|
Sa'id Ibn Amr Al-Harashi
Sa'id ibn Amr al-Harashi (, ) was a prominent Arab general and governor of the Umayyad Caliphate, who played an important role in the Arab–Khazar wars. Biography Sa'id ibn Amr al-Harashi was a Qaysi from Qinnasrin, Syria.Crone (1980), p. 144Blankinship (1994), p. 150 He appears on the side of the Umayyad prince and general Maslama ibn Abd al-Malik in 720, when the latter was sent into Iraq to quell Yazid ibn al-Muhallab's rebellion. Umar ibn Hubayra, who was installed as the new governor of Iraq, appointed Sa'id as governor of Basra, and, shortly after (in 722–723), of Khurasan. In this position, Sa'id was able to swiftly restore the Muslim position in Transoxiana, which was threatened by a large-scale Soghdian rebellion and the first attacks of the Turgesh nomads. Sa'id rallied the Muslims and took to the offensive, crushing the Soghdian rebels near Samarkand and then proceeding to capture the important city of Khujand, thereby restoring Muslim control over most of T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qinnasrin
Qinnašrīn (; ; ; ), was a historical town in northern Syria. The town was situated southwest of Aleppo on the west bank of the Queiq (historically, the Belus) and was connected to Aleppo with a major road during Roman times. Some scholars propose that the ruins of Qinnašrīn are located at al-Hadher to the east of the Queiq River, while Chalcis' location was at the modern Syrian village of Al-Iss, Aleppo Governorate to the west of the river. Others think that Qinnasrin has always been located at al-Iss from the Hellenistic to the Ayyubid period. History Hellenistic and Roman periods According to Appian, Chalcis was founded by Seleucus I Nicator (reigned 305-281 BC), and named after Chalcis in Euboea. Chalcis was distinguished from ''Chalcis sub Libanum'' (modern Anjar, Lebanon) by its river, the ancient Belus. The river—but not the city—was named for the Semitic god Bel or Baʿal. In 92 AD, Chalcis received the title "Flavia", in honor of Emperor Domitian, to be kn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gold Dinar
The gold dinar () is an Islamic medieval gold coin first issued in AH 77 (696–697 CE) by Caliph Abd al-Malik ibn Marwan. The weight of the dinar is 1 mithqal (). The word ''dinar'' comes from the Latin word denarius, which was a silver coin. The name "dinar" is also used for Sasanid, Kushan, and Kidarite gold coins, though it is not known what the contemporary name was. The first dinars were issued by the Umayyad Caliphate. Under the dynasties that followed the use of the dinar spread from Islamic Spain to Central Asia. Background Although there was a dictum that the Byzantine solidus was not to be used outside of the Byzantine empire, some of these coins became involved in distant trade; those then did not get re-minted by the imperial mints, and quickly became worn. Towards the end of the 7th century CE, Arabic copies of solidi – dinars issued by the caliph Abd al-Malik (685–705 CE), who had access to supplies of gold from the upper Nile – ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dirham
The dirham, dirhem or drahm is a unit of currency and of mass. It is the name of the currencies of Moroccan dirham, Morocco, the United Arab Emirates dirham, United Arab Emirates and Armenian dram, Armenia, and is the name of a currency subdivision in Jordanian dinar, Jordan, Libyan dinar, Libya, Qatari riyal, Qatar and Tajikistani somoni, Tajikistan. It was historically a silver coin. Unit of mass The dirham was a unit of mass used across North Africa, the Middle East, Persia and Ifat Sultanate, Ifat; later known as Adal Sultanate, Adal, with varying values. The value of Islamic dirham was 14 qirat. 10 dirham equals 7 mithqal (2.975 gm of silver). In the late Ottoman Empire (), the standard dirham was 3.207 gram, g; 400 dirhem equal one oka (measure), oka. The Ottoman dirham was based on the Sassanian, Sasanian drachm (in Middle Persian: 𐭦𐭥𐭦𐭭 ''drahm''), which was itself based on the Greek Ancient drachma, dram/drachma. In Egypt in 1895, it was equivalen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
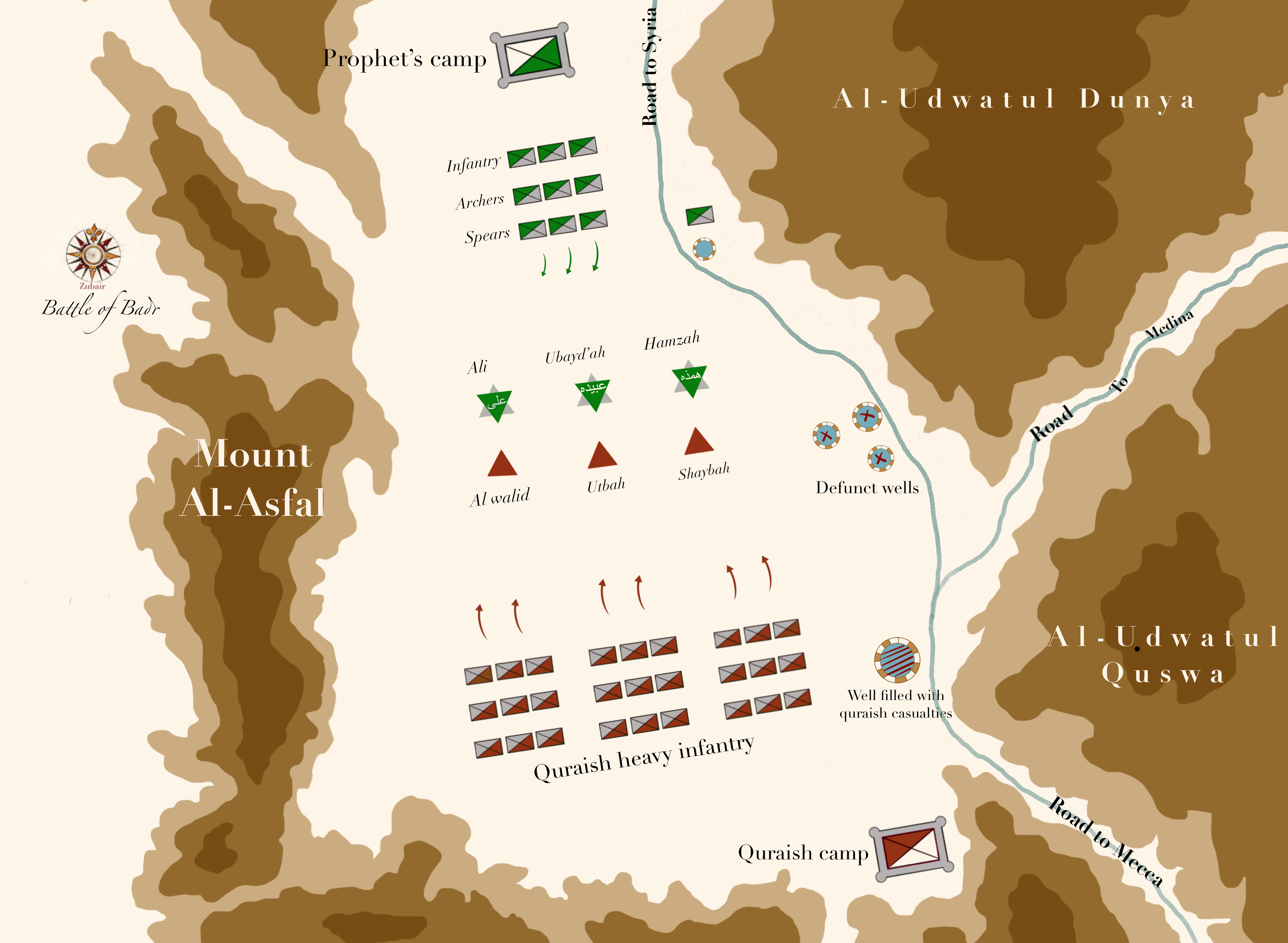
Battle Of Badr
The Battle of Badr or sometimes called The Raid of Badr ( ; ''Ghazwahu Badr''), also referred to as The Day of the Criterion (, ; ''Yawm al-Furqan'') in the Qur'an and by Muslims, was fought on 13 March 624 CE (17 Ramadan, 2 AH), near the present-day city of Badr, Al Madinah Province in Saudi Arabia. Muhammad, commanding an army of his Sahaba, defeated an army of the Quraysh led by Amr ibn Hishām, better known among Muslims as ''Abu Jahl''. The battle marked the beginning of the six-year war between Muhammad and his tribe. The Battle of Badr took place after five or six unsuccessful attempts by the Muslims to intercept and raid Meccan trade caravans between 623 and early 624 CE. Muhammad took keen interest in capturing Meccan caravans and their wealth after his migration to Medina. A few days before the battle, when he learnt of a Makkan caravan returning from the Levant led by Abu Sufyan ibn Harb, Muhammad gathered a small expeditionary force to raid it. Abu Sufyan, le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Rusafa, Syria
Al-Rusafa ( ''Ruṣāfa'', also spelled ''Rassafah'', ''Rosafah'' or ''Resafi'') is a Syrian village located in the Masyaf Subdistrict in Masyaf District, located west of Hama and about 10 kilometers southwest of Masyaf.Willey, 2005, p. 228. According to the Syria Central Bureau of Statistics (CBS), al-Rusafa had a population of 1,608 in the 2004 census. Its inhabitants are predominantly Alawites.Honigman, p. 791. It is the site of a former Ismaili fortress. Fortress At the northern edge of the village is the fortress of al-Rusafa, which is situated on a hill 60 meters higher than the village itself. The fortress is largely preserved, although it is mostly covered by trees and vegetation. In the medieval period, it acted as a subsidiary fortress for the main Ismaili fortress of Masyaf. At its largest extent, it measures roughly 75 meters by 30 meters and is oval-shaped. The fortress was constructed from stone from local quarries and it consists of three stories. The entrance i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hisham Ibn Abd Al-Malik
Hisham ibn Abd al-Malik ibn Marwan (; 6 February 743) was the tenth Umayyad caliph, ruling from 724 until his death in 743. Early life Hisham was born in Damascus, the administrative capital of the Umayyad Caliphate, in AH 72 (691–692 CE). His father was the Umayyad caliph Abd al-Malik ibn Marwan, Abd al-Malik (). His mother, A'isha, was a daughter of Hisham ibn Isma'il al-Makhzumi, Hisham ibn Isma'il of the Banu Makhzum, a prominent family of the Quraysh, and Abd al-Malik's longtime governor of the Islamic holy cities of Mecca and Medina. According to the history of al-Tabari (d. 923), Hisham was given the ''kunya (Arabic), kunya'' (patronymic) of Abu al-Walid. There is little information about Hisham's early life. He was too young to play any political or military role during his father's reign. He supposedly led the Hajj pilgrimage to Mecca once during his brother al-Walid I's reign () and while there, met a respected descendant of Caliph Ali (), Ali al-Sajjad, Zayn al-Abid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Marj Ardabil
The Battle of Marj Ardabil or the Battle of Ardabil was fought on the plains surrounding the city of Ardabil in northwestern Iran in AD 730. A Khazar army led by Barjik, the son of the Khazar khagan, invaded the Umayyad provinces of Jibal and Iranian Azerbaijan in retaliation for Caliphate attacks on Khazaria during the course of the decades-long Khazar-Arab War of the early 8th century. Barjik's expedition into northern Iran (and later into Kurdistan and northern Mesopotamia) may have been an attempt to establish Khazar rule south of the Caucasus Mountains. An outnumbered force led by the Umayyad general al-Jarrah ibn Abdallah engaged the Khazars for three days. Ultimately, abandoned by many of their ''mawali'' auxiliaries, the Caliph's forces were overwhelmed and defeated. During the course of the battle, al-Jarrah was killed. The victorious Barjik mounted his head on top of the throne from which he commanded the battles of his Middle Eastern campaign. According to the his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kazar
The Khazars ; 突厥可薩 ''Tūjué Kěsà'', () were a nomadic Turkic people who, in the late 6th century CE, established a major commercial empire covering the southeastern section of modern European Russia, southern Ukraine, Crimea, and Kazakhstan. They created what, for its duration, was the most powerful polity to emerge from the break-up of the Western Turkic Khaganate. Astride a major artery of commerce between Eastern Europe and Southwestern Asia, Khazaria became one of the foremost trading empires of the early medieval world, commanding the western marches of the Silk Road and playing a key commercial role as a crossroad between China, the Middle East, and Kievan Rus'. For some three centuries (–965), the Khazars dominated the vast area extending from the Volga-Don steppes to the eastern Crimea and the northern Caucasus. Khazaria long served as a buffer state between the Byzantine Empire, the nomads of the northern steppes, and the Umayyad and Abbasid Caliphates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Map Of The Caucasus, 740 CE
A map is a symbolic depiction of interrelationships, commonly spatial, between things within a space. A map may be annotated with text and graphics. Like any graphic, a map may be fixed to paper or other durable media, or may be displayed on a transitory medium such as a computer screen. Some maps change interactively. Although maps are commonly used to depict geographic elements, they may represent any space, real or fictional. The subject being mapped may be two-dimensional such as Earth's surface, three-dimensional such as Earth's interior, or from an abstract space of any dimension. Maps of geographic territory have a very long tradition and have existed from ancient times. The word "map" comes from the , wherein ''mappa'' meant 'napkin' or 'cloth' and ''mundi'' 'of the world'. Thus, "map" became a shortened term referring to a flat representation of Earth's surface. History Maps have been one of the most important human inventions for millennia, allowing humans t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muslim Ibn Sa'id Al-Kilabi
Muslim ibn Sa'id ibn Aslam ibn Zur'ah ibn Amr ibn Khuwaylid al-Sa'iq al-Kilabi () was governor of Khurasan for the Umayyad Caliphate in 723–724. He is best known for his efforts to conciliate the native population of Transoxiana and for the major military defeat at the " Day of Thirst" against the Türgesh. Life Muslim had a distinguished ancestry: his grandfather Aslam served as governor of Khurasan in 671–675, and his father Sa'id was a partisan of the powerful governor of Iraq, al-Hajjaj ibn Yusuf, who rewarded his loyalty by appointing him as governor of Makran. They were the Basran branch of a clan of the Kilab tribe that was mostly concentrated in the Jazira (Upper Mesopotamia) (see Zufar ibn al-Harith al-Kilabi). When his father was killed during his governorship, Muslim was raised as a foster-son by al-Hajjaj, alongside his own sons. His first official post was as a provincial sub-governor under the governor of Basra, Adi ibn Artat, and he reportedly acquitted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jizya
Jizya (), or jizyah, is a type of taxation levied on non-Muslim subjects of a state governed by Sharia, Islamic law. The Quran and hadiths mention jizya without specifying its rate or amount,Sabet, Amr (2006), ''The American Journal of Islamic Social Sciences'' 24:4, Oxford; pp. 99–100. and the application of jizya varied in the course of Islamic history. However, scholars largely agree that early Muslim rulers adapted some of the existing systems of taxation and modified them according to Islamic religious law.online Historically, the jizya tax has been understood in Islam as a fee for protection provided by the Muslim ruler to non-Muslims, for the exemption from military service for non-Muslims, for the permission to practice a non-Muslim faith with some communal autonomy in a Muslim state, and as material proof of the non-Muslims' allegiance to the Muslim state and its laws. The majority of Muslim jurists required adult, free, sane men, males among the dhimma community to pay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |