|
Randomized Rounding
In computer science and operations research, randomized rounding is a widely used approach for designing and analyzing approximation algorithms. Many combinatorial optimization problems are computationally intractability (complexity), intractable to solve exactly (to optimality). For such problems, randomized rounding can be used to design fast (polynomial time) approximation algorithms—that is, algorithms that are guaranteed to return an approximately optimal solution given any input. The basic idea of randomized rounding is to convert an optimal solution of a linear programming relaxation, relaxation of the problem into an approximately-optimal solution to the original problem. The resulting algorithm is usually analyzed using the probabilistic method. Overview The basic approach has three steps: # Formulate the problem to be solved as an integer linear program (ILP). # Compute an optimal fractional solution x to the linear programming relaxation (LP) of the ILP. # Rou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Computer Science
Computer science is the study of computation, information, and automation. Computer science spans Theoretical computer science, theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, and information theory) to Applied science, applied disciplines (including the design and implementation of Computer architecture, hardware and Software engineering, software). Algorithms and data structures are central to computer science. The theory of computation concerns abstract models of computation and general classes of computational problem, problems that can be solved using them. The fields of cryptography and computer security involve studying the means for secure communication and preventing security vulnerabilities. Computer graphics (computer science), Computer graphics and computational geometry address the generation of images. Programming language theory considers different ways to describe computational processes, and database theory concerns the management of re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Derandomization
A randomized algorithm is an algorithm that employs a degree of randomness as part of its logic or procedure. The algorithm typically uses uniformly random bits as an auxiliary input to guide its behavior, in the hope of achieving good performance in the "average case" over all possible choices of random determined by the random bits; thus either the running time, or the output (or both) are random variables. There is a distinction between algorithms that use the random input so that they always terminate with the correct answer, but where the expected running time is finite (Las Vegas algorithms, for example Quicksort), and algorithms which have a chance of producing an incorrect result (Monte Carlo algorithms, for example the Monte Carlo algorithm for the MFAS problem) or fail to produce a result either by signaling a failure or failing to terminate. In some cases, probabilistic algorithms are the only practical means of solving a problem. In common practice, randomized algor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Turán's Theorem
In graph theory, Turán's theorem bounds the number of edges that can be included in an undirected graph that does not have a clique (graph theory), complete subgraph of a given size. It is one of the central results of extremal graph theory, an area studying the largest or smallest graphs with given properties, and is a special case of the forbidden subgraph problem on the maximum number of edges in a graph that does not have a given subgraph. An example of an n-vertex (graph theory), vertex graph that does not contain any (r+1)-vertex clique K_ may be formed by partitioning the set of n vertices into r parts of equal or nearly equal size, and connecting two vertices by an edge whenever they belong to two different parts. The resulting graph is the Turán graph T(n,r). Turán's theorem states that the Turán graph has the largest number of edges among all -free -vertex graphs. Turán's theorem, and the Turán graphs giving its extreme case, were first described and studied by Hun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Probabilistic Method
In mathematics, the probabilistic method is a nonconstructive method, primarily used in combinatorics and pioneered by Paul Erdős, for proving the existence of a prescribed kind of mathematical object. It works by showing that if one randomly chooses objects from a specified class, the probability that the result is of the prescribed kind is strictly greater than zero. Although the proof uses probability, the final conclusion is determined for ''certain'', without any possible error. This method has now been applied to other areas of mathematics such as number theory, linear algebra, and real analysis, as well as in computer science (e.g. randomized rounding), and information theory. Introduction If every object in a collection of objects fails to have a certain property, then the probability that a random object chosen from the collection has that property is zero. Thus, by contraposition, if the probability that a random object chosen from the collection has that property is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Approximation Algorithm
In computer science and operations research, approximation algorithms are efficient algorithms that find approximate solutions to optimization problems (in particular NP-hard problems) with provable guarantees on the distance of the returned solution to the optimal one. Approximation algorithms naturally arise in the field of theoretical computer science as a consequence of the widely believed P ≠ NP conjecture. Under this conjecture, a wide class of optimization problems cannot be solved exactly in polynomial time. The field of approximation algorithms, therefore, tries to understand how closely it is possible to approximate optimal solutions to such problems in polynomial time. In an overwhelming majority of the cases, the guarantee of such algorithms is a multiplicative one expressed as an approximation ratio or approximation factor i.e., the optimal solution is always guaranteed to be within a (predetermined) multiplicative factor of the returned solution. However, there a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of Rigour#Mathematics, mathematically rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific Computational problem, problems or to perform a computation. Algorithms are used as specifications for performing calculations and data processing. More advanced algorithms can use Conditional (computer programming), conditionals to divert the code execution through various routes (referred to as automated decision-making) and deduce valid inferences (referred to as automated reasoning). In contrast, a Heuristic (computer science), heuristic is an approach to solving problems without well-defined correct or optimal results.David A. Grossman, Ophir Frieder, ''Information Retrieval: Algorithms and Heuristics'', 2nd edition, 2004, For example, although social media recommender systems are commonly called "algorithms", they actually rely on heuristics as there is no truly "correct" recommendation. As an e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Analysis Of Algorithms
In computer science, the analysis of algorithms is the process of finding the computational complexity of algorithms—the amount of time, storage, or other resources needed to execute them. Usually, this involves determining a function that relates the size of an algorithm's input to the number of steps it takes (its time complexity) or the number of storage locations it uses (its space complexity). An algorithm is said to be efficient when this function's values are small, or grow slowly compared to a growth in the size of the input. Different inputs of the same size may cause the algorithm to have different behavior, so best, worst and average case descriptions might all be of practical interest. When not otherwise specified, the function describing the performance of an algorithm is usually an upper bound, determined from the worst case inputs to the algorithm. The term "analysis of algorithms" was coined by Donald Knuth. Algorithm analysis is an important part of a broa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pessimistic Estimator
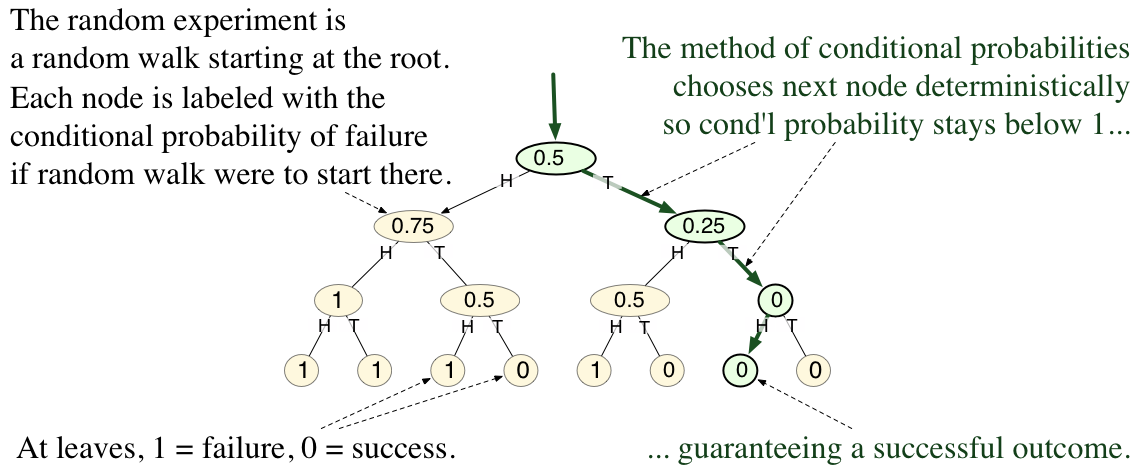
In mathematics and computer science, the method of conditional probabilities is a systematic method for converting non-constructive probabilistic existence proofs into efficient deterministic algorithms that explicitly construct the desired object. blog entry by Neal E. Young, accessed 19/04/2012 and 14/09/2023. Often, the is used to prove the existence of mathematical objects with some desired combinatorial properties. The proofs in that method work by showing that a random object, chosen from some probability distribution, has th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Method Of Conditional Probabilities
In mathematics and computer science, the method of conditional probabilities is a systematic method for converting non-constructive probabilistic existence proofs into efficient Deterministic algorithm, deterministic algorithms that explicitly construct the desired object. blog entry by Neal E. Young, accessed 19/04/2012 and 14/09/2023. Often, the probabilistic method is used to prove the existence of mathematical objects with some desired combinatorial properties. The proofs in that method work by showing that a random object, chosen from some probability distribution, has the desired properties with positive probability. Consequently, they are nonconstructive proof, nonconstructive — th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Boole's Inequality
In probability theory, Boole's inequality, also known as the union bound, says that for any finite or countable set of events, the probability that at least one of the events happens is no greater than the sum of the probabilities of the individual events. This inequality provides an upper bound on the probability of occurrence of at least one of a countable number of events in terms of the individual probabilities of the events. Boole's inequality is named for its discoverer, George Boole. Formally, for a countable set of events ''A''1, ''A''2, ''A''3, ..., we have :\left(\bigcup_^ A_i \right) \le \sum_^ (A_i). In measure-theoretic terms, Boole's inequality follows from the fact that a measure (and certainly any probability measure) is ''σ''- sub-additive. Thus Boole's inequality holds not only for probability measures , but more generally when is replaced by any finite measure. Proof Proof using induction Boole's inequality may be proved for finite collections of n e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Markov's Inequality
In probability theory, Markov's inequality gives an upper bound on the probability that a non-negative random variable is greater than or equal to some positive Constant (mathematics), constant. Markov's inequality is tight in the sense that for each chosen positive constant, there exists a random variable such that the inequality is in fact an equality. It is named after the Russian mathematician Andrey Markov, although it appeared earlier in the work of Pafnuty Chebyshev (Markov's teacher), and many sources, especially in Mathematical analysis, analysis, refer to it as Chebyshev's inequality (sometimes, calling it the first Chebyshev inequality, while referring to Chebyshev's inequality as the second Chebyshev inequality) or Irénée-Jules Bienaymé, Bienaymé's inequality. Markov's inequality (and other similar inequalities) relate probabilities to expected value, expectations, and provide (frequently loose but still useful) bounds for the cumulative distribution function of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Expected Value
In probability theory, the expected value (also called expectation, expectancy, expectation operator, mathematical expectation, mean, expectation value, or first Moment (mathematics), moment) is a generalization of the weighted average. Informally, the expected value is the arithmetic mean, mean of the possible values a random variable can take, weighted by the probability of those outcomes. Since it is obtained through arithmetic, the expected value sometimes may not even be included in the sample data set; it is not the value you would expect to get in reality. The expected value of a random variable with a finite number of outcomes is a weighted average of all possible outcomes. In the case of a continuum of possible outcomes, the expectation is defined by Integral, integration. In the axiomatic foundation for probability provided by measure theory, the expectation is given by Lebesgue integration. The expected value of a random variable is often denoted by , , or , with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |