|
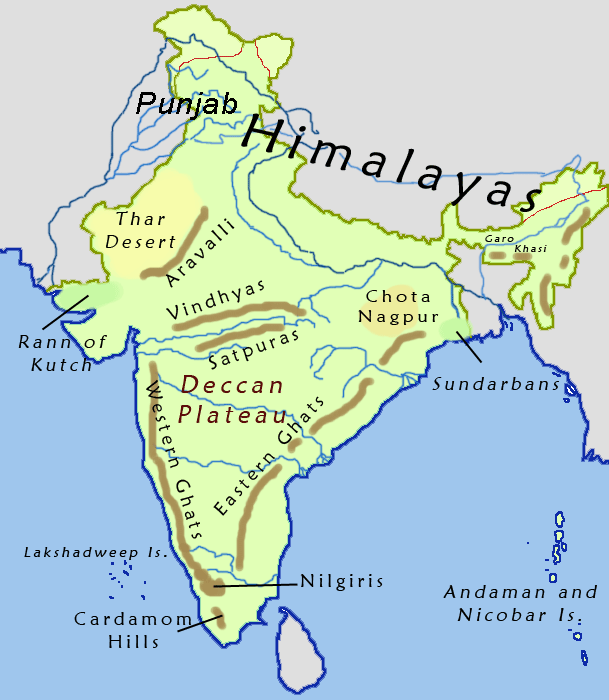
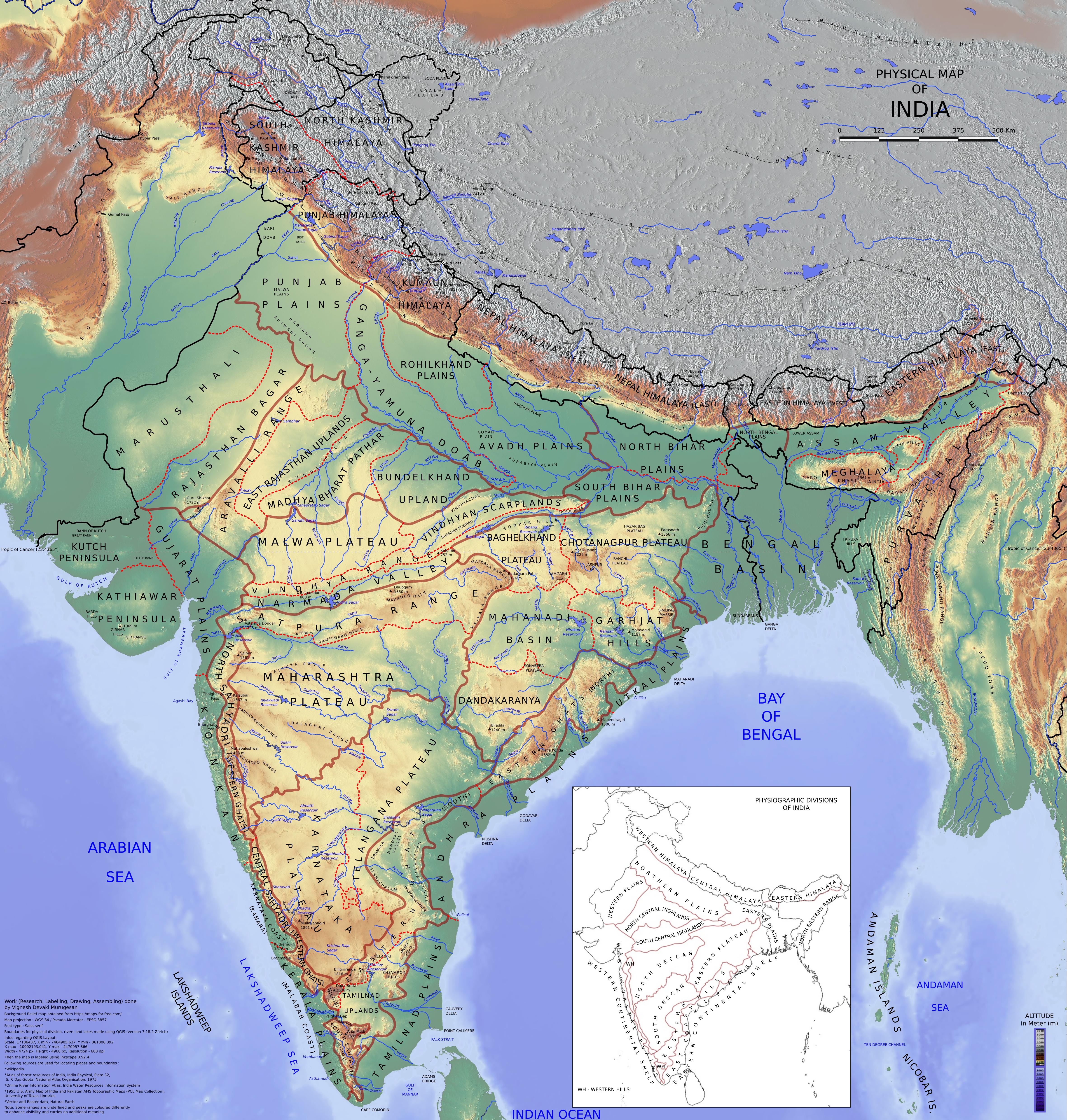
Satpura Range
The Satpura Range, formerly also known as the Seeonee Hills, is a range of hills in central India. The range rises in eastern Gujarat running east through the border of Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh and ends in Chhattisgarh. The range parallels the Vindhya Range to the north, and these two east–west ranges divide Indian Subcontinent into the Indo-Gangetic plain of northern India and the Deccan Plateau of the south. The Narmada River originates from north-eastern end of Satpura in Amarkantak, and runs in the depression between the Satpura and Vindhya ranges, draining the northern slope of the Satpura range, running west towards the Arabian Sea. The Tapti River originates in the eastern-central part of Satpura, crossing the range in the center and running west at the range's southern slopes before meeting the Arabian Sea at Surat, draining the central and southern slopes of the range. Multai, the place of Tapti river origin is located about 465 kilometer far, south-westerl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nandurbar
Nandurbar () is a city and a municipal council in Nandurbar district in the Indian state of Maharashtra. Nandurbar municipal corporation is the first municipal corporation. The District Nandurbar was formed from the district Dhule on July 1, 1998. Nandurbar is an administrative district in the northwest corner of (Khandesh region) of Maharashtra. On 1 July 1998 Dhule was bifurcated as two separate districts now known as Dhule and Nandurbar. The district headquarters is located in Nandurbar city. The district occupies an area of 5034 km2 and has a population of 1,311,709 of which 15.45% is urban (as of 2001). Nandurbar district is bounded to the south and south-east by Dhule district, to the west and north is the state of Gujarat, to the north and north-east is the state of Madhya Pradesh. The northern boundary of the district is defined by the great Narmada river. It came into the limelight during February 2006 bird flu crisis which struck many of its poultry farms. Thou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South India
South India, also known as Southern India or Peninsular India, is the southern part of the Deccan Peninsula in India encompassing the states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu and Telangana as well as the union territories of Lakshadweep and Puducherry, occupying 19.31% of India's area () and 20% of India's population. It is bound by the Bay of Bengal in the east, the Arabian Sea in the west and the Indian Ocean in the south. The geography of the region is diverse, with two mountain ranges, the Western and Eastern Ghats, bordering the plateau heartland. The Godavari, Krishna, Kaveri, Penna, Tungabhadra and Vaigai rivers are important non-perennial sources of water. Chennai, Bengaluru, Hyderabad, Coimbatore and Kochi are the largest urban areas in the region. The majority of the people in South India speak at least one of the four major Dravidian languages: Telugu, Tamil, Kannada and Malayalam. During its history, a number of dynastic kingdoms ruled ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narmada Valley
The Narmada River, previously also known as ''Narbada'' or anglicised as ''Nerbudda'', is the 5th longest river in India and overall the longest west-flowing river in the country. It is also the largest flowing river in the state of Madhya Pradesh. This river flows through the states of Madhya Pradesh and Gujarat in India. It is also known as the "Lifeline of Madhya Pradesh and Gujarat" due to its huge contribution to the two states in many ways. The Narmada River rises from the Amarkantak Plateau in Anuppur district in Madhya Pradesh. It forms the traditional boundary between North and South India and flows westwards for before draining through the Gulf of Khambhat into the Arabian Sea, west of Bharuch city of Gujarat. It is one of only two major rivers in peninsular India that runs from east to west (longest west flowing river), along with the Tapti River. It is one of the rivers in India that flows in a rift valley, bordered by the Satpura and Vindhya ranges. As a rift va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecoregion
An ecoregion (ecological region) is an ecological and geographic area that exists on multiple different levels, defined by type, quality, and quantity of environmental resources. Ecoregions cover relatively large areas of land or water, and contain characteristic, geographically distinct assemblages of natural communities and species. The biodiversity of flora, fauna and ecosystems that characterise an ecoregion tends to be distinct from that of other ecoregions. In theory, biodiversity or conservation ecoregions are relatively large areas of land or water where the probability of encountering different species and communities at any given point remains relatively constant, within an acceptable range of variation (largely undefined at this point). Ecoregions are also known as "ecozones" ("ecological zones"), although that term may also refer to biogeographic realms. Three caveats are appropriate for all bio-geographic mapping approaches. Firstly, no single bio-geographic fram ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Ghats
The Eastern Ghats is a mountain range that stretches along the East Coast of India, eastern coast of the Indian peninsula. Covering an area of , it traverses the states and union territories of India, states of Odisha, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu. The range forms a discontinuous chain of mountains along the eastern edge of the Deccan Plateau, stretching from north of the Mahanadi River in Odisha to Vaigai River in Tamil Nadu at the southern end of the peninsula. The Eastern Ghats meet the Western Ghats at the Nilgiris. The average elevation is around and Arma Konda is the highest peak in the mountains at . Geological evidence indicates that the mountains were formed during the archeozoic era and became part of the Indian subcontinent post the break-up of the supercontinent of Rodinia and the formation of Gondwana. The mountains were formed through further metamorphism during the mid-Proterozoic era. The northern section of the range has an elevation r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graben
In geology, a graben () is a depression (geology), depressed block of the Crust (geology), crust of a planet or moon, bordered by parallel normal faults. Etymology ''Graben'' is a loan word from German language, German, meaning 'ditch' or 'trench'. The first known usage of the word in the geologic context was by Eduard Suess in 1883. The plural form is either ''graben'' or ''grabens''. Formation A graben is a valley with a distinct escarpment on each side caused by the displacement of a block of land downward. Graben often occur side by side with Horst (geology), horsts. Horst and graben structures indicate tensional forces and crustal stretching. Graben are produced by sets of normal faults that have parallel fault traces, where the displacement of the hanging wall is downward, while that of the footwall is upward. The faults typically dip toward the center of the graben from both sides. Horsts are parallel blocks that remain between graben; the bounding faults of a horst t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horst (geology)
In physical geography and geology, a horst is a raised fault block bounded by Fault (geology), normal faults. Horsts are typically found together with grabens. While a horst is lifted or remains stationary, the grabens on either side Subsidence, subside. This is often caused by Extensional tectonics, extensional forces pulling apart the crust. Horsts may represent features such as plateaus, mountains, or ridges on either side of a valley. Horsts can range in size from small fault blocks up to large regions of stable continent that have not been folded or warped by tectonic forces. The word ''Horst'' in German language, German means "mass" or "heap" and was first used in the geological sense in 1883 by Eduard Suess in ''The Face of the Earth.''Originally published in 1883 in German as "Das Antlitz der Erde", translated and published in English in 1904 Geomorphology Horsts may have either symmetrical or asymmetrical cross-sections. If the normal faults to either side have similar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chota Nagpur Plateau
The Chota Nagpur Plateau () is a plateau in eastern India, which covers much of Jharkhand state as well as adjacent parts of Chhattisgarh, Odisha, West Bengal and Bihar. The Indo-Gangetic plain lies to the north and east of the plateau, and the basin of the Mahanadi river lies to the south. The total area of the Chota Nagpur Plateau is approximately . Etymology The name ''Nagpur'' is probably taken from Nagvanshi dynasty, Nagavanshis, who ruled in this part of the country. ''Chhota'' (''small'' in Hindi) is the misunderstood name of "Chuita" village in the outskirts of Ranchi, which has the remains of an old fort belonging to the Nagavanshis.John Wardle Houlton, Sir John Houlton, ''Bihar, the Heart of India'', pp. 127–128, Orient Longmans, 1949. Geology Formation The Chota Nagpur Plateau is a continental plateau—an extensive area of land thrust above the general land.The plateau is composed of Precambrian rocks (i.e., rocks more than about 540 million years old). T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bay Of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean. Geographically it is positioned between the Indian subcontinent and the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese peninsula, located below the Bengal region. Many South Asian and Southeast Asian Countries of the Bay of Bengal, countries are dependent on the Bay of Bengal. Geopolitically, the bay is bounded on the west and northwest by India, on the north by Bangladesh, and on the east by Myanmar and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India. Its southern limit is a line between Sangaman Kanda, Sri Lanka, and the northwesternmost point of Sumatra, Indonesia. Cox's Bazar Beach, Cox's Bazar, the longest sea beach in the world and Sundarbans, the largest mangrove forest and the natural habitat of the Bengal tiger, are located along the bay. The Bay of Bengal occupies an area of . A number of large rivers flow into the Bay of Bengal: the Ganges–Hooghly River, Hooghly, the Padma River, Padma, the Brahmaputra River, Brahmaputr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Godavari River
The Godavari (, Help:IPA/Sanskrit, [ɡod̪aːʋəɾiː]) is India's second longest river after the Ganges River, Ganga River and drains the third largest Drainage basin, basin in India, covering about 10% of India's total geographical area. Its River source, source is in Trimbakeshwar Range, Trimbakeshwar, Nashik, Maharashtra. It flows east for , draining the states of Maharashtra (48.6%), Telangana (18.8%), Andhra Pradesh (4.5%), Chhattisgarh (10.9%) and Odisha (5.7%). The river ultimately empties into the Bay of Bengal through an extensive network of distributaries. Its drainage basin is one of the largest in the Indian subcontinent, with only the Ganga and Indus rivers having a larger drainage basin. In terms of length, catchment area and discharge, the Godavari is the largest in peninsular India, and had been dubbed as the Dakshina Ganga (Southern Ganges). The river has been revered in Hindu texts, Hindu scriptures for many millennia and continues to harbour and nourish a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
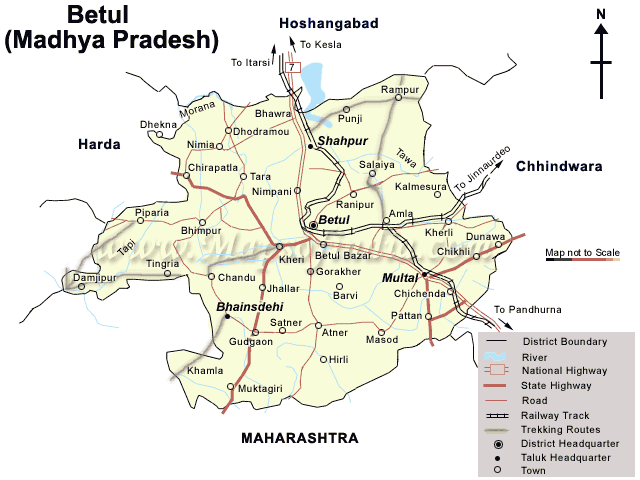
Multai
Multai is a town and a Nagar Palika in Betul district in the Indian States and territories of India, state of Madhya Pradesh. Multai is one of the southern cities of Madhya Pradesh, occupying almost half of the Satpura plateau. Considering the small villages around, it occupies a large area in width of the Satpura range between the valley of the Narmada on the north and the barer plains on the south. Forests lie to the west of the city between the districts of East Nimar and Amaraoti. It lies on the Northern bank of the Tapti and the place is also known for being the origin of the Tapti river. Geography Multai is located at . It has an average elevation of 749 metres (2457 feet). Two major rivers originate from Multai – Tapti River, Tapti and Wardha River, Wardha, the latter originating near Multai. Boundaries Multai is bounded on the north by town Amla, on the south by Amravati district of Maharashtra, on the east by Chhindwara District and on the west by the Dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |