|
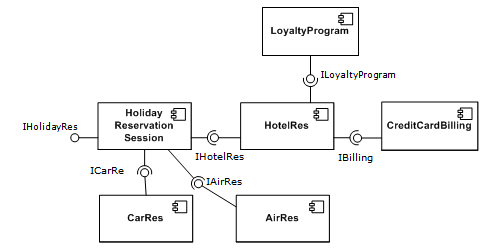
SDAI
ISO 10303-22 is a part of the ''implementation methods'' of STEP with the official title Standard data access interface or simply SDAI. SDAI defines an ''abstract'' Application Programming Interface (API) to work on application data according to a given data models defined in EXPRESS. SDAI itself is defined independent of a particular programming language. Language bindings exist for * Part 23 - '' C++ language binding of the standard data access interface'' * Part 24 - '' C binding of the standard data access interface'' * Part 27 - ''Java binding to the standard data access interface with Internet/Intranet extensions'' * The development of language bindings for FORTRAN and the interface definition language (IDL) of CORBA were canceled. The original intent of SDAI and its bindings to programming languages was to achieve portability of software applications from one implementation to another. This was soon abandoned because there were only a few commercial implementations and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISO 10303
ISO 10303 (Automation systems and integration — Product data representation and exchange)ISO 10303-1:1994 Industrial automation systems and integration -- Product data representation and exchange -- Part 1: Overview and fundamental principles is a family of ISO standards for computer-interpretable representation (description) and exchange of product manufacturing information (PMI). It aims to provide interoperability between various computer-aided design (CAD) software, assist with automation in computer-aided manufacturing (CAM), and allows long-term archival of 3D, CAD and PDM data. It is known informally as "STEP", which stands for "''Standard for the Exchange of Product model data''". Due to a large scope ISO 10303 is subdivided into approximately 700 underlying standards total. The standard includes Parts 11-18 and Part 21 that describe EXPRESS data schema definition language and STEP-file (also STEP-XML) used for textual representation of PMI data codified by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISO 10303-21
STEP-file is a widely used data exchange form of ISO 10303, STEP. ISO 10303 can represent 3D objects in computer-aided design (CAD) and related information. A STEP-file is ASCII text with the format defined in ISO 10303-21 ''Clear Text Encoding of the Exchange Structure''. ISO 10303-21 defines the encoding mechanism for representing data conforming to a particular schema in the ISO 10303-11, EXPRESS data modeling language specified in ISO 10303-11. A STEP-File is also called ''p21-File'' and ''STEP Physical File''. The file extensions ''.stp'' and ''.step'' indicate that the file contains data conforming to STEP application protocols while the extension ''.p21'' should be used for all other purposes. The use of ISO 10303-21 is not limited to STEP. The Industry Foundation Classes and earlier CIMSteel Integration Standard (CIS/2) define an ISO 10303-11, EXPRESS schema for building information modeling data and Industry Foundation Classes#File Formats, specify ISO 10303-21 as an e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of STEP (ISO 10303) Parts
An incomplete list of parts making up STEP (ISO 10303): Descriptions methods * Part 1 - ''Overview and fundamental principles'' (1994). Unfortunately outdated, not covering the role of AICs and modules. * Part 11 - ''EXPRESS language reference manual'' * Part 12 - ''EXPRESS -I language reference manual (withdrawn)'' * Part 14 - ''EXPRESS -X language reference manual'' Implementation methods * Part 15 - ''SysML XMI to XSD transformation'' * Part 21 - STEP-File ''Clear text encoding of the exchange structure'' * Part 22 - SDAI ''Standard data access interface specification'' * Part 23 - ''C++ language binding of the standard data access interface'' * Part 24 - ''C language binding of the standard data access interface'' * Part 25 - ''EXPRESS to OMG XMI binding'' * Part 26 - ''Binary representation of EXPRESS-driven data'' using HDF5 * Part 27 - ''Java TM programming language binding to the standard data access interface with Internet/Intranet extensions'' * Part 28 - STEP-XML ''XM ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Application Programming Interface
An application programming interface (API) is a connection between computers or between computer programs. It is a type of software Interface (computing), interface, offering a service to other pieces of software. A document or standard that describes how to build such a connection or interface is called an ''API specification''. A computer system that meets this standard is said to ''implement'' or ''expose'' an API. The term API may refer either to the specification or to the implementation. In contrast to a user interface, which connects a computer to a person, an application programming interface connects computers or pieces of software to each other. It is not intended to be used directly by a person (the end user) other than a computer programmer who is incorporating it into software. An API is often made up of different parts which act as tools or services that are available to the programmer. A program or a programmer that uses one of these parts is said to ''call'' that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISO 10303-11
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO ; ; ) is an independent, non-governmental, international standard development organization composed of representatives from the national standards organizations of member countries. Membership requirements are given in Article 3 of the ISO Statutes. ISO was founded on 23 February 1947, and () it has published over 25,000 international standards covering almost all aspects of technology and manufacturing. It has over 800 technical committees (TCs) and subcommittees (SCs) to take care of standards development. The organization develops and publishes international standards in technical and nontechnical fields, including everything from manufactured products and technology to food safety, transport, IT, agriculture, and healthcare. More specialized topics like electrical and electronic engineering are instead handled by the International Electrotechnical Commission.Editors of Encyclopedia Britannica. 3 June 2021.Internatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Language Binding
In programming and software design, a binding is an application programming interface (API) that provides glue code specifically made to allow a programming language to use a foreign library or operating system service (one that is not native to that language). Characteristics Binding generally refers to a mapping of one thing to another. In the context of software libraries, bindings are wrapper libraries that bridge two programming languages, so that a library written for one language can be used in another language. Many software libraries are written in system programming languages such as C or C++. To use such libraries from another language, usually of higher-level, such as Java, Common Lisp, Scheme, Python, or Lua, a binding to the library must be created in that language, possibly requiring recompiling the language's code, depending on the amount of modification needed. However, most languages offer a foreign function interface, such as Python's and OCaml's cty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C (programming Language)
C (''pronounced'' '' – like the letter c'') is a general-purpose programming language. It was created in the 1970s by Dennis Ritchie and remains very widely used and influential. By design, C's features cleanly reflect the capabilities of the targeted Central processing unit, CPUs. It has found lasting use in operating systems code (especially in Kernel (operating system), kernels), device drivers, and protocol stacks, but its use in application software has been decreasing. C is commonly used on computer architectures that range from the largest supercomputers to the smallest microcontrollers and embedded systems. A successor to the programming language B (programming language), B, C was originally developed at Bell Labs by Ritchie between 1972 and 1973 to construct utilities running on Unix. It was applied to re-implementing the kernel of the Unix operating system. During the 1980s, C gradually gained popularity. It has become one of the most widely used programming langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Java (programming Language)
Java is a High-level programming language, high-level, General-purpose programming language, general-purpose, Memory safety, memory-safe, object-oriented programming, object-oriented programming language. It is intended to let programmers ''write once, run anywhere'' (Write once, run anywhere, WORA), meaning that compiler, compiled Java code can run on all platforms that support Java without the need to recompile. Java applications are typically compiled to Java bytecode, bytecode that can run on any Java virtual machine (JVM) regardless of the underlying computer architecture. The syntax (programming languages), syntax of Java is similar to C (programming language), C and C++, but has fewer low-level programming language, low-level facilities than either of them. The Java runtime provides dynamic capabilities (such as Reflective programming, reflection and runtime code modification) that are typically not available in traditional compiled languages. Java gained popularity sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interface Definition Language
An interface description language or interface definition language (IDL) is a generic term for a language that lets a program or object written in one language communicate with another program written in an unknown language. IDLs are usually used to describe data types and interfaces in a language-independent way, for example, between those written in C++ and those written in Java. IDLs are commonly used in remote procedure call software. In these cases the machines at either end of the ''link'' may be using different operating systems and computer languages. IDLs offer a bridge between the two different systems. Software systems based on IDLs include Sun's ONC RPC, The Open Group's Distributed Computing Environment, IBM's System Object Model, the Object Management Group's CORBA (which implements OMG IDL, an IDL based on DCE/RPC) and Data Distribution Service, Mozilla's XPCOM, Microsoft's Microsoft RPC (which evolved into COM and DCOM), Facebook's Thrift and WSDL fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CORBA
The Common Object Request Broker Architecture (CORBA) is a standard defined by the Object Management Group (OMG) designed to facilitate the communication of systems that are deployed on diverse platforms. CORBA enables collaboration between systems on different operating systems, programming languages, and computing hardware. CORBA uses an object-oriented model although the systems that use the CORBA do not have to be object-oriented. CORBA is an example of the distributed object paradigm. While briefly popular in the mid to late 1990s, CORBA's complexity, inconsistency, and high licensing costs have relegated it to being a niche technology. Overview CORBA enables communication between software written in different languages and running on different computers. Implementation details from specific operating systems, programming languages, and hardware platforms are all removed from the responsibility of developers who use CORBA. CORBA normalizes the method-call semantics betwee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Domain
The public domain (PD) consists of all the creative work to which no Exclusive exclusive intellectual property rights apply. Those rights may have expired, been forfeited, expressly Waiver, waived, or may be inapplicable. Because no one holds the exclusive rights, anyone can legally use or reference those works without permission. As examples, the works of William Shakespeare, Ludwig van Beethoven, Miguel de Cervantes, Zoroaster, Lao Zi, Confucius, Aristotle, L. Frank Baum, Leonardo da Vinci and Georges Méliès are in the public domain either by virtue of their having been created before copyright existed, or by their copyright term having expired. Some works are not covered by a country's copyright laws, and are therefore in the public domain; for example, in the United States, items excluded from copyright include the formulae of Classical mechanics, Newtonian physics and cooking recipes. Other works are actively dedicated by their authors to the public domain (see waiver) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |