|
SAT Subject Tests
SAT Subject Tests were a set of multiple-choice standardized tests given by The College Board on individual topics, typically taken to improve a student's credentials for college admissions in the United States. For most of their existence, from their introduction in 1937 until 1994, the SAT Subject Tests were known as Achievement Tests, and until January 2005, they were known as SAT II: Subject Tests. They are still often remembered by these names. Unlike the Scholastic Aptitude Test (SAT) that the College Board offers, which are intended to measure general aptitude for academic studies, the Achievement Tests were intended to measure the level of knowledge and understanding in a variety of specific subjects. Like the SAT, the scores for an Achievement Test ranged from 200 (lowest) to 800 (highest). Many colleges used the SAT Subject Tests for admission, course placement, and to advise students about course selection. Achievement tests were generally only required by the most se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
College Board
The College Board, styled as CollegeBoard, is an American not-for-profit organization that was formed in December 1899 as the College Entrance Examination Board (CEEB) to expand access to higher education. While the College Board is not an association of colleges, it runs a membership association of Educational institution, institutions, including over 6,000 schools, colleges, universities, and other educational organizations. The College Board develops and administers standardized tests and curricula used by K–12 and post-secondary education institutions to promote college-readiness and as part of the college admissions process. The College Board is headquartered in New York City. David Coleman (education), David Coleman has been the CEO of the College Board since October 2012. He replaced Gaston Caperton, former List of governors of West Virginia, governor of West Virginia, who had held this position since 1999. The current president of the College Board is Jeremy Singer. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SAT Subject Test In Mathematics Level 1
The SAT Subject Test in Mathematics Level 1 (formerly known as Math I or MathIC (the "C" representing the use of a calculator)) was the name of a one-hour multiple choice test given on algebra, geometry, basic trigonometry, algebraic functions, elementary statistics and basic foundations of calculus by The College Board. A student chose whether to take the test depending upon college entrance requirements for the schools in which the student is planning to apply. Until 1994, the SAT Subject Tests were known as Achievement Tests; and from 1995 until January 2005, they were known as SAT IIs. Mathematics Level 1 was taken 109,048 times in 2006. The SAT Subject Test in Mathematics Level 2 covered more advanced content. On January 19, 2021, the College Board discontinued all SAT Subject tests, including the SAT Subject Test in Mathematics Level 1. This was effective immediately in the United States, and the tests were to be phased out by the following summer for international student ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biology
Biology is the scientific study of life and living organisms. It is a broad natural science that encompasses a wide range of fields and unifying principles that explain the structure, function, growth, History of life, origin, evolution, and distribution of life. Central to biology are five fundamental themes: the cell (biology), cell as the basic unit of life, genes and heredity as the basis of inheritance, evolution as the driver of biological diversity, energy transformation for sustaining life processes, and the maintenance of internal stability (homeostasis). Biology examines life across multiple biological organisation, levels of organization, from molecules and cells to organisms, populations, and ecosystems. Subdisciplines include molecular biology, physiology, ecology, evolutionary biology, developmental biology, and systematics, among others. Each of these fields applies a range of methods to investigate biological phenomena, including scientific method, observation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SAT Subject Test In Biology E/M
The SAT Subject Test in Biology was the name of a one-hour multiple choice test given on biology by the College Board. A student chose whether to take the test depending upon college entrance requirements for the schools in which the student is planning to apply. Until 1994, the SAT Subject Tests were known as Achievement Tests; and from 1995 until January 2005, they were known as SAT IIs. Of all SAT subject tests, the Biology E/M test was the only SAT II that allowed the test taker a choice between the ecological or molecular tests. A set of 60 questions was taken by all test takers for Biology and a choice of 20 questions was allowed between either the E or M tests. This test was graded on a scale between 200 and 800. The average for Molecular is 630 while Ecological is 591. On January 19 2021, the College Board discontinued all SAT Subject tests, including the SAT Subject Test in Biology E/M. This was effective immediately in the United States, and the tests were to be phased o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Function (mathematics)
In mathematics, a function from a set (mathematics), set to a set assigns to each element of exactly one element of .; the words ''map'', ''mapping'', ''transformation'', ''correspondence'', and ''operator'' are sometimes used synonymously. The set is called the Domain of a function, domain of the function and the set is called the codomain of the function. Functions were originally the idealization of how a varying quantity depends on another quantity. For example, the position of a planet is a ''function'' of time. History of the function concept, Historically, the concept was elaborated with the infinitesimal calculus at the end of the 17th century, and, until the 19th century, the functions that were considered were differentiable function, differentiable (that is, they had a high degree of regularity). The concept of a function was formalized at the end of the 19th century in terms of set theory, and this greatly increased the possible applications of the concept. A f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SAT Subject Test In Mathematics Level 2
In the U.S., the SAT Subject Test in Mathematics Level 2 (formerly known as Math II or Math IIC, the "C" representing the sanctioned use of a calculator), was a one-hour multiple choice test. The questions covered a broad range of topics. Approximately 10-14% of questions focused on numbers and operations, 48-52% focused on algebra and functions, 28-32% focused on geometry (coordinate, three-dimensional, and trigonometric geometry were covered; plane geometry was not directly tested), and 8-12% focused on data analysis, statistics and probability. Compared to Mathematics 1, Mathematics 2 was more advanced. Whereas the Mathematics 1 test covered Algebra II and basic trigonometry, a pre-calculus class was good preparation for Mathematics 2. On January 19, 2021, the College Board discontinued all SAT Subject tests, including the SAT Subject Test in Mathematics Level 2. This was effective immediately in the United States, and the tests were to be phased out by the following summer f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistics
Statistics (from German language, German: ', "description of a State (polity), state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a scientific, industrial, or social problem, it is conventional to begin with a statistical population or a statistical model to be studied. Populations can be diverse groups of people or objects such as "all people living in a country" or "every atom composing a crystal". Statistics deals with every aspect of data, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of statistical survey, surveys and experimental design, experiments. When census data (comprising every member of the target population) cannot be collected, statisticians collect data by developing specific experiment designs and survey sample (statistics), samples. Representative sampling assures that inferences and conclusions can reasonably extend from the sample ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algebraic Function
In mathematics, an algebraic function is a function that can be defined as the root of an irreducible polynomial equation. Algebraic functions are often algebraic expressions using a finite number of terms, involving only the algebraic operations addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and raising to a fractional power. Examples of such functions are: * f(x) = 1/x * f(x) = \sqrt * f(x) = \frac Some algebraic functions, however, cannot be expressed by such finite expressions (this is the Abel–Ruffini theorem). This is the case, for example, for the Bring radical, which is the function implicitly defined by : f(x)^5+f(x)+x = 0. In more precise terms, an algebraic function of degree in one variable is a function y = f(x), that is continuous in its domain and satisfies a polynomial equation of positive degree : a_n(x)y^n+a_(x)y^+\cdots+a_0(x)=0 where the coefficients are polynomial functions of , with integer coefficients. It can be shown that the same class ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trigonometry
Trigonometry () is a branch of mathematics concerned with relationships between angles and side lengths of triangles. In particular, the trigonometric functions relate the angles of a right triangle with ratios of its side lengths. The field emerged in the Hellenistic world during the 3rd century BC from applications of geometry to astronomical studies. The Greeks focused on the calculation of chords, while mathematicians in India created the earliest-known tables of values for trigonometric ratios (also called trigonometric functions) such as sine. Throughout history, trigonometry has been applied in areas such as geodesy, surveying, celestial mechanics, and navigation. Trigonometry is known for its many identities. These trigonometric identities are commonly used for rewriting trigonometrical expressions with the aim to simplify an expression, to find a more useful form of an expression, or to solve an equation. History Sumerian astronomers studied angle me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
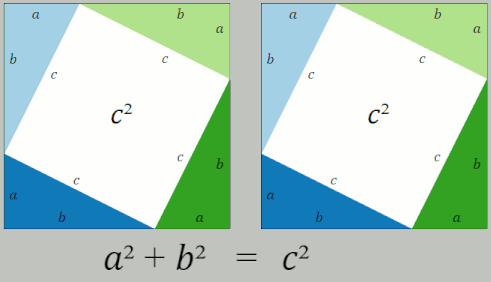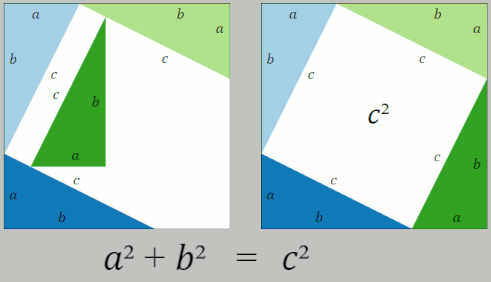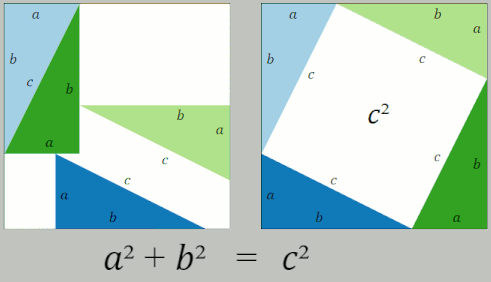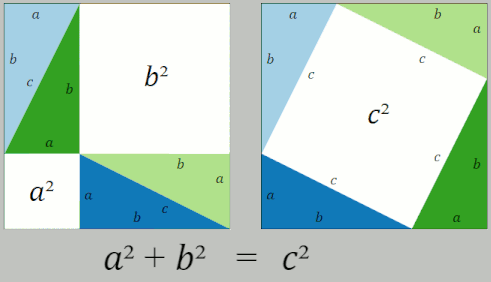
Pythagorean Theorem
In mathematics, the Pythagorean theorem or Pythagoras' theorem is a fundamental relation in Euclidean geometry between the three sides of a right triangle. It states that the area of the square whose side is the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares on the other two sides. The theorem can be written as an equation relating the lengths of the sides , and the hypotenuse , sometimes called the Pythagorean equation: :a^2 + b^2 = c^2 . The theorem is named for the Ancient Greece, Greek philosopher Pythagoras, born around 570 BC. The theorem has been Mathematical proof, proved numerous times by many different methods – possibly the most for any mathematical theorem. The proofs are diverse, including both Geometry, geometric proofs and Algebra, algebraic proofs, with some dating back thousands of years. When Euclidean space is represented by a Cartesian coordinate system in analytic geometry, Euclidean distance satisfies th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polynomials
In mathematics, a polynomial is a mathematical expression consisting of indeterminates (also called variables) and coefficients, that involves only the operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication and exponentiation to nonnegative integer powers, and has a finite number of terms. An example of a polynomial of a single indeterminate is . An example with three indeterminates is . Polynomials appear in many areas of mathematics and science. For example, they are used to form polynomial equations, which encode a wide range of problems, from elementary word problems to complicated scientific problems; they are used to define polynomial functions, which appear in settings ranging from basic chemistry and physics to economics and social science; and they are used in calculus and numerical analysis to approximate other functions. In advanced mathematics, polynomials are used to construct polynomial rings and algebraic varieties, which are central concepts in algebra and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monomials
In mathematics, a monomial is, roughly speaking, a polynomial which has only one term. Two definitions of a monomial may be encountered: # A monomial, also called a power product or primitive monomial, is a product of powers of variables with nonnegative integer exponents, or, in other words, a product of variables, possibly with repetitions. For example, x^2yz^3=xxyzzz is a monomial. The constant 1 is a primitive monomial, being equal to the empty product and to x^0 for any variable x. If only a single variable x is considered, this means that a monomial is either 1 or a power x^n of x, with n a positive integer. If several variables are considered, say, x, y, z, then each can be given an exponent, so that any monomial is of the form x^a y^b z^c with a,b,c non-negative integers (taking note that any exponent 0 makes the corresponding factor equal to 1). # A monomial in the first sense multiplied by a nonzero constant, called the coefficient of the monomial. A primitive monomial is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |