|
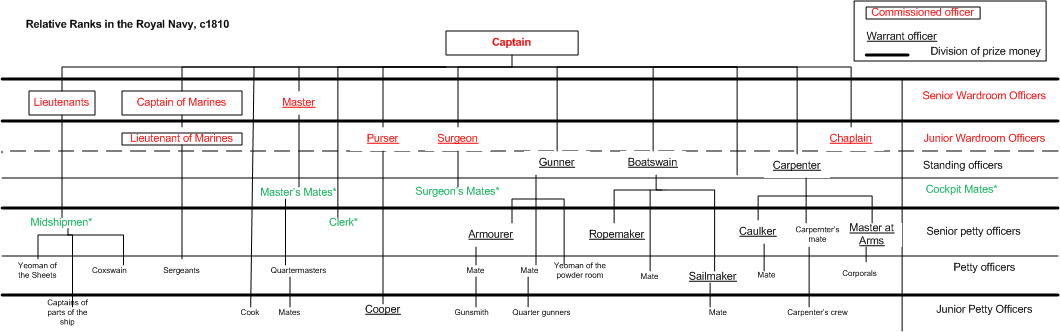
Seafarer's Professions And Ranks
Seafaring is a tradition that encompasses a variety of professions and ranks. Each of these roles carries unique responsibilities that are integral to the successful operation of a seafaring vessel. A ship's crew can generally be divided into ''four main categories'': the deck department, the engineering department, the steward's department, and other. The reasoning behind this is that a ship's bridge, filled with sophisticated navigational equipment, requires skills differing from those used on deck operations – such as berthing, cargo and/or military devices – which in turn requires skills different from those used in a ship's engine room and propulsion, and so on. The following is only a ''partial listing'' of professions and ranks. Ship operators have understandably employed a wide variety of positions, given the vast array of technologies, missions, and circumstances that ships have been subjected to over the years. There are some notable trends in modern or twenty- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Seafaring
Seamanship is the skill, art, competence (human resources), competence, and knowledge of operating a ship, boat or other craft on water. The'' Oxford Dictionary of English, Oxford Dictionary'' states that seamanship is "The skill, techniques, or practice of handling a ship or boat at sea." It involves topics and development of specialised skills, including navigation and international Admiralty law, maritime law and regulatory knowledge; weather, meteorology and forecasting; watchkeeping; ship-handling and small boat handling; operation of deck equipment, anchors and cables; ropework and line handling; communications; sailing; engines; execution of evolutions such as towing; cargo handling equipment, dangerous cargoes and cargo storage; dealing with emergencies; survival at sea and search and rescue; and fire fighting. The degree of knowledge needed within these areas is dependent upon the nature of the work and the type of vessel employed by a sailor, seafarer. History Shi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Radiotelegraphy
Wireless telegraphy or radiotelegraphy is the transmission of text messages by radio waves, analogous to electrical telegraphy using cables. Before about 1910, the term ''wireless telegraphy'' was also used for other experimental technologies for transmitting telegraph signals without wires. In radiotelegraphy, information is transmitted by pulses of radio waves of two different lengths called "dots" and "dashes", which spell out text messages, usually in Morse code. In a manual system, the sending operator taps on a switch called a telegraph key which turns the transmitter on and off, producing the pulses of radio waves. At the receiver the pulses are audible in the receiver's speaker as beeps, which are translated back to text by an operator who knows Morse code. Radiotelegraphy was the first means of radio communication. The first practical radio transmitters and receivers invented in 1894–1895 by Guglielmo Marconi used radiotelegraphy. It continued to be the only type ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Purser
A purser is the person on a ship principally responsible for the handling of money on board. On modern merchant ships, the purser is the officer responsible for all administration (including the ship's cargo and passenger manifests) and supply. Frequently, the cooks and stewards answer to the purser as well. They were also called a pusser in British naval slang. History The purser joined the warrant officer ranks of the Royal Navy in the early 14th century and existed as a naval rank until 1852. The development of the warrant officer system began in 1040, when five English ports began furnishing warships to King Edward the Confessor in exchange for certain privileges. They also furnished crews whose officers were the master, boatswain, carpenter and cook. Later these officers were "warranted" by the British Admiralty. Pursers received no pay but were entitled to profits made through their business activities. In the 18th century a purser would buy his warrant for £65 an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Royal Marines
The Royal Marines provide the United Kingdom's amphibious warfare, amphibious special operations capable commando force, one of the :Fighting Arms of the Royal Navy, five fighting arms of the Royal Navy, a Company (military unit), company strength sub-unit to the Special Forces Support Group, Special Forces Support Group (SFSG), landing craft crews, and the Naval Service's military bands. The Royal Marines trace their origins back to the formation of the "Duke of York and Albany's maritime regiment of Foot" on 28 October 1664, and the first Royal Marines Commando unit was formed at Deal, Kent, Deal in Kent on 14 February 1942 and designated "The Royal Marine Commando". The Royal Marines have seen action across many conflicts but do not have battle honours as such, but rather the "Great Globe itself" was chosen in 1827 by King George IV in their place to recognise the Marines' service and successes in multiple engagements in every quarter of the world. The Corps has close ties ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lieutenant
A lieutenant ( , ; abbreviated Lt., Lt, LT, Lieut and similar) is a Junior officer, junior commissioned officer rank in the armed forces of many nations, as well as fire services, emergency medical services, Security agency, security services and police forces. The rank in armies and air forces is often subdivided into subcategories of seniority. In Comparative navy officer ranks of Anglophone countries, English-speaking navies, lieutenants are often equivalent to the army rank of Captain (armed forces), captain; in other navies, the lieutenants are usually equal to their army counterparts. ''Lieutenant'' may also appear as part of a title used in various other organisations with a codified command structure. It often designates someone who is "second-in-command", and as such, may precede the name of the rank directly above it. For example, a "lieutenant master" is likely to be second-in-command to the "master" in an organisation using both ranks. Political uses include lieu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Warrant Officer
Warrant officer (WO) is a Military rank, rank or category of ranks in the armed forces of many countries. Depending on the country, service, or historical context, warrant officers are sometimes classified as the most junior of the commissioned officer ranks, the most senior of the non-commissioned officer (NCO) ranks, or in a separate category of their own. Warrant officer ranks are especially prominent in the militaries of Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth nations and the United States. The name of the rank originated in England in the Middle Ages, medieval England. It was first used during the 13th century, in the Royal Navy, where warrant officers achieved the designation by virtue of their accrued experience or seniority, and technically held the rank by a warrant (law)#United Kingdom, warrant, rather than by a formal Commission (document), commission (as in the case of a commissioned officer). Nevertheless, WOs in the British services have traditionally been considered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Navigation
Navigation is a field of study that focuses on the process of monitoring and controlling the motion, movement of a craft or vehicle from one place to another.Bowditch, 2003:799. The field of navigation includes four general categories: land navigation, marine navigation, air navigation, aeronautic navigation, and space navigation. It is also the term of art used for the specialized knowledge used by navigators to perform navigation tasks. All navigational techniques involve locating the navigator's Position (geometry), position compared to known locations or patterns. Navigation, in a broader sense, can refer to any skill or study that involves the determination of position and Relative direction, direction. In this sense, navigation includes orienteering and pedestrian navigation. For marine navigation, this involves the safe movement of ships, boats and other nautical craft either on or underneath the water using positions from navigation equipment with appropriate nautical char ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Master (naval)
The master, or sailing master, is a historical rank for a naval officer trained in and responsible for the navigation of a sailing vessel. In the Royal Navy, the master was originally a warrant officer who ranked with, but after, the lieutenants. The rank became a commissioned officer rank and was renamed navigating lieutenant in 1867; the rank gradually fell out of use from around 1890 since all lieutenants were required to pass the same examinations. When the United States Navy was formed in 1794, master was listed as one of the warrant officer ranks and ranked between midshipmen and lieutenants. The rank was also a commissioned officer rank from 1837 until it was replaced with the current rank of lieutenant, junior grade in 1883. France Within the French Navy, there exists a number of "master" ranks. Russia Until 1733 the sailing masters in the Imperial Russian Navy were rated as petty officers, but in that year the rank of ''Master'' was introduced after the British ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
First-rate
In the rating system of the Royal Navy used to categorise sailing warships, a first rate was the designation for the largest ships of the line. Originating in the Jacobean era with the designation of Ships Royal capable of carrying at least 400 men, the size and establishment of first-rates evolved over the following 250 years to eventually denote ships of the line carrying at least 80 guns across three gundecks. By the end of the eighteenth century, a first-rate carried no fewer than 100 guns and more than 850 crew, and had a measurement ( burthen) tonnage of some 2,000 tons. Origins The concept of a rating system for British naval vessels dates to the accession of James I of England, following which the fleet was formally divided into "great", "middling" and "lesser" craft. A 1618 commission of enquiry added a further designation of "Ships Royal" for the largest and most prestigious vessels in the fleet, each capable of carrying at least 400 men. The first Ships Royal – ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Frigate
A frigate () is a type of warship. In different eras, the roles and capabilities of ships classified as frigates have varied. The name frigate in the 17th to early 18th centuries was given to any full-rigged ship built for speed and maneuverability, intended to be used in scouting, escort and patrol roles. The term was applied loosely to ships varying greatly in design. In the second quarter of the 18th century, what is now generally regarded as the 'true frigate' was developed in France. This type of vessel was characterised by possessing only one armed deck, with an unarmed deck below it used for berthing the crew. Late in the 19th century (British and French prototypes were constructed in 1858), a type of powerful ironclad warships was developed, and because they had a single gun deck, the term 'frigate' was used to describe them. Later developments in ironclad ships rendered the 'frigate' designation obsolete and the term fell out of favour. During the Second World War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lieutenant
A lieutenant ( , ; abbreviated Lt., Lt, LT, Lieut and similar) is a Junior officer, junior commissioned officer rank in the armed forces of many nations, as well as fire services, emergency medical services, Security agency, security services and police forces. The rank in armies and air forces is often subdivided into subcategories of seniority. In Comparative navy officer ranks of Anglophone countries, English-speaking navies, lieutenants are often equivalent to the army rank of Captain (armed forces), captain; in other navies, the lieutenants are usually equal to their army counterparts. ''Lieutenant'' may also appear as part of a title used in various other organisations with a codified command structure. It often designates someone who is "second-in-command", and as such, may precede the name of the rank directly above it. For example, a "lieutenant master" is likely to be second-in-command to the "master" in an organisation using both ranks. Political uses include lieu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Commissioned Officer
An officer is a person who holds a position of authority as a member of an armed force or uniformed service. Broadly speaking, "officer" means a commissioned officer, a non-commissioned officer (NCO), or a warrant officer. However, absent contextual qualification, the term typically refers only to a force's ''commissioned officers'', the more senior members who derive their authority from a commission from the head of state. Numbers The proportion of officers varies greatly. Commissioned officers typically make up between an eighth and a fifth of modern armed forces personnel. In 2013, officers were the senior 17% of the British armed forces, and the senior 13.7% of the French armed forces. In 2012, officers made up about 18% of the German armed forces, and about 17.2% of the United States armed forces. Historically armed forces have generally had much lower proportions of officers. During the First World War, fewer than 5% of British soldiers were officers (partly beca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |