|
SGML Catalog
A Formal Public Identifier (FPI) is a short piece of text with a particular structure that may be used to uniquely identify a product, specification or document. FPIs were introduced as part of Standard Generalized Markup Language (SGML), and serve particular purposes in formats historically derived from SGML (HTML and XML). Some of their most common uses are as part of document type declarations (DOCTYPEs) and document type definitions (DTDs) in SGML, XML and historically HTML, but they are also used in the vCard and iCalendar file formats to identify the software product which generated the file. More recently, Uniform Resource Identifiers (URIs) and universally unique identifiers (UUIDs) are usually used to uniquely identify objects. FPIs have become a legacy system. Syntax An FPI consists of an ''owner identifier'', followed by a double slash (), followed by a ''text identifier''. For example, the identifier "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01//EN" can be broken down into two parts: the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Generalized Markup Language
The Standard Generalized Markup Language (SGML; ISO 8879:1986) is a standard for defining generalized markup languages for documents. ISO 8879 Annex A.1 states that generalized markup is "based on two postulates": * Declarative: Markup should describe a document's structure and other attributes rather than specify the processing that needs to be performed, because it is less likely to conflict with future developments. * Rigorous: In order to allow markup to take advantage of the techniques available for processing, markup should rigorously define objects like programs and databases. DocBook SGML and LinuxDoc are examples which used SGML tools. Standard versions SGML is an ISO standard: "ISO 8879:1986 Information processing – Text and office systems – Standard Generalized Markup Language (SGML)", of which there are three versions: * Original ''SGML'', which was accepted in October 1986, followed by a minor Technical Corrigendum. * ''SGML (ENR)'', in 1996, resu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
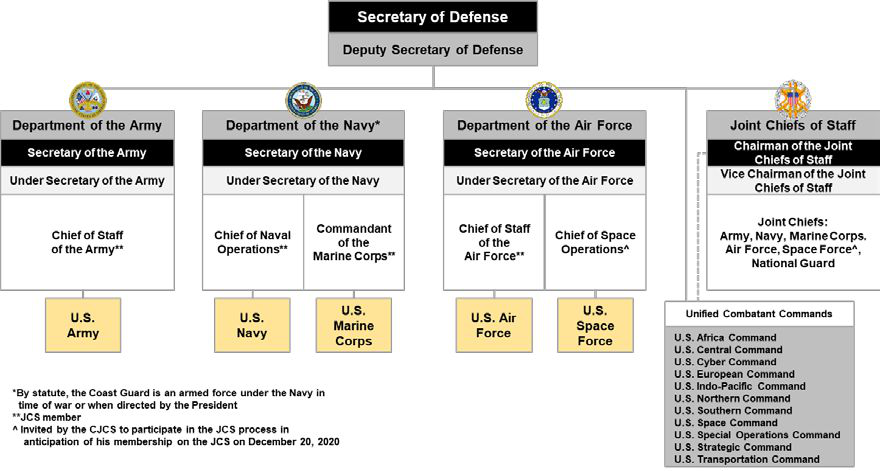
United States Department Of Defense
The United States Department of Defense (DoD, USDOD, or DOD) is an United States federal executive departments, executive department of the federal government of the United States, U.S. federal government charged with coordinating and supervising the six U.S. armed services: the United States Army, Army, United States Navy, Navy, United States Marine Corps, Marines, United States Air Force, Air Force, United States Space Force, Space Force, the United States Coast Guard, Coast Guard for some purposes, and related functions and agencies. As of November 2022, the department has over 1.4 million active-duty uniformed personnel in the six armed services. It also supervises over 778,000 National Guard (United States), National Guard and reservist personnel, and over 747,000 civilians, bringing the total to over 2.91 million employees. Headquartered at the Pentagon in Arlington County, Virginia, just outside Washington, D.C., the Department of Defense's stated mission is "to provid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISO 639-3
ISO 639-3:2007, ''Codes for the representation of names of languages – Part 3: Alpha-3 code for comprehensive coverage of languages'', is an international standard for language codes in the ISO 639 series. It defines three-letter codes for identifying languages. The standard was published by International Organization for Standardization (ISO) on 1 February 2007. As of 2023, this edition of the standard has been officially withdrawn and replaced by ISO 639:2023. ISO 639-3 extends the ISO 639-2 alpha-3 codes with an aim to cover all known natural languages. The extended language coverage was based primarily on the language codes used in the ''Ethnologue'' (volumes 10–14) published by SIL International, which is now the registration authority for ISO 639-3. It provides an enumeration of languages as complete as possible, including living and extinct, ancient and constructed, major and minor, written and unwritten. However, it does not include reconstructed languages su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISO 639-1
ISO 639-1:2002, ''Codes for the representation of names of languages—Part 1: Alpha-2 code'', is the first part of the ISO 639 series of international standards for language codes. Part 1 covers the registration of "set 1" two-letter codes. There are 183 two-letter codes registered as of June 2021. The registered codes cover the world's major languages. Some languages do not have the ISO 639-1 codes because the standard was initially designed to represent major and primary national languages with well-established terminologies and lexicography. The ISO 639-1 is more restrictive than other ISO 639 standards, such as ISO 639-2 as well as ISO 639-3, which cover a wider range of languages and variations. These codes are a useful international and formal shorthand for indicating languages. Many multilingual websites use these codes to prefix URLs of specific language versions of their websites, for example, "ua." before the website name is the Ukrainian version of that website. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unicode
Unicode or ''The Unicode Standard'' or TUS is a character encoding standard maintained by the Unicode Consortium designed to support the use of text in all of the world's writing systems that can be digitized. Version 16.0 defines 154,998 Character (computing), characters and 168 script (Unicode), scripts used in various ordinary, literary, academic, and technical contexts. Unicode has largely supplanted the previous environment of a myriad of incompatible character sets used within different locales and on different computer architectures. The entire repertoire of these sets, plus many additional characters, were merged into the single Unicode set. Unicode is used to encode the vast majority of text on the Internet, including most web pages, and relevant Unicode support has become a common consideration in contemporary software development. Unicode is ultimately capable of encoding more than 1.1 million characters. The Unicode character repertoire is synchronized with Univers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HTML 4
Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) is the standard markup language for documents designed to be displayed in a web browser. It defines the content and structure of web content. It is often assisted by technologies such as Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) and scripting languages such as JavaScript, a programming language. Web browsers receive HTML documents from a web server or from local storage and render the documents into multimedia web pages. HTML describes the structure of a web page semantically and originally included cues for its appearance. HTML elements are the building blocks of HTML pages. With HTML constructs, images and other objects such as interactive forms may be embedded into the rendered page. HTML provides a means to create structured documents by denoting structural semantics for text such as headings, paragraphs, lists, links, quotes, and other items. HTML elements are delineated by ''tags'', written using angle brackets. Tags such as and directly intr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISO/IEC 2022
ISO/IEC 2022 ''Information technology—Character code structure and extension techniques'', is an ISO/ IEC standard in the field of character encoding. It is equivalent to the ECMA standard ECMA-35, the ANSI standard ANSI X3.41 and the Japanese Industrial Standard JIS X 0202. Originating in 1971, it was most recently revised in 1994. ISO 2022 specifies a general structure which character encodings can conform to, dedicating particular ranges of bytes ( 0x00–1F and 0x7F–9F) to be used for non-printing control codes for formatting and in-band instructions (such as line breaks or formatting instructions for text terminals), rather than graphical characters. It also specifies a syntax for escape sequences, multiple-byte sequences beginning with the control code, which can likewise be used for in-band instructions. Specific sets of control codes and escape sequences designed to be used with ISO 2022 include ISO/IEC 6429, portions of which are implemented by ANSI.SYS and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
File Format
A file format is a Computer standard, standard way that information is encoded for storage in a computer file. It specifies how bits are used to encode information in a digital storage medium. File formats may be either proprietary format, proprietary or open format, open. Some file formats are designed for very particular types of data: Portable Network Graphics, PNG files, for example, store Raster graphics, bitmapped Graphics file format, images using lossless data compression. Other file formats, however, are designed for storage of several different types of data: the Ogg format can act as a container format (digital), container for different types of multimedia including any combination of sound, audio and video, with or without text (such as subtitles), and metadata. A text file can contain any stream of characters, including possible control characters, and is encoded in one of various Character encoding, character encoding schemes. Some file formats, such as HTML, sca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coded Character Set
Character encoding is the process of assigning numbers to graphical characters, especially the written characters of human language, allowing them to be stored, transmitted, and transformed using computers. The numerical values that make up a character encoding are known as code points and collectively comprise a code space or a code page. Early character encodings that originated with optical or electrical telegraphy and in early computers could only represent a subset of the characters used in written languages, sometimes restricted to upper case letters, numerals and some punctuation only. Over time, character encodings capable of representing more characters were created, such as ASCII, the ISO/IEC 8859 encodings, various computer vendor encodings, and Unicode encodings such as UTF-8 and UTF-16. The most popular character encoding on the World Wide Web is UTF-8, which is used in 98.2% of surveyed web sites, as of May 2024. In application programs and operating system t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
XML Transformation Language
An XML transformation language is a programming language designed specifically to transform an ''input'' XML document into an ''output'' document which satisfies some specific goal. There are two special cases of transformation: * XML to XML: the ''output document'' is an XML document. * XML to Data: the ''output document'' is a byte stream. XML to XML As XML to XML transformation outputs an XML document, XML to XML transformation chains form XML pipelines. XML to Data The XML (EXtensible Markup Language) to Data transformation contains some important cases. The most notable one is XML to HTML (HyperText Markup Language), as an HTML document ''is not'' an XML document. SGML origins The earliest transformation languages predate the advent of XML as an SGML profile, and thus accept input in arbitrary SGML rather than specifically XML. These include the SGML-to-SGML link process definition (LPD) format defined as part of the SGML standard itself; in SGML (but not XML), the LPD ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISO 6523
ISO/IEC 6523, ''Information technology – Structure for the identification of organizations and organization parts'', is an international standard that defines a structure for uniquely identifying organizations and parts thereof in computer data interchange and specifies the registration procedure to obtain an ''International Code Designator (ICD)'' value for an identification scheme. The standard consists of two parts: Part 1: Identification of organization identification schemes defines a structure for the identification of organizations and parts thereof. The components of this structure are the following: * aInternational Code Designator (ICD)that uniquely identifies the authority which issued the code to the organization, up to 4 digits * aorganization identifier up to a maximum of 35 characters * an (optionalorganization part identifier (OPI) up to a maximum of 35 characters (an "organization part" can be ''any kind of entity'' within an organization.) * an (optional) OPI ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domain Name
In the Internet, a domain name is a string that identifies a realm of administrative autonomy, authority, or control. Domain names are often used to identify services provided through the Internet, such as websites, email services, and more. Domain names are used in various networking contexts and for application-specific naming and addressing purposes. In general, a domain name identifies a network domain or an Internet Protocol (IP) resource, such as a personal computer used to access the Internet, or a server computer. Domain names are formed by the rules and procedures of the Domain Name System (DNS). Any name registered in the DNS is a domain name. Domain names are organized in subordinate levels ('' subdomains'') of the DNS root domain, which is nameless. The first-level set of domain names are the ''top-level domains'' (TLDs), including the ''generic top-level domains'' (gTLDs), such as the prominent domains com, info, net, edu, and org, and the ''country code t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |