agricultural aircraft for Poland and Comecon countries to replace the less-capable PZL-101 Gawron and aging PZL Antonov An-2. (According to Comecon decisions, Polish industry was responsible for developing agricultural aircraft). There were several agricultural plane designs proposed in the early 1960s by a group of young designers from WSK PZL Warszawa-Okęcie, led by Andrzej Frydrychewicz. These proposals were made on their own initiative, but they were never realized because the USSR was content with the An-2 and was planning to replace it with a jet aircraft (later PZL M-15 Belphegor). The first was the PZL-101M Kruk 63 of 1963. That remained a paper airplane, but it did give its name to later designs. Next were the PZL-106 Kruk 65 (1965) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kharkiv KhAI-5
The Kharkiv KhAI-5, (sometimes Neman R-10) was a Soviet reconnaissance and light bomber aircraft, designed in the mid-1930s in the Kharkiv Aviation Institute (KhAI, - in Ukrainian: ХАІ), under the direction of Iosif Grigorevich Nyeman (sometimes written as Neman). Development The first prototype of the plane, with a factory designation KhAI-5 (ХАІ-5), flew in June 1936. Despite a lower performance, the aircraft won a contest against another reconnaissance plane design, the Kochyerigin R-9, and was accepted for a production with the military designation R-10 ('R' indicated ''razvyedchik'' meaning reconnaissance in Russian). It was a modern design for the time. 493 R-10s were manufactured in the Kharkiv and Saratov aviation plants by early 1940. The first series showed some teething problems, which resulted in Iosif Nyeman being arrested by the NKVD on December 11, 1938 under the accusation of sabotage and espionage, a common accusation at the time. In 1938 a variant, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shvetsov ASh-62 Installed In An-2
UEC-Aviadvigatel JSC (Russian: АО "ОДК-Авиадвигатель", lit. Aeroengine) is a Russian developer and builder of aircraft engines, most notably jet engines for commercial aircraft. Based at the Perm Engine Plant, its products power the Ilyushin Il-76MF, Ilyushin Il-96, Tupolev Tu-204, and Tupolev Tu-214. It also designs and builds high-efficiency gas turbine units for electric power stations and for gas pumping plants. The company has its background in the Experimental Design Bureau-19 plant, set up to manufacture aircraft engines. History Foundation and Shvetsov era Aviadvigatel can be traced back to the engine design and manufacturing factory (Plant No.19) founded in Perm Krai, Russian Soviet Republic, on 1 June 1934, to produce the Wright Cyclone-derived Shvetsov M-25. Arkadiy Shvetsov was named chief designer at the plant, which was also referred to as the ''Perm Design/Engine School''. The school was given the Soviet Experimental Design Bureau designati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
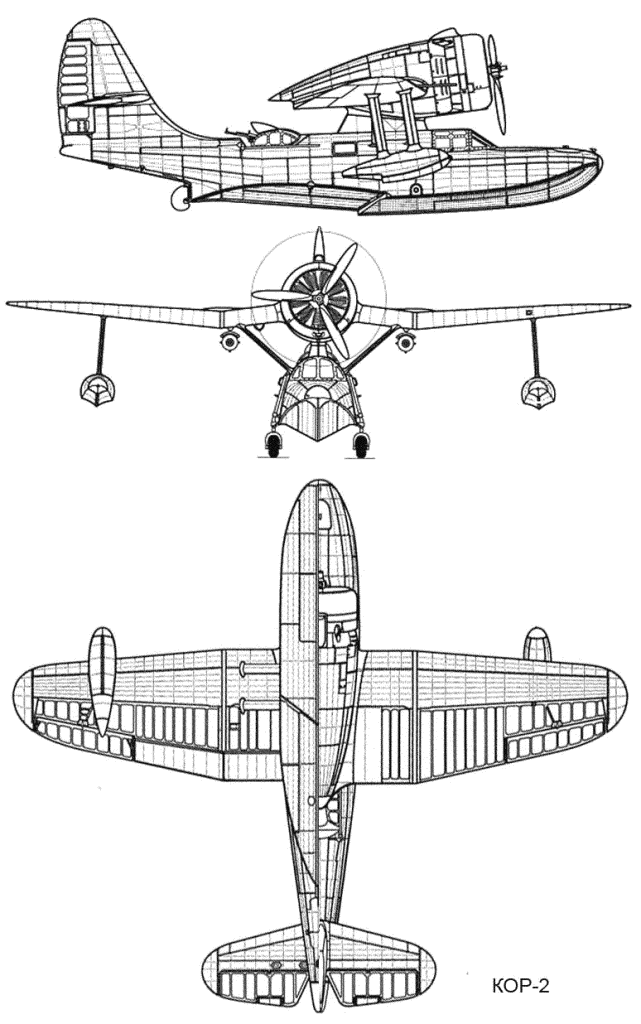
Beriev Be-4
The Beriev Be-4 (originally designated KOR-2) was a reconnaissance flying boat built to operate from Soviet warships during World War II. Design and development In 1939, Beriev was ordered to develop a successor to the KOR-1 design, which would overcome the numerous problems encountered in operational experience with that design. The new aircraft, with the in-house designation KOR-2, first flew on 21 October 1940 at the Beriev factory in Taganrog. The Be-4 was an elegant, parasol-winged monoplane with a slight inverse-gull wing. The large radial engine was mounted in a nacelle above the fuselage. Testing continued through January 1941, when series production was ordered under the designation Be-4, at a factory near Moscow. However, due to the start of World War II, only two aircraft were completed. The factory was dismantled, and evacuated to Omsk, then to Krasnoyarsk, where production resumed in May 1943 to the end of 1945. A total of 47 aircraft were eventually completed. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |