|
Schematic Overview Of Belgian Institutions
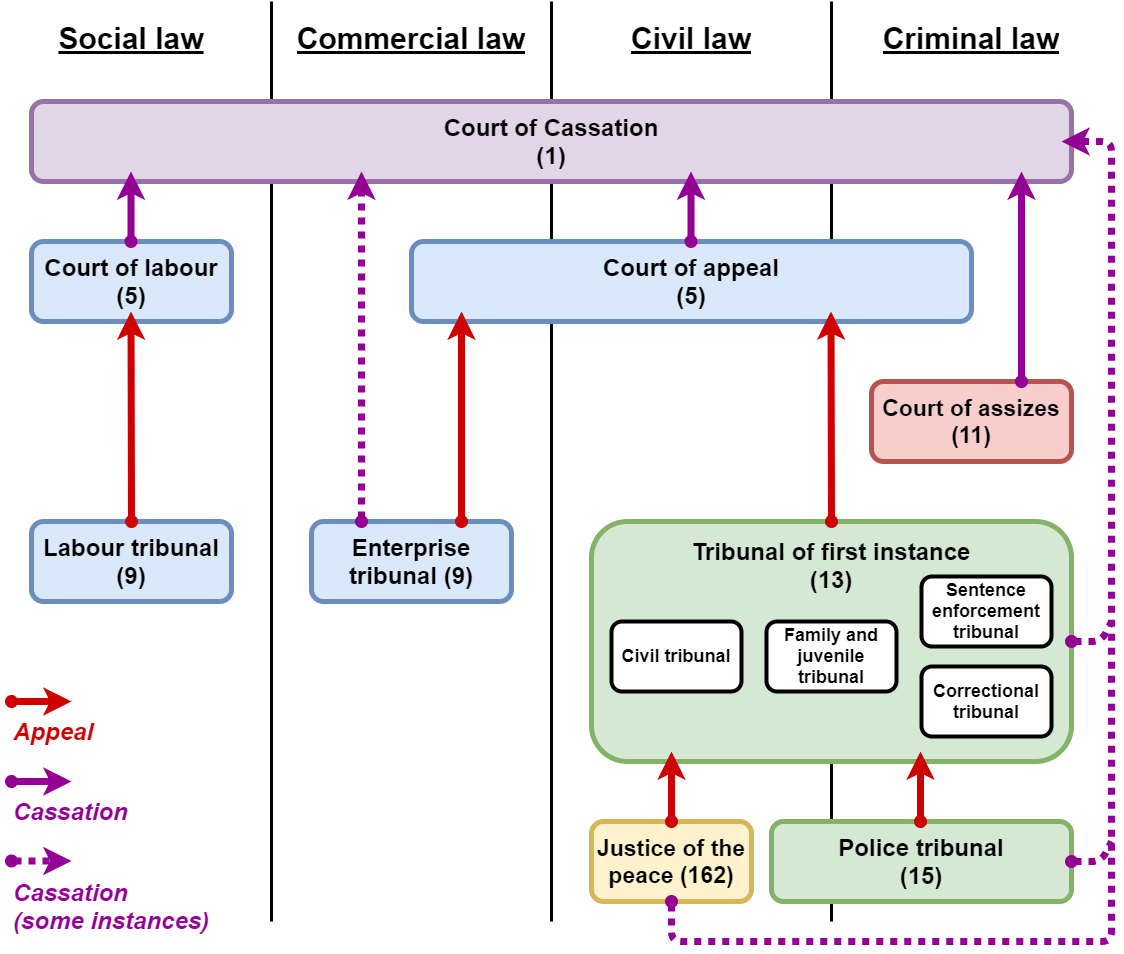
The table below provides a schematic and hierarchic overview of the institutions of the Belgian federated state, according to the principle of the separation of powers, Trias Politica (the theoretical concept of the separation of powers, Separation of political powers) in law-making, executive and judicial powers (the horizontal separation of powers) and according to their territorial level or so called subsidiarity (the vertical separation of powers). (*) a part of the executive responsibilities in Brussels are executed by the Flemish Community council (for Brussels) (VGC). This is not a government but a subsidiary executive organ. References {{Reflist External linksBelgian Government Portal Government of Belgium, * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Separation Of Powers
The separation of powers principle functionally differentiates several types of state (polity), state power (usually Legislature#Legislation, law-making, adjudication, and Executive (government)#Function, execution) and requires these operations of government to be conceptually and institutionally distinguishable and articulated, thereby maintaining the integrity of each. To put this model into practice, government is divided into structurally independent branches to perform various functions (most often a legislature, a judiciary and an administration, sometimes known as the ). When each function is allocated strictly to one branch, a government is described as having a high degree of separation; whereas, when one person or branch plays a significant part in the exercise of more than one function, this represents a fusion of powers. History Antiquity Polybius (''Histories'', Book 6, 11–13) described the Roman Republic as a mixed government ruled by the Roman Senate, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regions
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as areas, zones, lands or territories, are portions of the Earth's surface that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and the interaction of humanity and the environment ( environmental geography). Geographic regions and sub-regions are mostly described by their imprecisely defined, and sometimes transitory boundaries, except in human geography, where jurisdiction areas such as national borders are defined in law. More confined or well bounded portions are called '' locations'' or ''places''. Apart from the global continental regions, there are also hydrospheric and atmospheric regions that cover the oceans, and discrete climates above the land and water masses of the planet. The land and water global regions are divided into subregions geographically bounded by large geological features that influence large-scale ecologies, such as plains and features. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Court Of Assize (Belgium)
The court of assizes (, , ) is the trial court which tries the most serious crimes in the judicial system of Belgium. It is the highest Belgian court with criminal jurisdiction; as such, it is the only Belgian court that can sentence someone to Life imprisonment in Belgium, life imprisonment. The courts of assizes are not permanent courts; a new court of assizes is assembled for each new trial. There is a court of assizes in each of the ten provinces of Belgium, as well as one in the arrondissement of Brussels-Capital which is not part of any province. Further below, an overview is provided of the eleven courts of assizes and their seats. They are the only courts in Belgium for which the provinces are used as territorial subdivisions. They are also the only courts in Belgium that hold jury trials. The jury acts as sole trier of fact, but decides on the Sentence (law), penalty together with the judges. The trial by jury of certain crimes is laid down in article 150 of the Constit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Court Of Appeal (Belgium)
The courts of appeal (, , ) are the main appellate courts in the judicial system of Belgium, which hear appeals against judgements of the Tribunal of first instance (Belgium), tribunals of first instance, the Commercial Tribunal (Belgium), enterprise tribunals and the presidents of those tribunals in their judicial area. There are five courts of appeal for each of the five judicial areas, which are the largest geographical subdivisions of Belgium for judicial purposes. The division of the Belgian territory into the five judicial areas (Antwerp, Brussels, Ghent, Liège and Mons, Belgium, Mons) is laid down in article 156 of the Constitution of Belgium, Belgian Constitution. A judicial area covers multiple Arrondissements of Belgium, judicial arrondissements ("districts"), except for the judicial area of Mons. Each arrondissement has a tribunal of first instance. Further below, an overview is provided of the five courts of appeal and the judicial arrondissements their judicial area ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deputies
A legislator, or lawmaker, is a person who writes and passes laws, especially someone who is a member of a legislature. Legislators are often elected by the people, but they can be appointed, or hereditary. Legislatures may be supra-national (for example, the European Parliament), national, such as the Japanese Diet, sub-national as in provinces, or local. Overview The political theory of the separation of powers requires legislators to be independent individuals from the members of the executive and the judiciary. Certain political systems adhere to this principle, others do not. In the United Kingdom and other countries using the Westminster system, for example, the executive is formed almost exclusively from legislators (members of the parliament), and the executive Cabinet itself has delegated legislative power. In continental European jurisprudence and legal discussion, "the legislator" (') is the abstract entity that has produced the laws. When there is room ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provincial Governor
Provincial may refer to: Government & Administration * Provincial capitals, an administrative sub-national capital of a country * Provincial city (other) * Provincial minister (other) * Provincial Secretary, a position in Canadian government * Member of Provincial Parliament (other), a title for legislators in Ontario, Canada as well as Eastern Cape Province, South Africa. * Provincial council (other), various meanings * Sub-provincial city in the People's Republic of China Companies * The Provincial sector of British Rail, which was later renamed Regional Railways * Provincial Airlines, a Canadian airline * Provincial Insurance Company, a former insurance company in the United Kingdom Other Uses * Provincial Osorno, a football club from Chile * Provincial examinations, a school-leaving exam in British Columbia, Canada * A provincial superior of a religious order * Provincial park, the equivalent of national parks in the Canadian province ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provincial Council (Belgium)
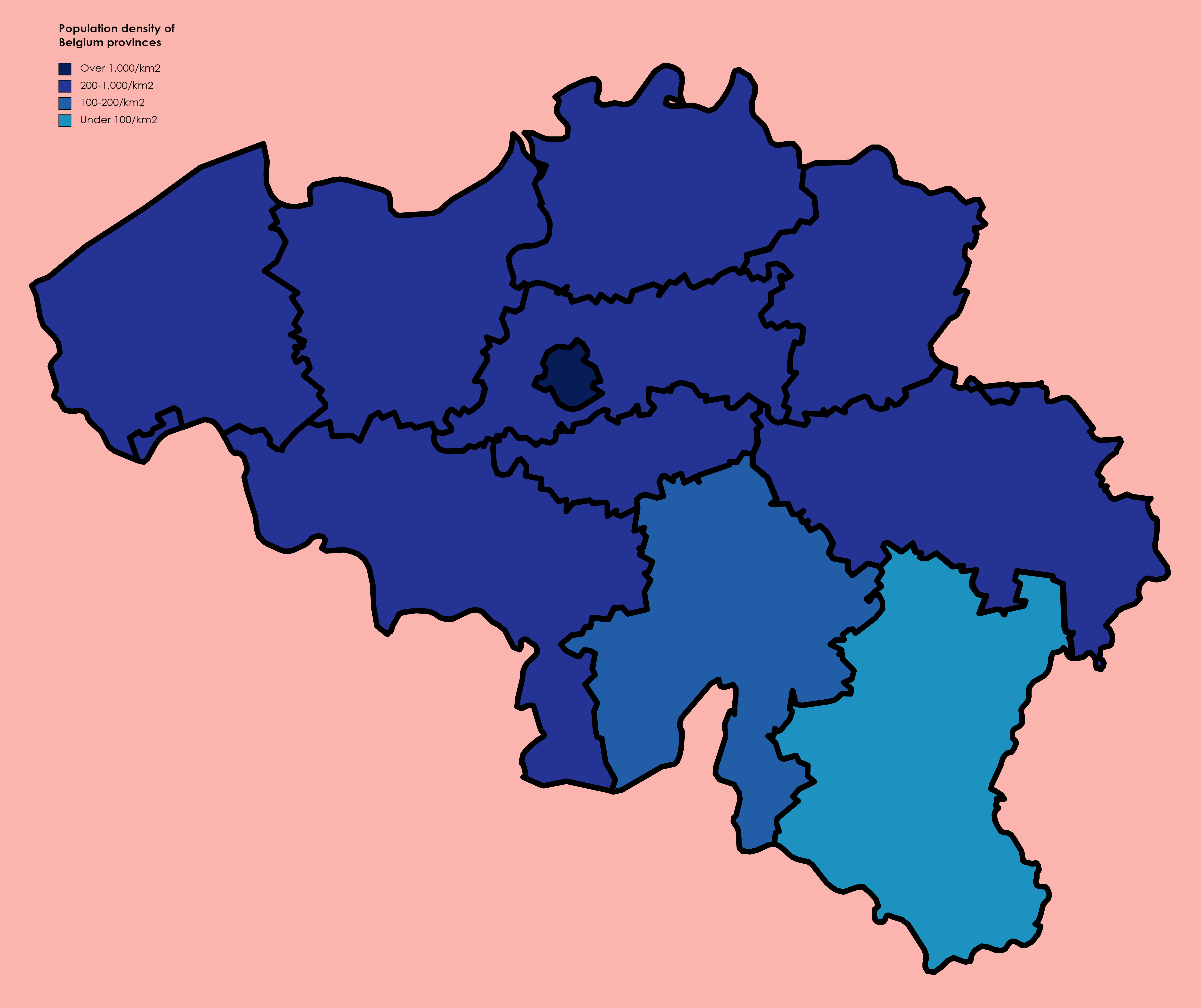
The Kingdom of Belgium is divided into three regions. Two of these regions, Flanders and Wallonia, are each subdivided into five provinces. The third region, Brussels, does not belong to any province, nor is it subdivided into provinces. Instead, it has amalgamated both regional and provincial functions into a single "Capital Region" administration. Most of the provinces take their name from earlier duchies and counties of similar location, while their territory is mostly based on the departments installed during French annexation. At the time of the creation of Belgium in 1830, only nine provinces existed, including the province of Brabant, which held the City of Brussels. In 1995, Brabant was split into three areas: Flemish Brabant, which became a part of the region of Flanders; Walloon Brabant, which became part of the region of Wallonia; and the Brussels-Capital Region, which became a third region. These divisions reflected political tensions between the French-speaking Wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provinces Of Belgium
The Kingdom of Belgium is divided into three Communities, regions, and language areas of Belgium, regions. Two of these regions, Flanders and Wallonia, are each subdivided into five provinces. The third region, Brussels, does not belong to any province, nor is it subdivided into provinces. Instead, it has amalgamated both regional and provincial functions into a single "Capital Region" administration. Most of the provinces take their name from earlier duchy, duchies and county, counties of similar location, while their territory is mostly based on the 130 departments of the First French Empire, departments installed during French annexation. At the time of the Independence of Belgium, creation of Belgium in 1830, only nine provinces existed, including the province of Brabant, which held the City of Brussels. In 1995, Brabant was split into three areas: Flemish Brabant, which became a part of the region of Flanders; Walloon Brabant, which became part of the region of Wallonia; an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brussels Capital Government
Brussels, officially the Brussels-Capital Region, (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) is a Communities, regions and language areas of Belgium#Regions, region of Belgium comprising #Municipalities, 19 municipalities, including the City of Brussels, which is the capital of Belgium. The Brussels-Capital Region is located in the central portion of the country. It is a part of both the French Community of Belgium and the Flemish Community, and is separate from the Flemish Region (Flanders), within which it forms an enclave, and the Walloon Region (Wallonia), located less than to the south. Brussels grew from a small rural settlement on the river Senne (river), Senne to become an important city-region in Europe. Since the end of the Second World War, it has been a major centre for international politics and home to numerous international organisations, politicians, Diplomacy, diplomats and civil servants. Brussels is the ''de facto' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |