|
Seawater Uranium Extraction
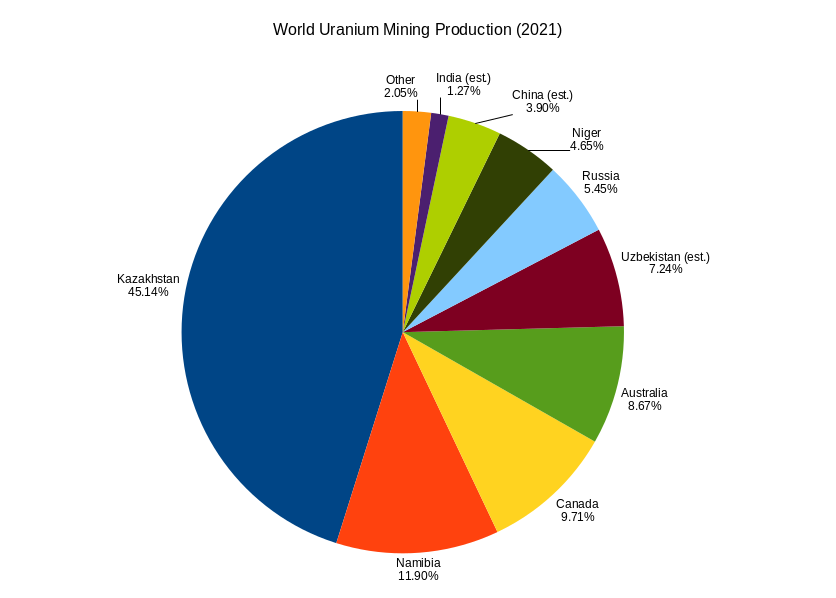
Uranium mining is the process of extraction of uranium ore from the earth. Over 50,000 tons of uranium were produced in 2019. Kazakhstan, Canada, and Australia were the top three uranium producers, respectively, and together account for 68% of world production. Other countries producing more than 1,000 tons per year included Namibia, Niger, Russia, Uzbekistan and China. Nearly all of the world's mined uranium is used to power nuclear power plants. Historically uranium was also used in applications such as uranium glass or ferrouranium but those applications have declined due to the radioactivity and toxicity of uranium and are nowadays mostly supplied with a plentiful cheap supply of depleted uranium which is also used in uranium ammunition. In addition to being cheaper, depleted uranium is also less radioactive due to a lower content of short-lived and than natural uranium. Uranium is mined by in-situ leaching (57% of world production) or by conventional underground or open ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Uranium Mining Production 2021
The world is the totality of entities, the whole of reality, or everything that Existence, exists. The nature of the world has been conceptualized differently in different fields. Some conceptions see the world as unique, while others talk of a "plurality of worlds". Some treat the world as #Monism and pluralism, one simple object, while others analyze the world as a complex made up of parts. In #Scientific cosmology, scientific cosmology, the world or universe is commonly defined as "the totality of all space and time; all that is, has been, and will be". #Theories of modality, Theories of modality talk of possible worlds as complete and consistent ways how things could have been. #Phenomenology, Phenomenology, starting from the horizon of co-given objects present in the periphery of every experience, defines the world as the biggest horizon, or the "horizon of all horizons". In #Philosophy of mind, philosophy of mind, the world is contrasted with the mind as that which is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Uranium
Natural uranium (NU or Unat) is uranium with the same isotopic ratio as found in nature. It contains 0.711% uranium-235, 99.284% uranium-238, and a trace of uranium-234 by weight (0.0055%). Approximately 2.2% of its radioactivity comes from uranium-235, 48.6% from uranium-238, and 49.2% from uranium-234. Natural uranium can be used to fuel both low- and high-power nuclear reactors. Historically, graphite-moderated reactors and heavy water-moderated reactors have been fueled with natural uranium in the pure metal (U) or uranium dioxide (UO2) ceramic forms. However, experimental fuelings with uranium trioxide (UO3) and triuranium octaoxide (U3O8) have shown promise. The 0.72% uranium-235 is not sufficient to produce a self-sustaining critical chain reaction in light water reactors or nuclear weapons; these applications must use enriched uranium. Nuclear weapons take a concentration of 90% uranium-235, and light water reactors require a concentration of roughly 3% uranium-235 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diuranate
A uranate is a Ternary compound, ternary oxide involving the element uranium in one of the oxidation states 4, 5 or 6. A typical chemical formula is MxUyOz, where M represents a cation. The uranium atom in uranates(VI) has two short collinear U–O bonds and either four or six more next nearest oxygen atoms. The structures are infinite lattice structures with the uranium atoms linked by bridging oxygen atoms. Uranium oxides are the foundation of the nuclear fuel cycle ("ammonium diuranate" and "sodium diuranate" are intermediates in the production of uranium oxide nuclear fuels) and their long-term geological disposal requires a thorough understanding of their chemical reactivity, phase transitions, and physical and chemical properties. Synthesis A method of general applicability involves combining two oxides in a high temperature reaction. For example, :Na2O + UO3 → Na2UO4 Another method is the thermal decomposition of a complex, such as an acetate complex. For example, micro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martin Heinrich Klaproth
Martin Heinrich Klaproth (1 December 1743 – 1 January 1817) was a German chemist. He trained and worked for much of his life as an apothecary, moving in later life to the university. His shop became the second-largest apothecary in Berlin, and the most productive artisanal chemical research center in Europe. Klaproth was a major systematizer of analytical chemistry, and an independent inventor of gravimetric analysis. His attention to detail and refusal to ignore discrepancies in results led to improvements in the use of apparatus. He was a major figure in understanding the composition of minerals and characterizing the elements. Klaproth discovered uranium (1789) and zirconium (1789). He was also involved in the discovery or co-discovery of titanium (1795), strontium (1793), cerium (1803), and chromium (1797) and confirmed the previous discoveries of tellurium (1798) and beryllium (1798). Klaproth was a member and director of the Berlin Academy of Scienc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mine On North Star Mountain, Colorado, 1879 - DPLA - 8d26e9b730b93baaee786d34e8d61abb (cropped)
Mine, mines, miners or mining may refer to: Extraction or digging *Miner, a person engaged in mining or digging *Mining, extraction of mineral resources from the ground through a mine Grammar *Mine, a first-person English possessive pronoun Military * Mining (military), digging under a fortified military position to penetrate its defenses * Mine warfare ** Anti-tank mine, a land mine made for use against armored vehicles ** Antipersonnel mine, a land mine targeting people walking around, either with explosives or poison gas ** Bangalore mine, colloquial name for the Bangalore torpedo, a man-portable explosive device for clearing a path through wire obstacles and land mines ** Cluster bomb, an aerial bomb which releases many small submunitions, which often act as mines ** Land mine, explosive mines placed under or on the ground ** Naval mine, or sea mine, a mine at sea, either floating or on the sea bed, often dropped via parachute from aircraft, or otherwise lain by surface sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uranium Nitride
Uranium nitrides is any of a family of several ceramic materials: uranium mononitride (UN), uranium sesquinitride (U2N3) and uranium dinitride (UN2). The word nitride refers to the −3 oxidation state of the nitrogen bound to the uranium. Uranium nitride has been considered as a potential nuclear fuel and will be used as such in the BREST-300 nuclear reactor currently under construction in Russia. It is said to be safer, stronger, denser, more thermally conductive and having a higher temperature tolerance. Challenges to implementation of the fuel include a complex conversion route from enriched UF6, the need to prevent oxidation during manufacturing and the need to define and license a final disposal route. The necessity to use expensive, highly isotopically enriched 15N is a significant factor to overcome. This is necessary due to the (relatively) high neutron capture cross-section of the far-more-common 14N, which affects the neutron economy of a reactor. Synthesis Carbotherm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uranium Hydride
Uranium hydride may refer to the following chemical compounds: * Uranium(III) hydride * Uranium(IV) hydride See also * Uranium hydride bomb {{Short pages monitor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uranium Carbide
Uranium carbide, a carbide of uranium, is a hard refractory ceramic material. It comes in several stoichiometries (''x'' differs in ), such as uranium methanide (UC, CAS number 12070-09-6), uranium sesquicarbide (U2C3, CAS number 12076-62-9), and uranium acetylide (UC2, CAS number 12071-33-9). Like uranium dioxide and some other uranium compounds, uranium carbide can be used as a nuclear fuel for nuclear reactors, usually in the form of pellets or tablets. Uranium carbide fuel was used in late designs of nuclear thermal rockets. Uranium carbide pellets are used as fuel kernels for the US version of pebble bed reactors; the German version uses uranium dioxide instead. As nuclear fuel, uranium carbide can be used either on its own, or mixed with plutonium carbide (PuC and Pu2C3). The mixture is also labeled as uranium-plutonium carbide ( (U,Pu)C ). Uranium carbide is also a popular target material for particle accelerators. Ammonia Ammonia is an inorganic chemical compo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uranium Hexafluoride
Uranium hexafluoride, sometimes called hex, is the inorganic compound with the formula . Uranium hexafluoride is a volatile, white solid that is used in enriching uranium for nuclear reactors and nuclear weapons. Preparation Uranium dioxide is converted with hydrofluoric acid (HF) to uranium tetrafluoride: : The resulting is subsequently oxidized with fluorine to give the hexafluoride: : In samples contaminated with uranium trioxide, uranyl fluoride, an oxyfluoride compound is produced in the HF step: : which can be fluorinated to produce the same product, uranium hexafluoride. : The fluorination step in both reactions above are highly exothermic. Properties Physical properties At atmospheric pressure, sublimes at 56.5 °C. The solid-state structure was determined by neutron diffraction at 77 K and 293 K.J. C. Taylor, P. W. Wilson, J. W. Kelly: „The structures of fluorides. I. Deviations from ideal symmetry in the structure of crystalline UF6: a neutron diffract ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Highly Enriched Uranium
Enriched uranium is a type of uranium in which the percent composition of uranium-235 (written 235U) has been increased through the process of isotope separation. Naturally occurring uranium is composed of three major isotopes: uranium-238 (238U with 99.2732–99.2752% natural abundance), uranium-235 (235U, 0.7198–0.7210%), and uranium-234 (234U, 0.0049–0.0059%). 235U is the only nuclide existing in nature (in any appreciable amount) that is fissile with thermal neutrons. Enriched uranium is a critical component for both civil nuclear power generation and military nuclear weapons. Low-enriched uranium (20% 235U, typically >85%) is used for the cores of many nuclear weapons, as well as compact reactors for naval propulsion and research, as well as breeder reactors. There are about 2,000 tonnes of highly enriched uranium in the world. Enrichment methods were first developed on a large scale by the Manhattan Project. Its gaseous diffusion method was used in the 1940s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light Water Reactor
The light-water reactor (LWR) is a type of thermal-neutron reactor that uses normal water, as opposed to heavy water, as both its coolant and neutron moderator; furthermore a solid form of fissile elements is used as fuel. Thermal-neutron reactors are the most common type of nuclear reactor, and light-water reactors are the most common type of thermal-neutron reactor. There are three varieties of light-water reactors: the pressurized water reactor (PWR), the boiling water reactor (BWR), and (most designs of) the supercritical water reactor (SCWR). History Early concepts and experiments After the discoveries of fission, moderation and of the theoretical possibility of a nuclear chain reaction, early experimental results rapidly showed that natural uranium could only undergo a sustained chain reaction using graphite or heavy water as a moderator. While the world's first reactors ( CP-1, X10 etc.) were successfully reaching criticality, uranium enrichment began to devel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |