|
Schultz's Rule
Schultz's rule is a rule developed by Adolph Hans Schultz, declaring a relationship between the first tooth eruption of the molar versus the permanent teeth and the progress or aging of its carrier. It states that species that live longer have more wear on deciduous teeth and as a result start replacing them relatively early in life. Which is an indicator for examining fossil data. According to research, '' Myotragus balearicus'' follows Schultz's Rule. See also * Diphyodont * Polyphyodont * Tooth development A tooth (: teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, teari ... References Further reading * * Tooth development Animal anatomy Paleontological concepts and hypotheses {{dentistry-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adolph Hans Schultz
Adolf (also spelt Adolph or Adolphe, Adolfo, and when Latinisation (literature), Latinised Adolphus) is a given name with German language, German origins. The name is a Compound (linguistics), compound derived from the Old High German ''Athalwolf'' (or ''Hadulf''), a composition of ''athal'', or ''adal'', meaning "noble" (or '':wikt:hadu-, had(u)''-, meaning "battle, combat"), and ''wolf''. The name is cognate to the Anglo-Saxons, Anglo-Saxon name ''Æthelwulf'' (also Eadulf or Eadwulf). The name can also be derived from the ancient Germanic elements "Wald" meaning "power", "brightness" and wolf (Waldwulf). Due to its extremely negative associations with the Nazi leader Adolf Hitler, the name has greatly declined in popularity since the end of World War II. Similar names include Lithuanian language, Lithuanian Adolfas and Latvian language, Latvian Ādolfs. The female forms Adolphine (name), Adolphine and Adolpha are far more rare than the male names. Adolphus can also appear as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
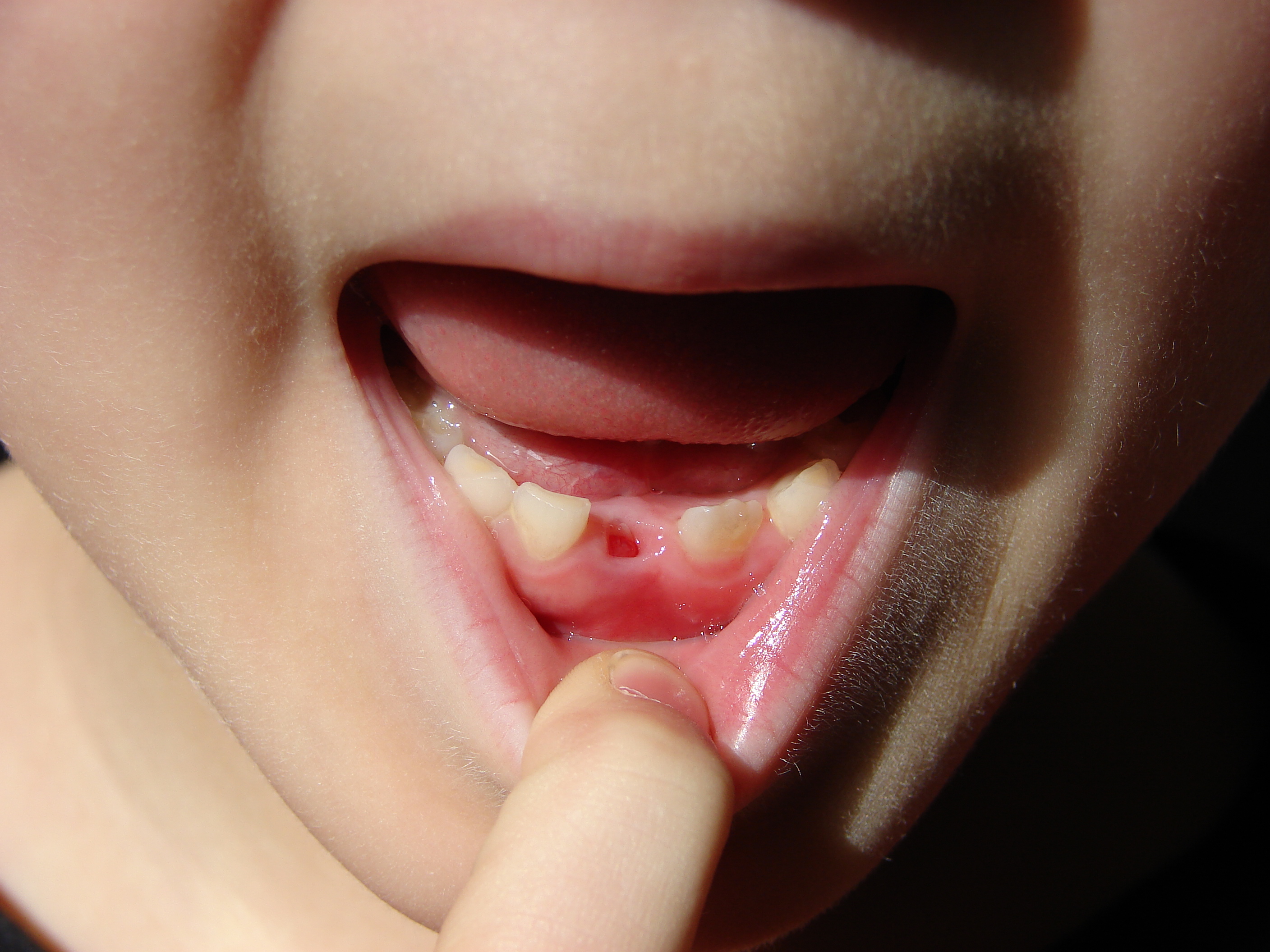
Tooth Eruption
Tooth eruption is a process in tooth development in which the teeth enter the mouth and become visible. It is currently believed that the periodontal ligament plays an important role in tooth eruption. The first human teeth to appear, the deciduous (primary) teeth (also known as baby or milk teeth), erupt into the mouth from around 6 months until 2 years of age, in a process known as "teething". These teeth are the only ones in the mouth until a person is about 6 years old creating the primary dentition stage. At that time, the first permanent tooth erupts and begins a time in which there is a combination of primary and permanent teeth, known as the mixed dentition stage, which lasts until the last primary tooth is lost. Then, the remaining permanent teeth erupt into the mouth during the permanent dentition stage. Theories Although researchers agree that tooth eruption is a complex process, there is little agreement on the identity of the mechanism that controls eruption. There ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
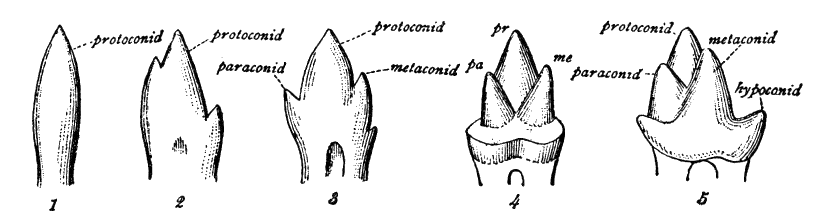
Molar (tooth)
The molars or molar teeth are large, flat teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammals. They are used primarily to grind food during chewing. The name ''molar'' derives from Latin, ''molaris dens'', meaning "millstone tooth", from ''mola'', millstone and ''dens'', tooth. Molars show a great deal of diversity in size and shape across the mammal groups. The third molar of humans is sometimes vestigial. Human anatomy In humans, the molar teeth have either four or five cusps. Adult humans have 12 molars, in four groups of three at the back of the mouth. The third, rearmost molar in each group is called a wisdom tooth. It is the last tooth to appear, breaking through the front of the gum at about the age of 20, although this varies among individuals and populations, and in many cases the tooth is missing. The human mouth contains upper (maxillary) and lower (mandibular) molars. They are: maxillary first molar, maxillary second molar, maxillary third mol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deciduous Teeth
Deciduous teeth or primary teeth, also informally known as baby teeth, milk teeth, or temporary teeth,Fehrenbach, MJ and Popowics, T. (2026). ''Illustrated Dental Embryology, Histology, and Anatomy'', 6th edition, Elsevier, page 287–296. are the first set of teeth in the growth and development of humans and other diphyodonts, which include most mammals but not elephants, kangaroos, or manatees, which are polyphyodonts. Deciduous teeth Animal tooth development, develop during the embryonic stage of development and tooth eruption, erupt (break through the gums and become visible in the mouth) during infancy. They are usually lost and replaced by permanent teeth, but in the absence of their permanent replacements, they can remain functional for many years into adulthood. Development Formation Primary teeth start to form during the embryonic phase of human development (biology), human life. The development of primary teeth starts at the sixth week of tooth development as the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myotragus Balearicus
''Myotragus'' (Neo-Latin, derived from the Greek: , "mouse-goat") is an extinct genus of goat-antelope in the tribe Caprini which lived on the Balearic Islands of Mallorca and Menorca in the western Mediterranean until its extinction around 4,500 years ago. The fossil record of ''Myotragus'' on the Balearic Islands extends over 5 million years back to the early Pliocene on Mallorca, where it presumably arrived after the evaporation of the Mediterranean Sea during the Messinian Salinity Crisis (around 5.96-5.33 million years ago). ''Myotragus'' is represented by six sequential chronospecies representing gradual change in morphology''.'' The youngest and best known species, ''M. balearicus,'' is noted for a number of unusual morphological adaptions, including forward facing eyes suggestive of binocular vision, as well as a long lifespan, which developed in an unusual ecosystem where only a few other mammal species were present, terrestrial predators were absent, and ''Myotragus' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diphyodont
A diphyodont is any animal with two sets of teeth, initially the ''deciduous'' set and consecutively the '' permanent'' set. Most mammals are diphyodonts—as to chew their food they need a strong, durable and complete set of teeth. Diphyodonts contrast with ''polyphyodonts'', whose teeth are constantly replaced. Diphyodonts also differ from '' monophyodonts'', which are animals who have only one set of teeth that does not change over a long period of growth. In diphyodonts, the number of teeth that are replaced varies from species to species. In humans, a set of twenty deciduous teeth, or "milk teeth", are replaced by a completely new set of thirty-two adult teeth. In some cases hypodontia or hyperdontia occurs, the latter in cleidocranial dysostosis and Gardner's syndrome. In the hare the anterior incisors are not replaced but the posterior smaller incisors are replaced. Not much is known about the developmental mechanisms regulating diphyodont replacement. The house shre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyphyodont
A polyphyodont is any animal whose tooth (animal), teeth are continually replaced. In contrast, diphyodonts are characterized by having only two successive sets of teeth. Polyphyodonts include most toothed fishes (most notably sharks), many reptiles such as crocodiles and geckos, and most other vertebrates, with mammals being the main exception (though Polyphyodont#Evolution in mammals, not absolute). Growth New, permanent teeth grow in the jaws, usually under or just behind the old tooth, from stem cells in the dental lamina. Young animals typically have a full set of teeth when they hatch; there is no tooth change in the egg. Within days, tooth replacement begins, usually in the back of the jaw continuing forward like a wave. On average a tooth is replaced every few months. Crocodilia Crocodilia are the only non-mammalian vertebrates with tooth sockets. Alligators grow a successional tooth (a small replacement tooth) under each mature functional tooth for replacement once a y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tooth Development (other)
{{Disambiguation ...
Tooth development may refer to: *Animal tooth development *Human tooth development Tooth development or odontogenesis is the complex process by which teeth form from embryonic cells, grow, and erupt into the mouth. For human teeth to have a healthy oral environment, all parts of the tooth must develop during appropriate sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tooth Development
A tooth (: teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, tearing food, for defensive purposes, to intimidate other animals often including their own, or to carry prey or their young. The roots of teeth are covered by gums. Teeth are not made of bone, but rather of multiple tissues of varying density and hardness that originate from the outermost embryonic germ layer, the ectoderm. The general structure of teeth is similar across the vertebrates, although there is considerable variation in their form and position. The teeth of mammals have deep roots, and this pattern is also found in some fish, and in crocodilians. In most teleost fish, however, the teeth are attached to the outer surface of the bone, while in lizards they are attached to the inner surface of the jaw by one side. In cartilaginous fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Anatomy
Anatomy () is the branch of Morphology (biology), morphology concerned with the study of the internal structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having its beginnings in prehistoric times. Anatomy is inherently tied to developmental biology, embryology, comparative anatomy, evolutionary biology, and phylogeny, as these are the processes by which anatomy is generated, both over immediate and long-term timescales. Anatomy and physiology, which study the structure and function (biology), function of organisms and their parts respectively, make a natural pair of related disciplines, and are often studied together. Human anatomy is one of the essential basic sciences that are applied in medicine, and is often studied alongside physiology. Anatomy is a complex and dynamic field that is constantly evolving as discoveries are made. In recent years, there has been a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |