|
Spica
Spica is the brightest object in the constellation of Virgo and one of the 20 brightest stars in the night sky. It has the Bayer designation α Virginis, which is Latinised to Alpha Virginis and abbreviated Alpha Vir or α Vir. Analysis of its parallax shows that it is located 250 light-years from the Sun. It is a spectroscopic binary star and rotating ellipsoidal variable; a system whose two stars are so close together they are egg-shaped rather than spherical, and can only be separated by their spectra. The primary is a blue giant and a variable star of the Beta Cephei type. Spica, along with Arcturus and Denebola—or Regulus, depending on the source—forms the Spring Triangle asterism, and, by extension, is also part of the Great Diamond together with the star Cor Caroli. Nomenclature In 2016, the International Astronomical Union organized a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) to catalog and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN's first bulletin o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spring Triangle
The Spring Triangle is an asterism_(astronomy), astronomical asterism involving an imaginary triangle drawn upon the celestial sphere, with its defining vertices at Arcturus, Spica, and Regulus. This triangle connects the constellations of Boötes, Virgo (constellation), Virgo, and Leo (constellation), Leo. It is visible in the evening rising in the southeastern sky of the northern hemisphere, Northern Hemisphere between March and May and setting until August, while at morning rising and setting from November to the end of February. George Lovi of Sky & Telescope magazine had a slightly different Spring Triangle, including the tail of Leo, with Denebola replacing Regulus. Although Denebola is dimmer, this triangle is more nearly equilateral. These stars, together with Cor Caroli, form parts of a larger spring asterism called the Great Diamond. The stars of the Spring Triangle Arcturus (α Boötes) Arcturus is a giant orange star in the constellation Boötes. Located only 37 l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
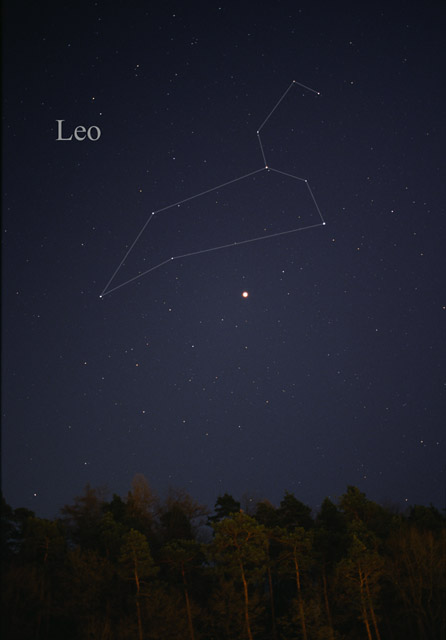
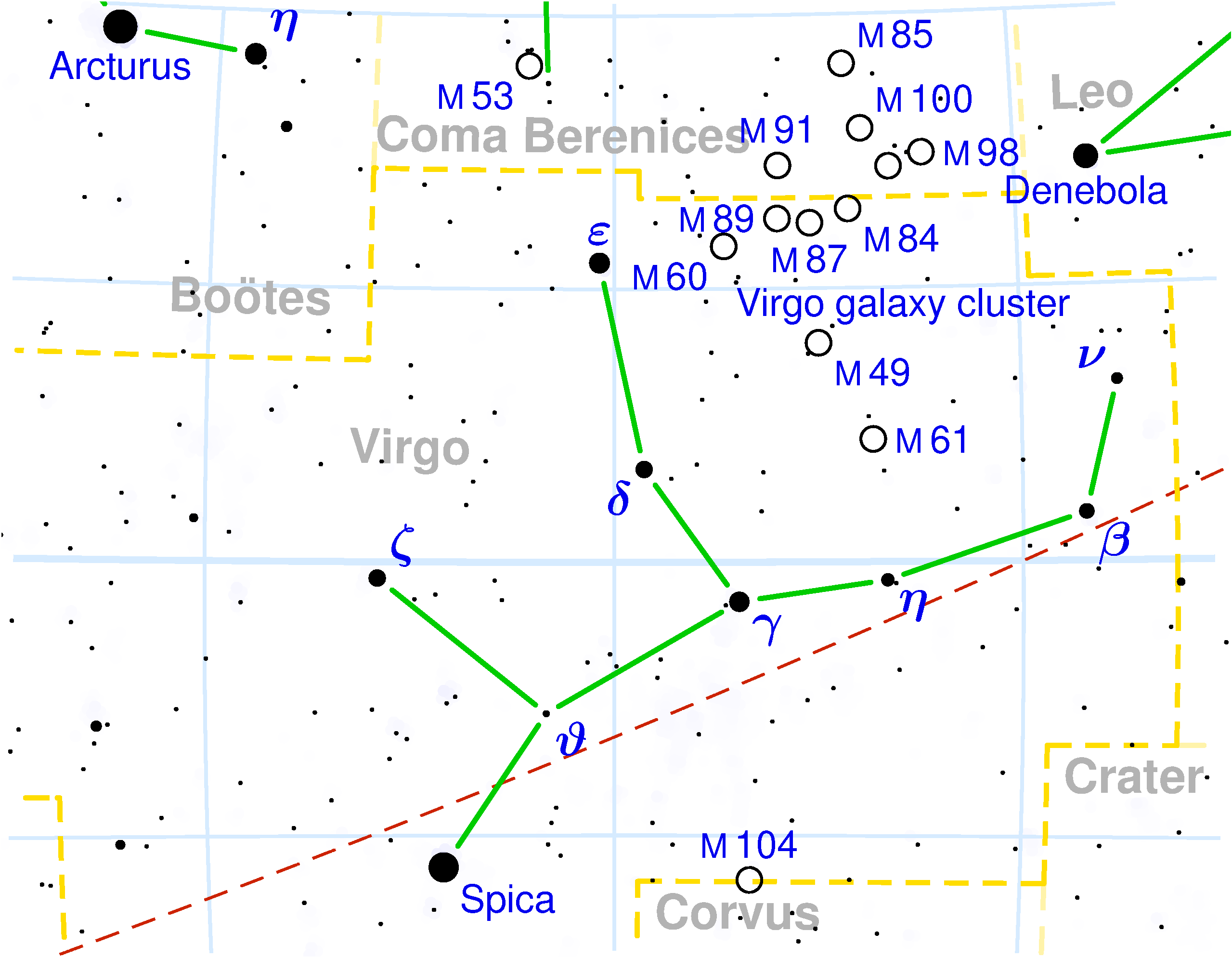
Virgo (constellation)
Virgo is one of the constellations of the zodiac. The name is for maiden in Latin and its traditional astrological symbol is . Between Leo (constellation), Leo to the west and Libra (constellation), Libra to the east, lying in the south, it is the second-largest constellation in the sky (after Hydra (constellation), Hydra) and the largest constellation in the zodiac. The ecliptic intersects the celestial equator within this constellation and Pisces (constellation), Pisces. Underlying these technical two definitions, the sun passes directly overhead of the equator, within this constellation, at the September equinox. Virgo can be easily found through its brightest star, Spica, (in Latin "grain headed"). Location Virgo is prominent in the spring sky in the Northern Hemisphere, visible all night in March and April. As the largest zodiac constellation, the Sun takes 44 days to pass through it, longer than any other. From 1990 and until 2062, this will take place from September 16 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arcturus
, - bgcolor="#FFFAFA" , Note (category: variability): , , H and K emission vary. Arcturus is a red giant star in the Northern celestial hemisphere, northern constellation of Boötes, and the brightest star in the constellation. It has the Bayer designation α Boötis, which is Latinisation of names, Latinized to Alpha Boötis and abbreviated Alf Boo or α Boo. With an apparent visual magnitude of −0.05, it is the List of brightest stars, fourth-brightest star in the night sky and the brightest in the northern celestial hemisphere. Arcturus forms one corner of the Spring Triangle Asterism (astronomy), asterism. Located relatively close at 36.7 light-years from the Sun, Arcturus is a red giant of Stellar classification, spectral type K1.5III—an aging star around 7.1 billion years old that has used up its Stellar core, core hydrogen and stellar evolution, evolved off the main sequence. It is about the same mass Solar mass, as the Sun, but has expanded to 25 times Sol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotating Ellipsoidal Variable
Rotating ellipsoidal variables are a class of close binary variable star systems whose components are ellipsoidal. They are not eclipsing, but fluctuations in apparent magnitude occur due to changes in the amount of light emitting area visible to the observer. Typical brightness fluctuations do not exceed 0.1 magnitudes. The brightest rotating ellipsoidal variable is Spica Spica is the brightest object in the constellation of Virgo and one of the 20 brightest stars in the night sky. It has the Bayer designation α Virginis, which is Latinised to Alpha Virginis and abbreviated Alpha Vir or α Vir. Analys ... (α Virginis). List of variables References External links OGLE Atlas of Variable Star Light Curves - Ellipsoidal variables * * {{var-star-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asterism (astronomy)
An asterism is an observational astronomy, observed pattern or group of stars in the sky. Asterisms can be any identified star pattern, and therefore are a more general concept than the IAU designated constellations, 88 formally defined constellations. Constellations are based upon asterisms, but unlike asterisms, constellations are defined regions with official boundaries which together encompass the entire sky. Asterisms range from simple shapes of just a few stars to more complex collections of many stars covering large portions of the sky. The stars themselves may be bright naked-eye objects or fainter, even telescopic, but they are generally all of a similar brightness to each other. The larger brighter asterisms are useful for people who are familiarizing themselves with the night sky. The patterns of stars seen in asterisms are not necessarily a product of any physical association between the stars, but are rather the result of the particular perspectives of their observ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotating Ellipsoidal Variable
Rotating ellipsoidal variables are a class of close binary variable star systems whose components are ellipsoidal. They are not eclipsing, but fluctuations in apparent magnitude occur due to changes in the amount of light emitting area visible to the observer. Typical brightness fluctuations do not exceed 0.1 magnitudes. The brightest rotating ellipsoidal variable is Spica Spica is the brightest object in the constellation of Virgo and one of the 20 brightest stars in the night sky. It has the Bayer designation α Virginis, which is Latinised to Alpha Virginis and abbreviated Alpha Vir or α Vir. Analys ... (α Virginis). List of variables References External links OGLE Atlas of Variable Star Light Curves - Ellipsoidal variables * * {{var-star-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Cephei Variable
Beta Cephei variables, also known as Beta Canis Majoris stars, are variable stars that exhibit small rapid variations in their brightness due to pulsations of the stars' surfaces, thought due to the unusual properties of iron at temperatures of 200,000 K in their interiors. These stars are usually hot blue-white stars of spectral class B and should not be confused with Cepheid variables, which are named after Delta Cephei and are luminous supergiant stars. Properties Beta Cephei variables are somewhat evolved stars of masses between about 7 and 20 M_\odot (that is, 7–20 times as massive as the Sun). Among their number are some of the brightest stars in the sky, such as Beta Crucis and Beta Centauri; Spica is also classified as a Beta Cephei variable but mysteriously stopped pulsating in 1970. Typically, they change in brightness by 0.01 to 0.3 magnitudes with periods of 0.1 to 0.3 days (2.4–7.2 hours). The prototype of these variable stars, Beta Cephei, shows variation in ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ζ Virginis
Zeta Virginis (ζ Virginis, abbreviated Zeta Vir, ζ Vir) is a binary star in the zodiac constellation of Virgo. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of +3.376 and is located about a half degree south of the celestial equator. Based on parallax measurements obtained during the Hipparcos mission, it is about distant from the Sun. The two components are designated Zeta Virginis A (officially named Heze , a mid-20th-century name for the system) and B. Nomenclature ''ζ Virginis'' ( Latinised to ''Zeta Virginis'') is the system's Bayer designation. The designations of the two components as ''Zeta Virginis A'' and ''B'' derive from the convention used by the Washington Multiplicity Catalog (WMC) for multiple star systems, and adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). Zeta Virginis bore the name ''Heze'' in a 1951 publication, ''Atlas Coeli'' ( Skalnate Pleso Atlas of the Heavens), by Czech astronomer Antonín Bečvář. Its origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Diamond
The Great Diamond, also called the Diamond of Virgo, is an asterism that can be seen during spring evenings in the Northern Hemisphere. It is composed of the following stars: *Cor Caroli (α CVn), in Canes Venatici * Denebola (β Leo), the tail of Leo *Spica (α Vir), the wheat of Virgo *Arcturus (α Boo), the brightest star in Boötes The Great Diamond is larger than the Big Dipper. The three southernmost stars are sometimes regarded as being their own asterism, the Spring Triangle. Lying within the Great Diamond is the set of stars traditionally assigned to Coma Berenices. Many nearby galaxies, including galaxies in the Virgo Cluster, are within this asterism, and some of these galaxies can easily be observed with amateur telescopes. See also * Winter Triangle * Summer Triangle * Winter Hexagon The Winter Hexagon is an asterism appearing to be in the form of a hexagon with vertices at Rigel, Aldebaran, Capella, Pollux, Procyon, and Sirius. It is mostly upon the No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Brightest Stars
This is a list of stars arranged by their apparent magnitude – their brightness as observed from Earth. It includes all stars brighter than magnitude +2.50 in visible light, measured using a ''V''-band filter in the UBV photometric system. Stars in binary systems (or other multiples) are listed by their ''total'' or ''combined'' brightness if they appear as a single star to the naked eye, or listed separately if they do not. As with all magnitude systems in astronomy, the scale is logarithmic and inverted i.e. lower/more negative numbers are brighter. Most stars on this list appear bright from Earth because they are nearby, not because they are intrinsically luminous. For a list which compensates for the distances, converting the ''apparent'' magnitude to the ''absolute'' magnitude, see the list of most luminous stars. Measurement The Sun is the brightest star as viewed from Earth, at −26.78 mag. The second brightest is Sirius at −1.46 mag. Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denebola
Denebola is the second-brightest individual star in the zodiac constellation of Leo.The two components of the γ Leonis double star, which are unresolved to the naked eye, have a combined magnitude brighter than it. It is the easternmost of the bright stars of Leo. It has the Bayer designation Beta Leonis or β Leonis, which are abbreviated Beta Leo or β Leo. Denebola is an A-type main sequence star with 75% more mass than the Sun and 15 times the Sun's luminosity. Based on parallax measurements from the Hipparcos astrometry satellite, the star is at a distance of from the Sun. Its apparent visual magnitude is 2.14, making it readily visible to the naked eye. Denebola is a Delta Scuti type variable star, meaning its luminosity varies very slightly over a period of a few hours. Nomenclature ''β Leonis'' ( Latinised to ''Beta Leonis'') is the star's Bayer designation. In Johann Bayer's ''Uranometria'' (1603), it was designated β (Beta) as the second-brightest sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary Star
A binary star or binary star system is a system of two stars that are gravitationally bound to and in orbit around each other. Binary stars in the night sky that are seen as a single object to the naked eye are often resolved as separate stars using a telescope, in which case they are called ''visual binaries''. Many visual binaries have long orbital periods of several centuries or millennia and therefore have orbits which are uncertain or poorly known. They may also be detected by indirect techniques, such as spectroscopy (''spectroscopic binaries'') or astrometry (''astrometric binaries''). If a binary star happens to orbit in a plane along our line of sight, its components will eclipse and transit each other; these pairs are called ''eclipsing binaries'', or, together with other binaries that change brightness as they orbit, ''photometric binaries''. If components in binary star systems are close enough, they can gravitationally distort each other's outer stellar atmospheres. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |