|
Saints Faith, Hope And Charity
Saints Faith, Hope, and Charity (or Love) (), are a group of Christian martyred saints who are venerated together with their mother, Sophia of Rome, Sophia ("Sophia (wisdom), Wisdom"). Although earlier editions of the Roman Martyrology commemorated Saints Faith, Hope and Charity on 1 August and their mother Sophia on 30 September, the present text of this official but professedly incomplete catalogue of saints of the Roman Catholic Church has no feast dedicated to the three saints or their mother: the only Sophia included is an early Christian virgin martyr of Picenum in Italy, commemorated with her companion Vissia on 12 April; another early Christian martyr, Saint Faith (Fides), of Aquitania (southern France), is celebrated on 6 October, a Saint Hope (Spes), an abbot of Nursia who died in about 517, is commemorated on 23 May, and saint Charity (Caritas) is included, although saints with somewhat similar names, Carissa and Carissima, are given, respectively under 16 April and 7 S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint
In Christianity, Christian belief, a saint is a person who is recognized as having an exceptional degree of sanctification in Christianity, holiness, imitation of God, likeness, or closeness to God in Christianity, God. However, the use of the term ''saint'' depends on the context and Christian denomination, denomination. In Anglican Communion, Anglican, Oriental Orthodox, and Lutheranism, Lutheran doctrine, all of their faithful deceased in Heaven are considered to be saints, but a selected few are considered worthy of greater honor or emulation. Official Ecclesiastical polity, ecclesiastical recognition, and veneration, is conferred on some denominational saints through the process of canonization in the Catholic Church or glorification in the Eastern Orthodox Church after their approval. In many Protestant denominations, and following from Pauline usage, ''saint'' refers broadly to any holy Christian, without special recognition or selection. While the English word ''saint'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milan
Milan ( , , ; ) is a city in northern Italy, regional capital of Lombardy, the largest city in Italy by urban area and the List of cities in Italy, second-most-populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of nearly 1.4 million, while its Metropolitan City of Milan, metropolitan city has 3.2 million residents. Within Europe, Milan is the fourth-most-populous List of urban areas in the European Union, urban area of the EU with 6.17 million inhabitants. According to national sources, the population within the wider Milan metropolitan area (also known as Greater Milan) is estimated between 7.5 million and 8.2 million, making it by far the List of metropolitan areas of Italy, largest metropolitan area in Italy and List of metropolitan areas in Europe, one of the largest in the EU.* * * * Milan is the economic capital of Italy, one of the economic capitals of Europe and a global centre for business, fashion and finance. Milan is reco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holy Wisdom
Holy Wisdom (, ) is a concept in Christian theology. Christian theology received the Old Testament personification of Wisdom (Hebrew ''Chokmah'') as well as the concept of Sophia (wisdom), Wisdom (''Sophia'') from Greek philosophy, especially Platonism. In Christology, Christ the Logos as God the Son was identified with Divine Wisdom from earliest times. There has also been a minority position which identified Wisdom with the Holy Spirit in Christianity, Holy Spirit instead. Furthermore, in Christian mysticism, mystical interpretations forwarded in Russian Orthodoxy, known as Sophiology, Holy Wisdom as a feminine principle came to be identified with the Theotokos (Mother of God) rather than with Christ himself. Similar interpretations were proposed in feminist theology as part of the "Gender of God in Christianity, God and Gender" debate in the 1990s. Old Testament In the Septuagint, the Greek noun ''sophia'' is the translation of Biblical Hebrew, Hebrew "wisdom". Wisdom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Faith
Saint Faith, Saint Faith of Conques or Saint Faith of Agen (; ; ) is a saint who is said to have been a girl or young woman of Agen in Aquitaine. Her legend recounts how she was arrested during persecution of Christians by the Roman Empire and refused to make pagan sacrifices. Saint Faith was tortured to death with a red-hot brazier. Her death is sometimes said to have occurred in the year 287 or 290, sometimes in the large-scale Diocletianic Persecution beginning in 303. She is listed as "Sancta Fides, Virgin and martyr", in the martyrologies. The center of her cult was transferred to the Abbey of Sainte-Foy, Conques, where her relics arrived in the ninth century, stolen from Agen by a monk from the Abbey nearby at Conques. Legend A number of legends exist regarding Faith, and she was confused with the three legendary sisters known as Faith, Hope, and Charity. She is recorded in the ''Martyrologium Hieronymianum'' under October 6, but the date of her death is not given. A ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cologne Cathedral
Cologne Cathedral (, , officially , English: Cathedral Church of Saint Peter) is a cathedral in Cologne, North Rhine-Westphalia belonging to the Catholic Church. It is the seat of the Archbishop of Cologne and of the administration of the Archdiocese of Cologne. It is a renowned monument of German Catholicism and Gothic architecture and was declared a World Heritage Site in 1996. It is Germany's most visited landmark, attracting an average of 6 million people a year. At , the cathedral is the tallest twin-spired church in the world, the second tallest church in Europe after Ulm Minster, and the third tallest church of any kind in the world. Construction of Cologne Cathedral began in 1248 but was halted in the years around 1560, unfinished. Attempts to complete the construction began around 1814 but the project was not properly funded until the 1840s. The edifice was completed to its original medieval plan in 1880. The towers for its two huge spires give the cathedral the larg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
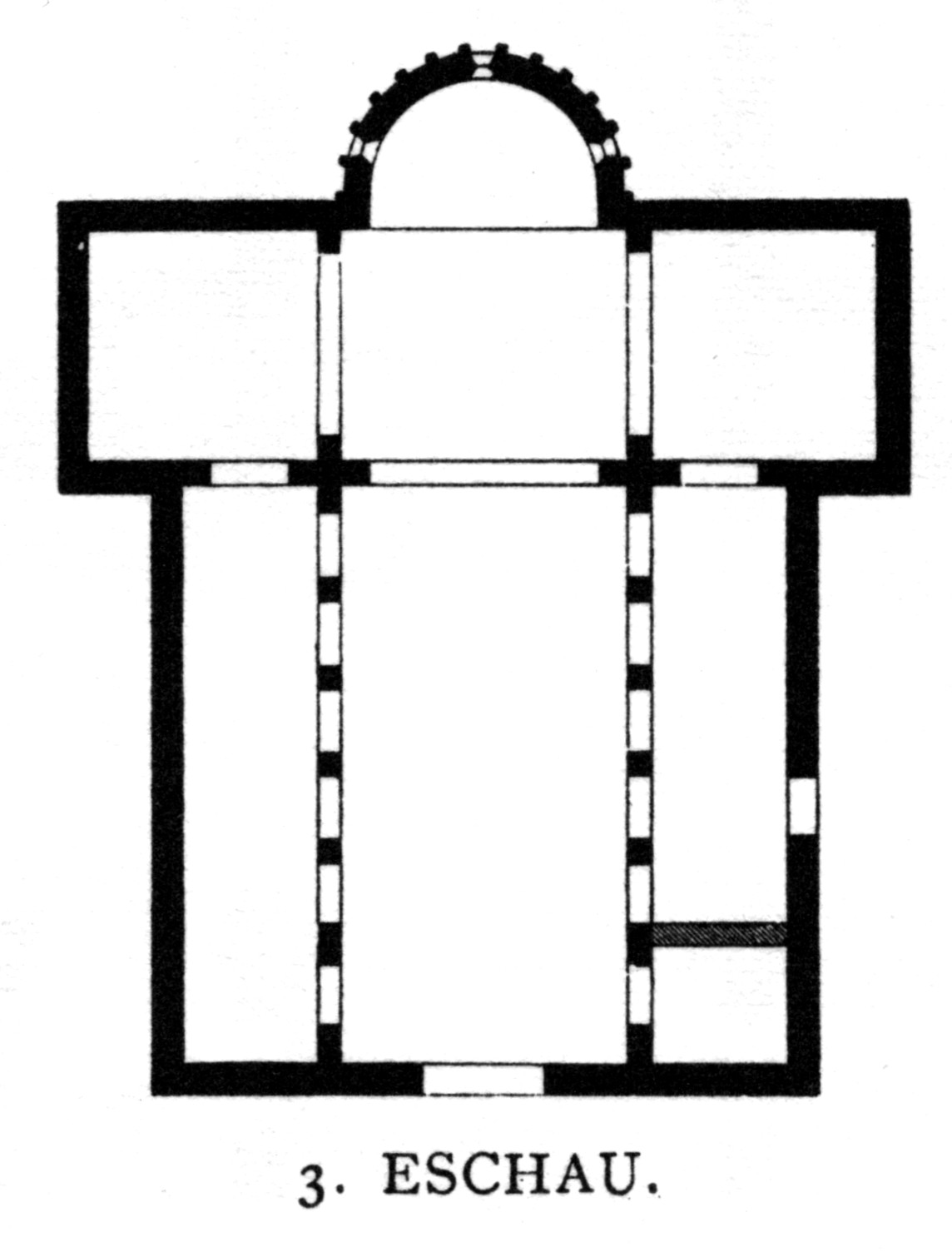
Eschau, Bas-Rhin
Eschau (; ) is a commune in the Bas-Rhin department in Grand Est in north-eastern France. It is situated 8 km south of Strasbourg. Population Sights Eschau's main sight is the '' Église Saint-Trophime'', a Romanesque church dedicated to Trophimus of Arles. The building dates back to the 8th century but has been rebuilt several times until the end of the 13th century. It contains relics of Sophia the Martyr in a Gothic chasse and several wooden polychrome 15th-century Gothic statues. The 12th-century cloister has been destroyed but several capitals and other pieces of Romanesque sculpture by the Master of Eschau have survived and are on display in the Musée de l'Œuvre Notre-Dame. See also * Communes of the Bas-Rhin department The following is a list of the 514 communes of the Bas-Rhin department of France. The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2025): [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Trophimus' Church, Eschau
Saint Trophimus' Church () is a Romanesque church in Eschau, a small town in the suburbs of Strasbourg, the historical capital of Alsace. The church is dedicated to Trophimus of Arles. It houses relics of Saint Sophia (French: ''Sainte Sophie'') since 777 and is a place of Christian pilgrimage, especially for members of the Russian Orthodox Church. It is classified as a Monument historique by the French Ministry of Culture since 1898. History The church was originally part of a Benedictine abbey founded by the bishop of Strasbourg, in 770. On 10 May 777, Remigius brought relics of Sophia and her daughters from Rome, where they had been given to him by Pope Adrian I. He dedicated the abbey to St Sophia, and the church both to Mary and St Trophimus. Remigius died on 23 March 783 and was buried in the church. The church was destroyed by the Hungarians in 926. It was rebuilt in 996 by bishop . In 1143, the number of pilgrims to the relics was so considerable that abbess Chuneg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lexikon Für Theologie Und Kirche
' (''Lexicon of Theology and the Church''; commonly abbreviated ''LThK'') is a German-language Catholic theological encyclopedia. Three editions have appeared so far, all published by Herder-Verlag in Freiburg im Breisgau. First edition: 1930 to 1938 The first edition of the was edited by Michael Buchberger, bishop of Regensburg, between 1930 and 1938. It was an emended and expanded version of an earlier work in two volumes entitled ' (Munich, 1904–1912). The editor's goal was to create a modern '' summa theologiae'', i.e. a reference work that would cover all aspects of Catholic teaching, life and practice. This edition contained 10 volumes. Second edition: 1957 to 1968 The second edition of the work was prepared between 1957 and 1968 by Josef Höfer and Karl Rahner. At that time, the Catholic Church was experiencing drastic changes, culminating in the Second Vatican Council. As a result, the ten volumes of the encyclopedia and the additional volume containing the index ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theological Virtues
Theological virtues are virtues associated in Christian theology and philosophy with salvation resulting from the grace of God. Virtues are traits or qualities which dispose one to conduct oneself in a morally good manner. Traditionally the theological virtues have been named faith, hope, and charity (love). They are coupled with the four natural or cardinal virtues, and opposed to the seven deadly sins. The medieval Catholic philosopher Thomas Aquinas explained that these virtues are called theological virtues "first, because their object is God, inasmuch as they direct us aright to God: secondly, because they are infused in us by God alone: thirdly, because these virtues are not made known to us, save by Divine revelation, contained in Holy Writ". Background 1 Corinthians 13 The first mention in Christian literature of the three theological virtues is in St. Paul's first letter to the Thessalonians 1:3, "...calling to mind your work of faith and labor of love and endurance in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodelinda
Theodelinda, also spelled ''Theudelinde'' ( 570 – 628 AD), was a queen of the Lombards by marriage to two consecutive Lombard rulers, Autari and then Agilulf, and regent of Lombardia during the minority of her son Adaloald, and co-regent when he reached majority, from 616 to 626. For well over thirty years, she exercised influence across the Lombard realm, which comprised most of Italy between the Apennines and the Alps. Life She was the daughter of duke Garibald I of Bavaria and Waldrada. Born a Bavarian princess to King Garibald, Theodelinda's heritage included being descended on her mother's side from the previous Lombard king, Waco, whose family had ruled seven generations prior according tradition. First marriage Theodelinda was married first in 588 to Authari, king of the Lombards, son of King Cleph. There are indications that Pope Gregory I may have had an interest in encouraging this marriage as it would tie a Bavarian Catholic with the Arian Lombards, something he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salzburg
Salzburg is the List of cities and towns in Austria, fourth-largest city in Austria. In 2020 its population was 156,852. The city lies on the Salzach, Salzach River, near the border with Germany and at the foot of the Austrian Alps, Alps mountains. The town occupies the site of the Roman settlement of ''Iuvavum''. Founded as an episcopal see in 696, it became a Prince-Archbishopric of Salzburg, seat of the archbishop in 798. Its main sources of income were salt extraction, trade, as well as gold mining. The Hohensalzburg Fortress, fortress of Hohensalzburg, one of the largest medieval fortresses in Europe, dates from the 11th century. In the 17th century, Salzburg became a centre of the Counter-Reformation, with monasteries and numerous Baroque churches built. Salzburg has an extensive cultural and educational history, being the birthplace of Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart and being home to three universities and a large student population. Today, along with Vienna and the Tyrol (st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pilgrim
The asterisk ( ), from Late Latin , from Ancient Greek , , "little star", is a typographical symbol. It is so called because it resembles a conventional image of a heraldic star. Computer scientists and mathematicians often vocalize it as star (as, for example, in ''the A* search algorithm'' or '' C*-algebra''). An asterisk is usually five- or six-pointed in print and six- or eight-pointed when handwritten, though more complex forms exist. Its most common use is to call out a footnote. It is also often used to censor offensive words. In computer science, the asterisk is commonly used as a wildcard character, or to denote pointers, repetition, or multiplication. History The asterisk was already in use as a symbol in ice age cave paintings. There is also a two-thousand-year-old character used by Aristarchus of Samothrace called the , , which he used when proofreading Homeric poetry to mark lines that were duplicated. Origen is known to have also used the ast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |