|
Scottish History
The recorded history of Scotland begins with the Scotland during the Roman Empire, arrival of the Roman Empire in the 1st century, when the Roman province, province of Roman Britain, Britannia reached as far north as the Antonine Wall. North of this was Caledonia, inhabited by the ''Picti'', whose uprisings forced Rome's legions back to Hadrian's Wall. As Rome finally Roman withdrawal from Britain, withdrew from Britain, a Gaels, Gaelic tribe from Ireland called the ''Scoti'' began colonising Western Scotland and Wales. Before Roman times, prehistoric Scotland entered the Neolithic Era about 4000 BC, the Bronze Age about 2000 BC, and the Iron Age around 700 BC. The Gaelic kingdom of Dál Riata was founded on the west coast of Scotland in the Scotland in the Early Middle Ages, 6th century. In the following century, History of Christianity in Ireland, Irish missionaries introduced the previously Pictish religion, pagan Picts to Celtic Christianity. Following S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scotland
Scotland is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It contains nearly one-third of the United Kingdom's land area, consisting of the northern part of the island of Great Britain and more than 790 adjacent Islands of Scotland, islands, principally in the archipelagos of the Hebrides and the Northern Isles. To the south-east, Scotland has its Anglo-Scottish border, only land border, which is long and shared with England; the country is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, the North Sea to the north-east and east, and the Irish Sea to the south. The population in 2022 was 5,439,842. Edinburgh is the capital and Glasgow is the most populous of the cities of Scotland. The Kingdom of Scotland emerged as an independent sovereign state in the 9th century. In 1603, James VI succeeded to the thrones of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland, forming a personal union of the Union of the Crowns, three kingdo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
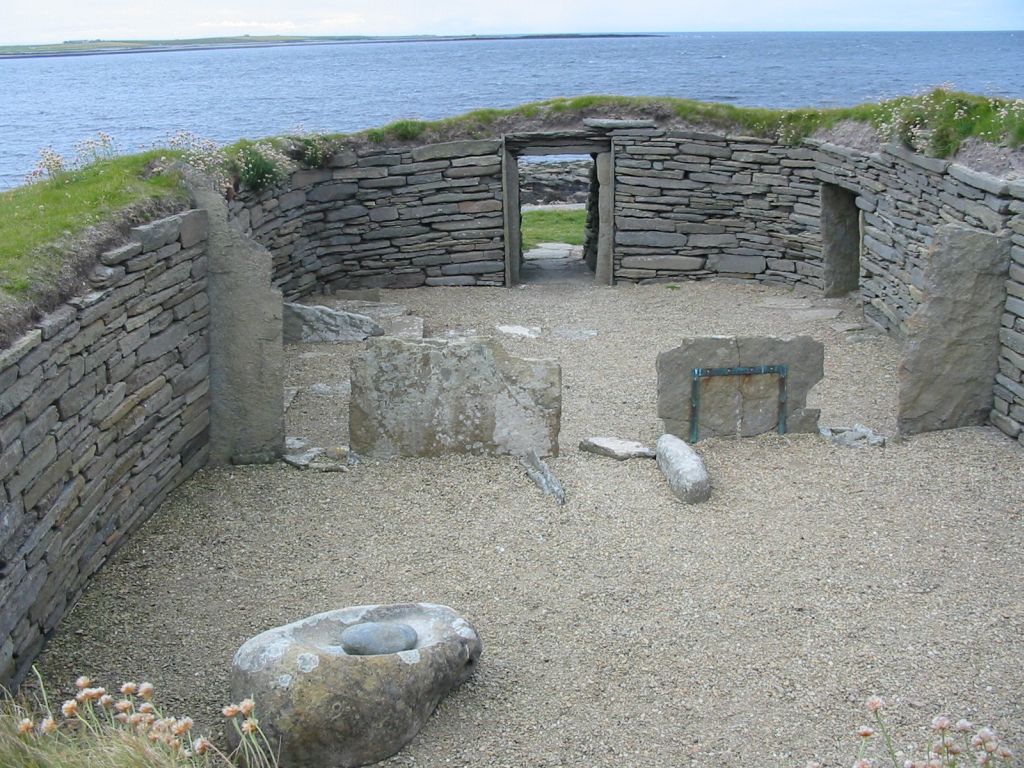
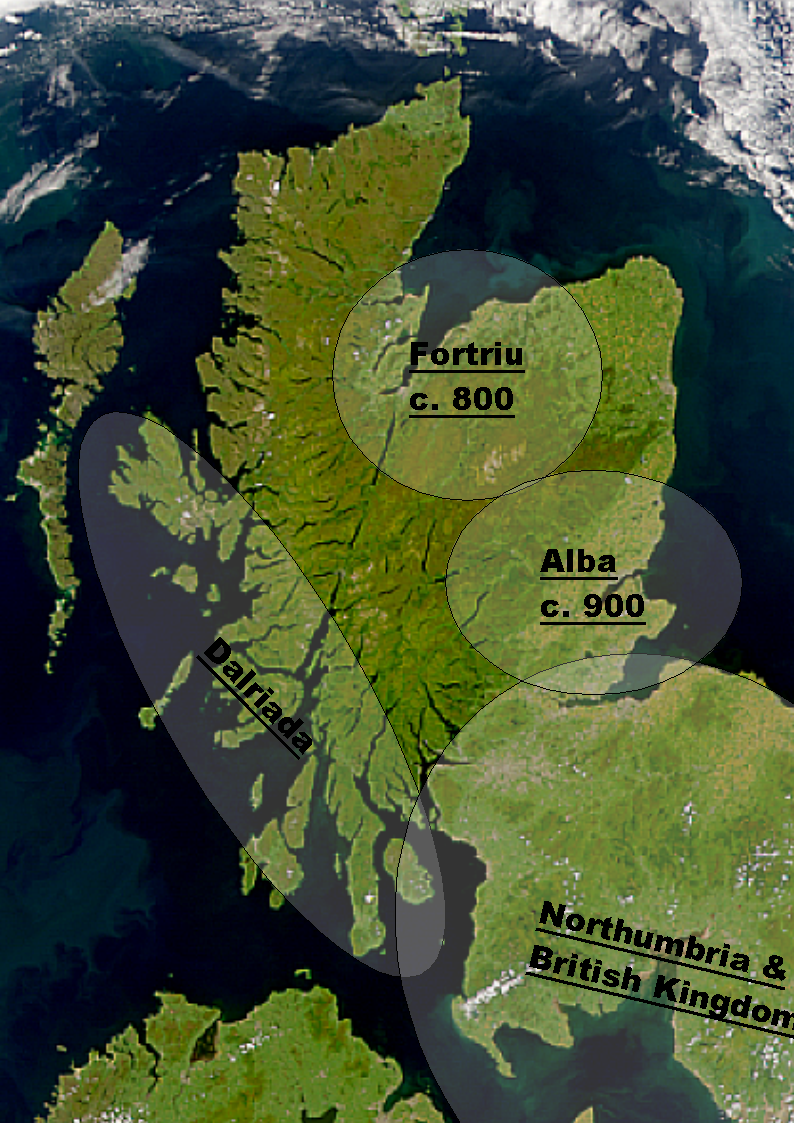
Scotland In The Early Middle Ages
Scotland was divided into a series of kingdoms in the Early Middle Ages, i.e. between the end of Roman authority in Roman Britain, southern and central Britain from around 400 AD and Origins of the Kingdom of Alba, the rise of the kingdom of Alba in 900 AD. Of these, the four most important to emerge were the Picts, the Gaels of Dál Riata, the Britons of Alt Clut, and the Anglian kingdom of Bernicia. After the arrival of the Vikings in the late 8th century, Scandinavian rulers and colonies were established on the islands and along parts of the coasts. In the 9th century, the House of Alpin combined the lands of the Scots and Picts to form a single kingdom which constituted the basis of the Kingdom of Scotland. Scotland has an extensive coastline, vast areas of difficult terrain and poor agricultural land. In this period, more land became marginal due to climate change, resulting in relatively light human settlement, particularly in the interior and Scottish Highlands, Highlands. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Alpin
The House of Alpin, also known as the Alpinid dynasty, Clann Chináeda, and Clann Chinaeda meic Ailpín, was the kin-group which ruled in Pictland, possibly Dál Riata, and then the kingdom of Alba from Constantine II (Causantín mac Áeda) in the 940s until the death of Malcolm II (Máel Coluim mac Cináeda) in 1034. Kings traced their descent from Kenneth MacAlpin (and not from his father, Alpín mac Echdach), and Irish genealogies in the Book of Ballymote and the Book of Lecan refer to the kindred as ''Clann Cináeda meic Ailpín'' by prioritising descent from Kenneth. The origins of the family are uncertain. Later genealogies make Kenneth a descendant of Áed Find. While plausible, such claims are unprovable and appear only in the late tenth century. The associated idea that Kenneth had been a king in Dál Riata before he contended successfully for power in Pictland in the 840s, following the death of Eóganán mac Óengusa, is supported by nearly contemporary evide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Scotland
The Kingdom of Scotland was a sovereign state in northwest Europe, traditionally said to have been founded in 843. Its territories expanded and shrank, but it came to occupy the northern third of the island of Great Britain, sharing a Anglo-Scottish border, land border to the south with the Kingdom of England. During the Middle Ages, Scotland engaged in intermittent conflict with England, most prominently the Wars of Scottish Independence, which saw the Scots assert their independence from the English. Following the annexation of the Hebrides and the Northern Isles from Norway in 1266 and 1472 respectively, and the capture of Berwick upon Tweed, Berwick by England in 1482, the territory of the Kingdom of Scotland corresponded to that of modern-day Scotland, bounded by the North Sea to the east, the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, and the North Channel (British Isles), North Channel and Irish Sea to the southwest. In 1603, James VI of Scotland became King of England, joini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scotland In The High Middle Ages
The High Middle Ages of Scotland encompass Scotland in the era between the death of Donald II of Scotland, Domnall II in 900 AD and the death of King Alexander III of Scotland, Alexander III in 1286, which was an indirect cause of the Wars of Scottish Independence. At the close of the ninth century, various competing kingdoms occupied the territory of modern Scotland. Scandinavian influence was dominant in the northern and western islands, Britons (historical), Brythonic culture in the southwest, the Anglo-Saxon or English Kingdom of Northumbria in the southeast and the Picts, Pictish and Gaels, Gaelic Kingdom of Alba in the east, north of the River Forth. By the tenth and eleventh centuries, northern Great Britain was increasingly dominated by Gaelic culture, and by the Gaelic regal lordship of ''Alba'', known in Latin as either ''Albania'' or ''Scotia'', and in English language, English as "Scotland". From its base in the east, this kingdom acquired control of the lands lying ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viking Invasions Of Scotland
Scandinavian Scotland was the period from the 8th to the 15th centuries during which Vikings and Norse settlers, mainly Norwegians and to a lesser extent other Scandinavians, and their descendants colonised parts of what is now the periphery of modern Scotland. Viking influence in the area commenced in the late 8th century, and hostility between the Scandinavian earls of Orkney and the emerging thalassocracy of the Kingdom of the Isles, the rulers of Ireland, Dál Riata and Alba, and intervention by the crown of Norway were recurring themes. Scandinavian-held territories included the Northern Isles of Orkney and Shetland, the Hebrides, the islands of the Firth of Clyde and associated mainland territories including Caithness and Sutherland. The historical record from Scottish sources is weak, with the Irish annals and the later Norse sagas, of which the ''Orkneyinga saga'' is the principal source of information, sometimes contradictory although modern archaeology is beginning to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northumbria
Northumbria () was an early medieval Heptarchy, kingdom in what is now Northern England and Scottish Lowlands, South Scotland. The name derives from the Old English meaning "the people or province north of the Humber", as opposed to the Southumbria, people south of the Humber, Humber Estuary. What was to become Northumbria started as two kingdoms, Deira in the south and Bernicia in the north. Conflict in the first half of the seventh century ended with the murder of the last king of Deira in 651, and Northumbria was thereafter unified under Bernician kings. At its height, the kingdom extended from the Humber, Peak District and the River Mersey on the south to the Firth of Forth on the north. Northumbria ceased to be an independent kingdom in the mid-tenth century when Deira was conquered by the Danelaw, Danes and formed into the Kingdom of York. The rump Earl of Northumbria, Earldom of Bamburgh maintained control of Bernicia for a period of time; however, the area north of R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Saxons
The Anglo-Saxons, in some contexts simply called Saxons or the English, were a Cultural identity, cultural group who spoke Old English and inhabited much of what is now England and south-eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. They traced their origins to Germanic peoples, Germanic settlers who became one of the most important cultural groups in Britain by the 5th century. The Anglo-Saxon period in Britain is considered to have started by about 450 and ended in 1066, with the Norman conquest of England, Norman Conquest. Although the details of Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, their early settlement and History of Anglo-Saxon England, political development are not clear, by the 8th century an Anglo-Saxon cultural identity which was generally called had developed out of the interaction of these settlers with the existing Romano-British culture. By 1066, most of the people of what is now England spoke Old English, and were considered English. Viking and Norman invasions chang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Rite
The Roman Rite () is the most common ritual family for performing the ecclesiastical services of the Latin Church, the largest of the ''sui iuris'' particular churches that comprise the Catholic Church. The Roman Rite governs Rite (Christianity), rites such as the Roman Mass and the Liturgy of the Hours as well as the manner in which Sacraments of the Catholic Church, sacraments and Blessing in the Catholic Church, blessings are performed. The Roman Rite developed in the Latin language in the city of Rome and, while distinct Latin liturgical rites such as the Ambrosian Rite remain, the Roman Rite has gradually been adopted almost everywhere in the Latin Church. In medieval times there were numerous local variants, even if all of them did not amount to distinct rites, yet uniformity increased as a result of the invention of printing and in obedience to the decrees of the Council of Trent of 1545–1563 (see ''Quo primum''). Several Latin liturgical rites which had survived into th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nechtan Mac Der-Ilei
Naiton son of Der-Ilei (; died 732), also called Naiton son of Dargart (), was king of the Picts between 706–724 and between 728–729. He succeeded his brother Bridei IV in 706. He is associated with significant religious reforms in Pictland. He abdicated in 724 in favour of his nephew and became a monk. In 728 and 729 he fought in a four-sided war for the Pictish throne. Background It has been argued that Nechtan son of Derile should be identified with the Nechtan son of Dargart mentioned in the Annals of Ulster in 710. Dargart is taken to be the Dargart mac Finguine who died in 686, a member of the Cenél Comgaill kindred of Dál Riata. On this basis, and because Bede mentions that the Picts allowed for matrilineal succession in exceptional cases, it is thought that Der-Ilei (Bridei III) was Nechtan's mother. Other brothers and half-brothers of Nechtan and Bridei would include Ciniod or Cináed, killed in 713; Talorcan son of Drestan, a half-brother or foster-brother ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gregorian Mission
The Gregorian missionJones "Gregorian Mission" ''Speculum'' p. 335 or Augustinian missionMcGowan "Introduction to the Corpus" ''Companion to Anglo-Saxon Literature'' p. 17 was a Christian mission sent by Pope Pope Gregory I, Gregory the Great in 596 to convert Britain's Anglo-Saxons.Mayr-Harting ''Coming of Christianity'' p. 50 The mission was headed by Augustine of Canterbury. By the time of the death of the last missionary in 653, the mission had Christianisation of Anglo-Saxon England, established Christianity among the southern Anglo-Saxons. Along with the Irish and Franks, Frankish missions it converted Anglo-Saxons in other parts of Britain as well and influenced the Hiberno-Scottish missions to continental Europe. When the Roman Empire recalled its Roman legion, legions from the province of Roman Britain, Britannia in 410, parts of the island had already been Anglo-Saxon invasion of Britain, settled by Anglo-Saxon paganism, pagan Germanic peoples, Germanic tribes who, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saxon England
Anglo-Saxon England or early medieval England covers the period from the end of Roman Empire, Roman imperial rule in Roman Britain, Britain in the 5th century until the Norman Conquest in 1066. Compared to modern England, the territory of the Anglo-Saxons stretched north to present day Lothian in southeastern Scotland, whereas it did not initially include western areas of England such as Cornwall, Herefordshire, Shropshire, Cheshire, Lancashire, and Cumbria. The 5th and 6th centuries involved the collapse of economic networks and political structures and also saw a radical change to a new Anglo-Saxon language and culture. This change was driven by movements of peoples as well as changes which were happening in both northern Gaul and the North Sea coast of what is now Germany and the Netherlands. The Anglo-Saxon language, also known as Old English, was a close relative of languages spoken in the latter regions, and genetic studies have confirmed that there was significant migrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |