|
Scanning Transmission Electron Microscopy
A scanning transmission electron microscope (STEM) is a type of transmission electron microscope (TEM). Pronunciation is [stɛm] or [ɛsti:i:ɛm]. As with a conventional transmission electron microscope (CTEM), images are formed by electrons passing through a sufficiently thin specimen. However, unlike CTEM, in STEM the electron beam is focused to a fine spot (with the typical spot size 0.05 – 0.2 nm) which is then scanned over the sample in a raster illumination system constructed so that the sample is illuminated at each point with the beam parallel to the optical axis. The rastering of the beam across the sample makes STEM suitable for analytical techniques such as Z-contrast annular dark-field imaging, and spectroscopic mapping by energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) spectroscopy, or electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS). These signals can be obtained simultaneously, allowing direct correlation of images and spectroscopic data. A ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STEM Fig
Stem or STEM most commonly refers to: * Plant stem, a structural axis of a vascular plant * Crown group#Stem groups, Stem group * Science, technology, engineering, and mathematics Stem or STEM can also refer to: Language and writing * Word stem, part of a word responsible for its lexical meaning ** Stemming, a process in natural language processing * Stem (music), in music notation, the vertical lines directly connected to the note head * Stem (typography), the main vertical stroke of a letter * Stem, the opening of a multiple choice question Music and audio * Stem (audio), a collection of audio sources mixed together to be dealt with downstream as one unit * Stem (music), a part of a written musical note * Stem mixing and mastering, a method of mixing audio material * The Stems, an Australian garage punk band * Stem (DJ Shadow song), "Stem" (DJ Shadow song), 1996 * Stem (Ringo Sheena song), "Stem" (Ringo Sheena song), 2003 * "Stem", a song by Hayden from the 1995 album ''Ever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
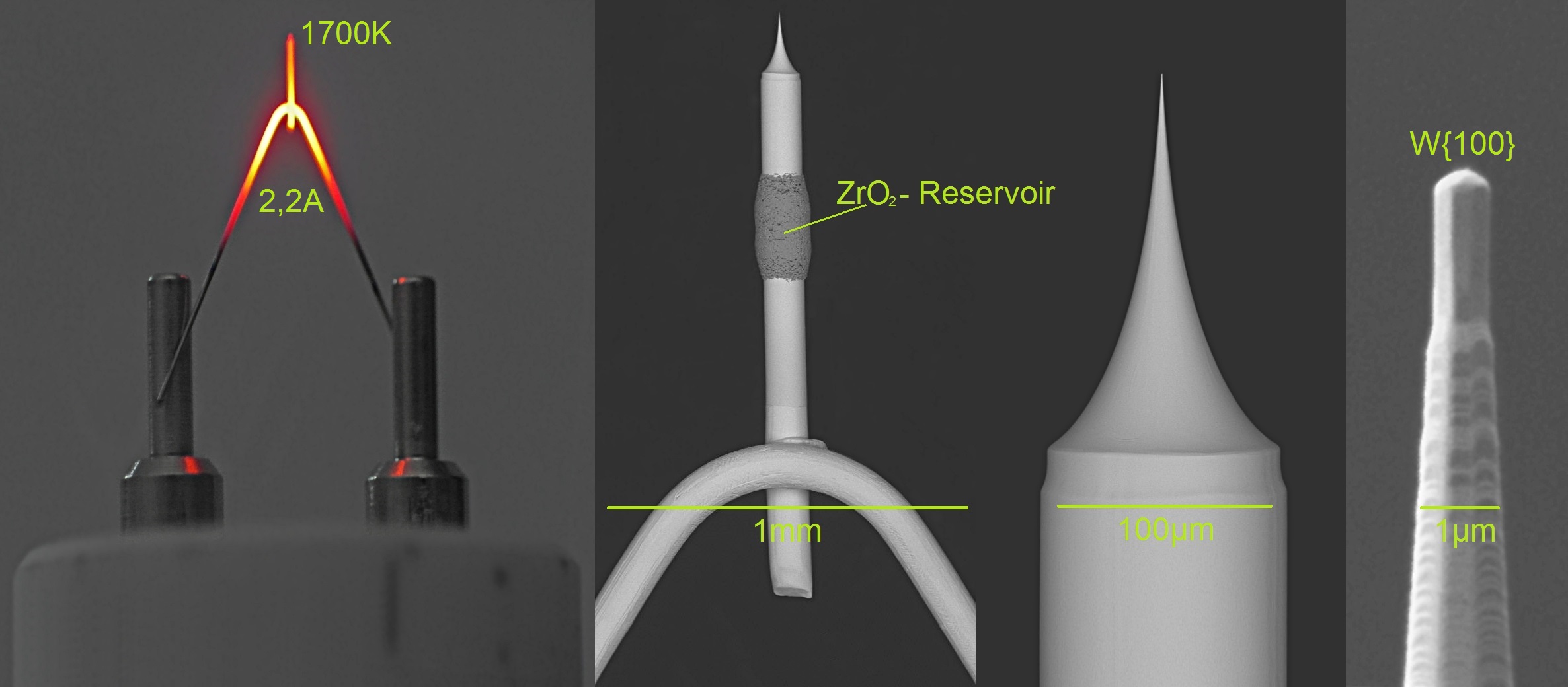
Field Emission Gun
A field emission gun (FEG) is a type of electron gun in which a sharply pointed Müller-type emitter is held at several kilovolts negative potential relative to a nearby electrode, so that there is sufficient potential gradient at the emitter surface to cause field electron emission. Emitters are either of cold-cathode type, usually made of single crystal tungsten sharpened to a tip radius of about 100 nm, or of the Walter H. Schottky, Schottky type, in which thermionic emission is enhanced by barrier lowering in the presence of a high electric field. Schottky emitters are made by coating a tungsten tip with a layer of zirconium oxide (ZrO2) decreasing the work function of the tip by approximately 2.7 electronvolt, eV. In electron microscopes, a field emission gun is used to produce an electron beam that is smaller in diameter, more Coherence (physics), coherent and with up to three orders of magnitude greater current density or brightness than can be achieved with conventio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferromagnetic Domains In Spiral Pattern For Fe60Al40
Ferromagnetism is a property of certain materials (such as iron) that results in a significant, observable magnetic permeability, and in many cases, a significant magnetic coercivity, allowing the material to form a permanent magnet. Ferromagnetic materials are noticeably attracted to a magnet, which is a consequence of their substantial magnetic permeability. Magnetic permeability describes the induced magnetization of a material due to the presence of an external magnetic field. For example, this temporary magnetization inside a steel plate accounts for the plate's attraction to a magnet. Whether or not that steel plate then acquires permanent magnetization depends on both the strength of the applied field and on the coercivity of that particular piece of steel (which varies with the steel's chemical composition and any heat treatment it may have undergone). In physics, multiple types of material magnetism have been distinguished. Ferromagnetism (along with the similar effec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aharonov–Bohm Effect
The Aharonov–Bohm effect, sometimes called the Ehrenberg–Siday–Aharonov–Bohm effect, is a quantum mechanics, quantum-mechanical phenomenon in which an electric charge, electrically charged point particle, particle is affected by an electromagnetic potential (\varphi, \mathbf), despite being confined to a region in which both the magnetic field \mathbf and electric field \mathbf are zero. The underlying mechanism is the coupling (physics), coupling of the electromagnetic potential with the Argument (complex analysis), complex phase of a charged particle's wave function, and the Aharonov–Bohm effect is accordingly illustrated by double-slit experiment, interference experiments. The most commonly described case, sometimes called the Aharonov–Bohm solenoid effect, takes place when the wave function of a charged particle passing around a long solenoid experiences a Phase (waves), phase shift as a result of the enclosed magnetic field, despite the magnetic field being negl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planck Constant
The Planck constant, or Planck's constant, denoted by h, is a fundamental physical constant of foundational importance in quantum mechanics: a photon's energy is equal to its frequency multiplied by the Planck constant, and the wavelength of a matter wave equals the Planck constant divided by the associated particle momentum. The constant was postulated by Max Planck in 1900 as a proportionality constant needed to explain experimental black-body radiation. Planck later referred to the constant as the "quantum of Action (physics), action". In 1905, Albert Einstein associated the "quantum" or minimal element of the energy to the electromagnetic wave itself. Max Planck received the 1918 Nobel Prize in Physics "in recognition of the services he rendered to the advancement of Physics by his discovery of energy quanta". In metrology, the Planck constant is used, together with other constants, to define the kilogram, the SI unit of mass. The SI units are defined in such a way that, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matter Wave
Matter waves are a central part of the theory of quantum mechanics, being half of wave–particle duality. At all scales where measurements have been practical, matter exhibits wave-like behavior. For example, a beam of electrons can be diffracted just like a beam of light or a water wave. The concept that matter behaves like a wave was proposed by French physicist Louis de Broglie () in 1924, and so matter waves are also known as de Broglie waves. The ''de Broglie wavelength'' is the wavelength, , associated with a particle with momentum through the Planck constant, : \lambda = \frac. Wave-like behavior of matter has been experimentally demonstrated, first for electrons in 1927 and for other elementary particles, neutral atoms and molecules in the years since. Matter waves have more complex velocity relations than solid objects and they also differ from electromagnetic waves (light). Collective matter waves are used to model phenomena in solid state physics; standing matte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Field
A magnetic field (sometimes called B-field) is a physical field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to the magnetic field. A permanent magnet's magnetic field pulls on ferromagnetic materials such as iron, and attracts or repels other magnets. In addition, a nonuniform magnetic field exerts minuscule forces on "nonmagnetic" materials by three other magnetic effects: paramagnetism, diamagnetism, and antiferromagnetism, although these forces are usually so small they can only be detected by laboratory equipment. Magnetic fields surround magnetized materials, electric currents, and electric fields varying in time. Since both strength and direction of a magnetic field may vary with location, it is described mathematically by a function (mathematics), function assigning a Euclidean vector, vector to each point of space, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Field
An electric field (sometimes called E-field) is a field (physics), physical field that surrounds electrically charged particles such as electrons. In classical electromagnetism, the electric field of a single charge (or group of charges) describes their capacity to exert attractive or repulsive forces on another charged object. Charged particles exert attractive forces on each other when the sign of their charges are opposite, one being positive while the other is negative, and repel each other when the signs of the charges are the same. Because these forces are exerted mutually, two charges must be present for the forces to take place. These forces are described by Coulomb's law, which says that the greater the magnitude of the charges, the greater the force, and the greater the distance between them, the weaker the force. Informally, the greater the charge of an object, the stronger its electric field. Similarly, an electric field is stronger nearer charged objects and weaker f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lorentz Force
In electromagnetism, the Lorentz force is the force exerted on a charged particle by electric and magnetic fields. It determines how charged particles move in electromagnetic environments and underlies many physical phenomena, from the operation of electric motors and particle accelerators to the behavior of plasmas. The Lorentz force has two components. The electric force acts in the direction of the electric field for positive charges and opposite to it for negative charges, tending to accelerate the particle in a straight line. The magnetic force is perpendicular to both the particle's velocity and the magnetic field, and it causes the particle to move along a curved trajectory, often circular or helical in form, depending on the directions of the fields. Variations on the force law describe the magnetic force on a current-carrying wire (sometimes called Laplace force), and the electromotive force in a wire loop moving through a magnetic field, as described by Faraday's la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stem Dpc Schematic Magnetic Explanation
Stem or STEM most commonly refers to: * Plant stem, a structural axis of a vascular plant * Stem group * Science, technology, engineering, and mathematics Stem or STEM can also refer to: Language and writing * Word stem, part of a word responsible for its lexical meaning ** Stemming, a process in natural language processing * Stem (music), in music notation, the vertical lines directly connected to the note head * Stem (typography), the main vertical stroke of a letter * Stem, the opening of a multiple choice question Music and audio * Stem (audio), a collection of audio sources mixed together to be dealt with downstream as one unit * Stem (music), a part of a written musical note * Stem mixing and mastering, a method of mixing audio material * The Stems, an Australian garage punk band * "Stem" (DJ Shadow song), 1996 * "Stem" (Ringo Sheena song), 2003 * "Stem", a song by Hayden from the 1995 album '' Everything I Long For'' * "Stem", a song by Static-X from the 1999 album ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy
High-resolution transmission electron microscopy is an imaging mode of specialized transmission electron microscopes that allows for direct imaging of the atomic structure of samples. It is a powerful tool to study properties of materials on the atomic scale, such as semiconductors, metals, nanoparticles and sp2-bonded carbon (e.g., graphene, C nanotubes). While this term is often also used to refer to high resolution scanning transmission electron microscopy, mostly in high angle annular dark field mode, this article describes mainly the imaging of an object by recording the two-dimensional spatial wave amplitude distribution in the image plane, similar to a "classic" light microscope. For disambiguation, the technique is also often referred to as phase contrast transmission electron microscopy, although this term is less appropriate. At present, the highest point resolution realised in high resolution transmission electron microscopy is around . At these small scales, individual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atomic Number
The atomic number or nuclear charge number (symbol ''Z'') of a chemical element is the charge number of its atomic nucleus. For ordinary nuclei composed of protons and neutrons, this is equal to the proton number (''n''p) or the number of protons found in the nucleus of every atom of that element. The atomic number can be used to uniquely identify ordinary chemical elements. In an ordinary uncharged atom, the atomic number is also equal to the number of electrons. For an ordinary atom which contains protons, neutrons and electrons, the sum of the atomic number ''Z'' and the neutron number ''N'' gives the atom's atomic mass number ''A''. Since protons and neutrons have approximately the same mass (and the mass of the electrons is negligible for many purposes) and the mass defect of the nucleon binding is always small compared to the nucleon mass, the atomic mass of any atom, when expressed in daltons (making a quantity called the " relative isotopic mass"), is within 1% ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |