|
Segment Routing Over IPv6
Segment, segmentation, segmented, or segmental may refer to: Biology *Segmentation (biology), the division of body plans into a series of repetitive segments ** Segmentation in the human nervous system * Internodal segment, the portion of a nerve fiber between two Nodes of Ranvier *Segment, in fruit anatomy, a section of a citrus fruit *Parts of a genome, especially in virology Computing and communications * Episode§Segment (radio and television), sub-unit of an episode of radio or television or podcast *Memory segmentation, the division of computer memory into segments ** Segment descriptor ** Data segment ** Code segment *Image segmentation, the process of partitioning a digital image into multiple segments * Time-series segmentation, the process of partitioning a time-series into a sequence of discrete segments in order to reveal the underlying properties of its source * Network segmentation, splitting a computer network into subnetworks **Network segment *Packet segmentation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Segmentation (biology)
Segmentation in biology is the division of some animal and plant body plans into a linear series of repetitive segments that may or may not be interconnected to each other. This article focuses on the segmentation of animal body plans, specifically using the examples of the taxa Arthropoda, Chordata, and Annelida. These three groups form segments by using a "growth zone" to direct and define the segments. While all three have a generally segmented body plan and use a growth zone, they use different mechanisms for generating this patterning. Even within these groups, different organisms have different mechanisms for segmenting the body. Segmentation of the body plan is important for allowing free movement and development of certain body parts. It also allows for regeneration in specific individuals. Definition Segmentation is a difficult process to satisfactorily define. Many taxa (for example the molluscs) have some form of serial repetition in their units but are not conventi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Segment Architecture
{{more citations needed, date=October 2009 Segment architecture is a detailed, formal description of areas within an enterprise, used at the program or portfolio level to organize and align change activity. It defines a simple roadmap for a core mission area, business service, or enterprise service. Segment architecture is driven by business management and delivers products that improve the delivery of services to citizens and agency staff. From an investment perspective, segment architecture drives decisions for a business case or group of business cases supporting a core mission area or common or shared service. The primary stakeholders for segment architecture are business owners and managers. Segment architecture is related to Enterprise architecture (EA) through three principles: * Structure: segment architecture inherits the framework used by the EA, although it may be extended and specialized to meet the specific needs of a core mission area or common or shared service. * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Part (other)
Part, parts or PART may refer to: People *Part (surname) * Parts (surname) Arts, entertainment, and media * Part (music), a single strand or melody or harmony of music within a larger ensemble or a polyphonic musical composition * Part (bibliography), a sub-division of a volume or journal * ''Parts'' (book), a 1997 children's book by Tedd Arnold *Character (arts), in acting, a person or other being in a performed narrative Transportation * Pottstown Area Rapid Transit (PART), Pennsylvania, U.S. * Putnam Area Rapid Transit (PART), New York, U.S. * Piedmont Authority for Regional Transportation (PART), North Carolina, U.S. Other uses * Part (mathematics) or Mereology, the study of parts and the wholes they form * Part-of, the semantic relation of a part to the whole specific to linguistics *Spare part, an interchangeable part used for repair *Part number, identifier of a particular part design in engineering * Part (haircut), a hairstyle * Parts of Lincolnshire, geographic divisio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A-segment
The A-segment is the first category in the passenger car classification system defined by the European Commission. It is used for city cars, the smallest category of passenger cars defined. A-segment sales represented approximately 4.2% of the European market in 2024. It is approximately equivalent to the kei car class in Japan. Definition As of 2021, the A-segment category size spans from approximately to . Characteristics Body styles for A-segment cars in Europe are always hatchbacks. But as crossovers gain popularity, new models may shift to resemble crossovers. Examples of crossover city cars include Suzuki Ignis and Toyota Aygo X. Other body styles such as sedans are not present in this segment because these shapes largely prove impractical at typical A-segment dimensions. Current models In 2020 the ten highest selling A-segment cars in Europe were Fiat Panda, Fiat 500, Toyota Aygo, Renault Twingo, Volkswagen Up!, Hyundai i10, Kia Picanto, Peugeot 108, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euro Car Segment
Excepting those of the Europe-wide safety assessment program Euro NCAP, vehicle segments in Europe do not have formal characterization or regulations. Although the definition is vague, there is little overlap between segments A–F based on weight and size parameters. [Baidu] |
Market Segmentation
In marketing, market segmentation or customer segmentation is the process of dividing a consumer or business market into meaningful sub-groups of current or potential customers (or consumers) known as ''segments''. Its purpose is to identify profitable and growing segments that a company can target with distinct marketing strategies. In dividing or segmenting markets, researchers typically look for common characteristics such as shared needs, common interests, similar lifestyles, or even similar demographic profiles. The overall aim of segmentation is to identify ''high-yield segments'' – that is, those segments that are likely to be the most profitable or that have growth potential – so that these can be selected for special attention (i.e. become target markets). Many different ways to segment a market have been identified. Business-to-business (B2B) sellers might segment the market into different types of businesses or countries, while business-to-consumer (B2C) seller ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Segmentary Lineage
A segmentary lineage society has equivalent parts ("segments") held together by shared values. A segmentary lineage society is a type of tribal society. A close family is usually the smallest and closest segment and will generally stand together. That family is also a part of a larger segment of more distant cousins and their families, who will stand with each other when attacked by outsiders. They are then part of larger segments with the same characteristics. If there is a conflict between brothers, it will be settled by all the brothers, and cousins will not take sides. If the conflict is between cousins, brothers on one side will align against brothers on the other side. However, if the conflict is between a member of a tribe and a non-member, the entire tribe, including distant cousins, could mobilise against the outsider and his or her allies. That tiered mobilisation is traditionally expressed, for example, in the Bedouin saying: "Me and my brothers against my cousins, me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Text Segmentation
Text segmentation is the process of dividing written text into meaningful units, such as words, sentences, or topics. The term applies both to mental processes used by humans when reading text, and to artificial processes implemented in computers, which are the subject of natural language processing. The problem is non-trivial, because while some written languages have explicit word boundary markers, such as the word spaces of written English and the distinctive initial, medial and final letter shapes of Arabic, such signals are sometimes ambiguous and not present in all written languages. Compare speech segmentation, the process of dividing speech into linguistically meaningful portions. Segmentation problems Word segmentation Word segmentation is the problem of dividing a string of written language into its component words. In English and many other languages using some form of the Latin alphabet, the space is a good approximation of a word divider (word delimiter), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speech Segmentation
Speech segmentation is the process of identifying the boundaries between words, syllables, or phonemes in spoken natural languages. The term applies both to the mental processes used by humans, and to artificial processes of natural language processing. Speech segmentation is a subfield of general speech perception and an important subproblem of the technologically focused field of speech recognition, and cannot be adequately solved in isolation. As in most natural language processing problems, one must take into account context, grammar, and semantics, and even so the result is often a probabilistic division (statistically based on likelihood) rather than a categorical one. Though it seems that coarticulation—a phenomenon which may happen between adjacent words just as easily as within a single word—presents the main challenge in speech segmentation across languages, some other problems and strategies employed in solving those problems can be seen in the following sections. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
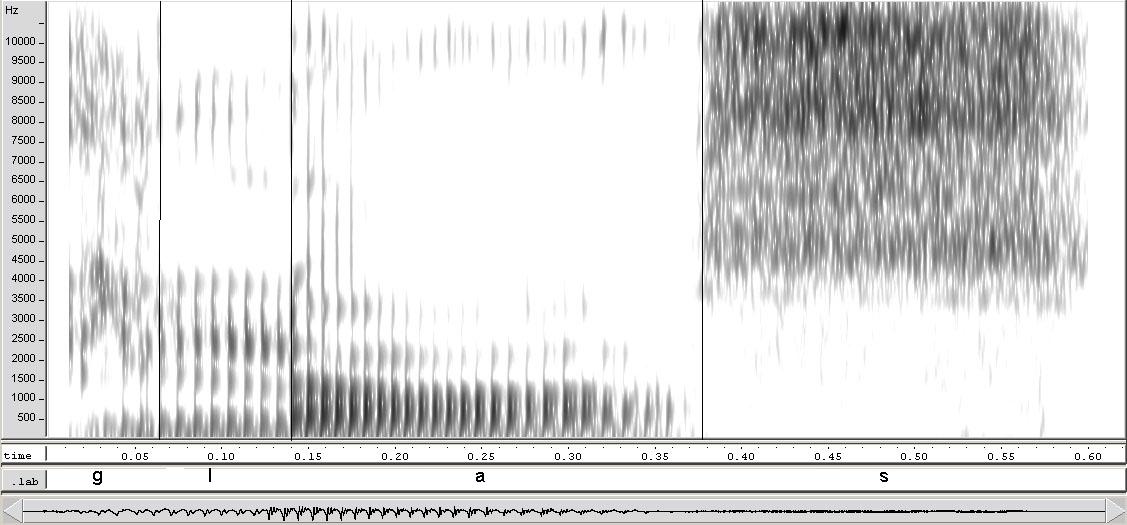
Segment (linguistics)
In linguistics, a segment is "any discrete unit that can be identified, either physically or auditorily, in the stream of speech". The term is most used in phonetics and phonology to refer to the smallest elements in a language, and this usage can be synonymous with the term phone. In spoken languages, segments will typically be grouped into consonants and vowels, but the term can be applied to any minimal unit of a linear sequence meaningful to the given field of analysis, such as a mora or a syllable in prosodic phonology, a morpheme in morphology, or a chereme in sign language analysis. Segments are called "discrete" because they are, at least at some analytical level, separate and individual, and temporally ordered. Segments are generally not completely discrete in speech production or perception, however. The articulatory, visual and acoustic cues that encode them often overlap. Examples of overlap for spoken languages can be found in discussions of phonological assim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Segment (handwriting)
A segment of handwriting is a piece of the pen-tip trajectory between two defined segmentation points. If the occurrence of a minimum in the absolute (tangential) velocity is used as a heuristic for segmentation, the pen-tip trajectory can be subdivided into segments corresponding to ballistic strokes. In handwriting recognition or optical character recognition, other terminologies may be used, such as the term glyph A glyph ( ) is any kind of purposeful mark. In typography, a glyph is "the specific shape, design, or representation of a character". It is a particular graphical representation, in a particular typeface, of an element of written language. A ... for a non-character (i.e.: sub character or multi-character) pattern. Penmanship {{typ-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arc (geometry)
In mathematics, a curve (also called a curved line in older texts) is an object similar to a line (geometry), line, but that does not have to be Linearity, straight. Intuitively, a curve may be thought of as the trace left by a moving point (geometry), point. This is the definition that appeared more than 2000 years ago in Euclid's Elements, Euclid's ''Elements'': "The [curved] line is […] the first species of quantity, which has only one dimension, namely length, without any width nor depth, and is nothing else than the flow or run of the point which […] will leave from its imaginary moving some vestige in length, exempt of any width." This definition of a curve has been formalized in modern mathematics as: ''A curve is the image (mathematics), image of an interval (mathematics), interval to a topological space by a continuous function''. In some contexts, the function that defines the curve is called a ''parametrization'', and the curve is a parametric curve. In this artic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |