|
Raman Microscope
The Raman microscope is a laser-based microscopic device used to perform Raman spectroscopy.''Microscopical techniques in the use of the molecular optics laser examiner Raman microprobe'', by M. E. Andersen, R. Z. Muggli, Analytical Chemistry, 1981, 53 (12), pp 1772–177/ref> The term MOLE (molecular optics laser examiner) is used to refer to the Raman-based microprobe. The technique used is named after C. V. Raman, who discovered the scattering properties in liquids. Configuration The Raman microscope begins with a standard optical microscope, and adds an excitation laser, laser rejection filters, a spectrometer or monochromator, and an optical sensitive detector such as a charge-coupled device (CCD), or photomultiplier tube, (PMT). Traditionally Raman microscopy was used to measure the Raman spectrum of a point on a sample, more recently the technique has been extended to implement Raman spectroscopy for direct chemical imaging over the whole field of view on a 3D sample. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confocal Raman Imaging Microscope Witec Alpha300
In geometry, confocal means having the same foci: confocal conic sections. * For an optical cavity consisting of two mirrors, confocal means that they share their foci. If they are identical mirrors, their radius of curvature, ''R''mirror, equals ''L'', where ''L'' is the distance between the mirrors. * In conic sections, it is said of two ellipses, two hyperbolas, or an ellipse and a hyperbola which share both foci with each other. If an ellipse and a hyperbola are confocal, they are perpendicular to each other. * In optics, it means that one focus or image point of one lens is the same as one focus of the next lens. See also *Confocal laser scanning microscopy *Confocal microscopy Confocal microscopy, most frequently confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) or laser confocal scanning microscopy (LCSM), is an optical imaging technique for increasing optical resolution and contrast of a micrograph by means of using a s ... * {{set index article, mathematics Elementary g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffraction-limited System
The resolution of an optical imaging system a microscope, telescope, or camera can be limited by factors such as imperfections in the lenses or misalignment. However, there is a principal limit to the resolution of any optical system, due to the physics of diffraction. An optical system with resolution performance at the instrument's theoretical limit is said to be diffraction-limited. The diffraction-limited angular resolution of a telescopic instrument is inversely proportional to the wavelength of the light being observed, and proportional to the diameter of its objective's entrance aperture. For telescopes with circular apertures, the size of the smallest feature in an image that is diffraction limited is the size of the Airy disk. As one decreases the size of the aperture of a telescopic lens, diffraction proportionately increases. At small apertures, such as f/22, most modern lenses are limited only by diffraction and not by aberrations or other imperfections in the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atomic Force Microscopy
Atomic force microscopy (AFM) or scanning force microscopy (SFM) is a very-high-resolution type of scanning probe microscopy (SPM), with demonstrated resolution on the order of fractions of a nanometer, more than 1000 times better than the optical diffraction limit. Overview Atomic force microscopy (AFM) is a type of scanning probe microscopy (SPM), with demonstrated resolution on the order of fractions of a nanometer, more than 1000 times better than the optical diffraction limit. The information is gathered by "feeling" or "touching" the surface with a mechanical probe. Piezoelectric elements that facilitate tiny but accurate and precise movements on (electronic) command enable precise scanning. Despite the name, the Atomic Force Microscope does not use the Nuclear force. Abilities The AFM has three major abilities: force measurement, topographic imaging, and manipulation. In force measurement, AFMs can be used to measure the forces between the probe and the sample as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Correlative Raman SEM Image Of Hematite Acquired With RISE Microscope
In grammar, a correlative is a word that is paired with another word with which it functions to perform a single function but from which it is separated in the sentence. In English, examples of correlative pairs are ''both–and, either–or, neither–nor, the–the'' ("the more the better"), ''so–that'' ("it ate so much food that it burst"), and ''if–then.'' In the Romance languages, the demonstrative pro-forms function as correlatives with the relative pro-forms, as ''autant–que'' in French; in English, demonstratives are not used in such constructions, which depend on the relative only: "I saw what you did", rather than *"I saw that, what you did". See also * Correlative conjunction *Pro-form In linguistics, a pro-form is a type of function word or expression that stands in for (expresses the same content as) another word, phrase, clause or sentence where the meaning is recoverable from the context. They are used either to avoid rep ... (namely section Table o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
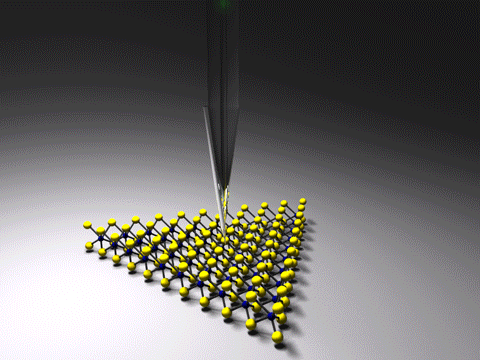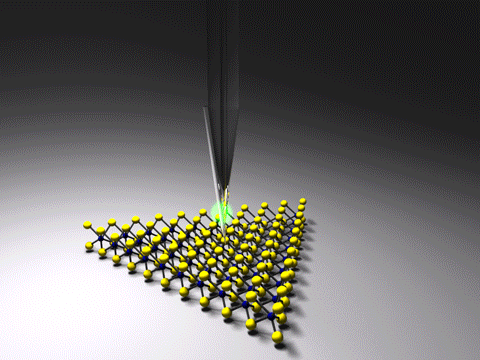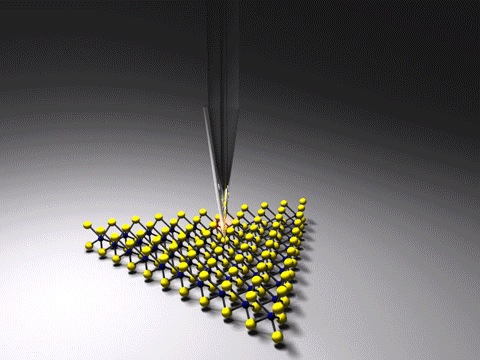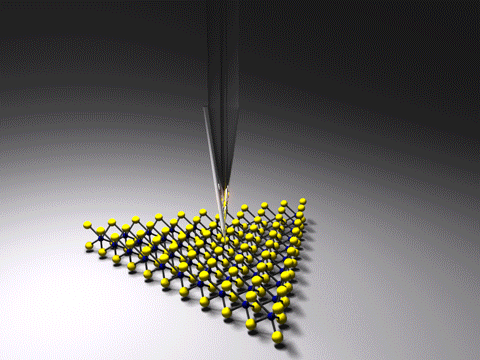
Tip-enhanced Raman Spectroscopy
Tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (TERS) is a variant of surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) that combines scanning probe microscopy with Raman spectroscopy. High spatial resolution chemical imaging is possible ''via'' TERS, with routine demonstrations of nanometer spatial resolution under ambient laboratory conditions, or better at ultralow temperatures and high pressure. The maximum resolution achievable using an optical microscope, including Raman microscopes, is limited by the Abbe limit, which is approximately half the wavelength of the incident light. Furthermore, with SERS spectroscopy the signal obtained is the sum of a relatively large number of molecules. TERS overcomes these limitations as the Raman spectrum obtained originates primarily from the molecules within a few tens of nanometers of the tip. History The earliest reports of tip enhanced Raman spectroscopy typically used a Raman microscope coupled with an atomic force microscope. Tip-enhanced Raman spectrosc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
YAG Laser )
{{disambig ...
YAG laser may refer to two types of lasers that use yttrium aluminum garnet (YAG): * Nd:YAG laser (doped with neodymium) * Er:YAG laser (doped with erbium Erbium is a chemical element with the symbol Er and atomic number 68. A silvery-white solid metal when artificially isolated, natural erbium is always found in chemical combination with other elements. It is a lanthanide, a rare-earth element, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diode-pumped Solid-state Laser
A diode-pumped solid-state laser (DPSSL) is a solid-state laser made by pumping a solid gain medium, for example, a ruby or a neodymium-doped YAG crystal, with a laser diode. DPSSLs have advantages in compactness and efficiency over other types, and high power DPSSLs have replaced ion lasers and flashlamp-pumped lasers in many scientific applications, and are now appearing commonly in green and other color laser pointers. Coupling The wavelength of laser diodes is tuned by means of temperature to produce an optimal compromise between the absorption coefficient in the crystal and energy efficiency (lowest possible pump photon energy). As waste energy is limited by the thermal lens this means higher power densities compared to high-intensity discharge lamps. High power lasers use a single crystal, but many laser diodes are arranged in strips (multiple diodes next to each other in one substrate) or stacks (stacks of substrates). This diode grid can be imaged onto the crystal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tungsten Diselenide
Tungsten diselenide is an inorganic compound with the formula WSe2. The compound adopts a hexagonal crystalline structure similar to molybdenum disulfide. Every tungsten atom is covalently bonded to six selenium ligands in a trigonal prismatic coordination sphere while each selenium is bonded to three tungsten atoms in a pyramidal geometry. The tungsten–selenium bond has a length of 0.2526 nm, and the distance between selenium atoms is 0.334 nm. It is a well studied example of a layered material. The layers stack together via van der Waals interactions. WSe2 is a very stable semiconductor in the group-VI transition metal dichalcogenides. Structure and properties The hexagonal (P63/mmc) polymorph 2H-WSe2 is isotypic with hexagonal MoS2. The two-dimensional lattice structure has W and Se arranged periodically in layers with hexagonal symmetry. Similar to graphite, van der Waals interactions hold the layers together; however, the 2D-layers in WSe2 are not atomical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molybdenum Disulfide
Molybdenum disulfide (or moly) is an inorganic compound composed of molybdenum and sulfur. Its chemical formula is . The compound is classified as a transition metal dichalcogenide. It is a silvery black solid that occurs as the mineral molybdenite, the principal ore for molybdenum.Sebenik, Roger F. ''et al''. (2005) "Molybdenum and Molybdenum Compounds", ''Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology''. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. is relatively unreactive. It is unaffected by dilute acids and oxygen. In appearance and feel, molybdenum disulfide is similar to graphite. It is widely used as a dry lubricant because of its low friction and robustness. Bulk is a diamagnetic, indirect bandgap semiconductor similar to silicon, with a bandgap of 1.23 eV. Single layer sheets act as a perfect mirror, reflecting 100% of incident photons. Production MoS2 is naturally found as either molybdenite, a crystalline mineral, or jordisite, a rare low temperature form of molybdenite. Molybdenite or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Nanotube
A scanning tunneling microscopy image of a single-walled carbon nanotube Rotating single-walled zigzag carbon nanotube A carbon nanotube (CNT) is a tube made of carbon with diameters typically measured in nanometers. ''Single-wall carbon nanotubes'' (''SWCNTs'') are one of the allotropes of carbon, intermediate between fullerene cages and flat graphene, with diameters in the range of a nanometre. Although not made this way, single-wall carbon nanotubes can be idealized as cutouts from a two-dimensional Hexagonal tiling, hexagonal lattice of carbon atoms rolled up along one of the Bravais lattice vectors of the hexagonal lattice to form a hollow cylinder. In this construction, periodic boundary conditions are imposed over the length of this roll-up vector to yield a helical lattice of seamlessly bonded carbon atoms on the cylinder surface. ''Multi-wall carbon nanotubes'' (''MWCNTs'') consisting of nested single-wall carbon nanotubes weakly bound together by van der Waals in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
J-aggregate
A J-aggregate is a type of dye with an absorption band that shifts to a longer wavelength (bathochromic shift) of increasing sharpness (higher absorption coefficient) when it aggregates under the influence of a solvent or additive or concentration as a result of supramolecular self-organisation. The dye can be characterized further by a small Stokes shift with a narrow band. The J in J-aggregate refers to E.E. Jelley who discovered the phenomenon in 1936. The dye is also called a Scheibe aggregate after G. Scheibe who also independently published on this topic in 1937. Scheibe and Jelley independently observed that in ethanol the dye PIC chloride has two broad absorption maxima at around 19,000 cm−1 and 20,500 cm−1 (526 and 488 nm respectively) and that in water a third sharp absorption maximum appears at 17,500 cm−1 (571 nm). The intensity of this band further increases on increasing concentration and on adding sodium chloride. In the oldest ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphene
Graphene () is an allotrope of carbon consisting of a single layer of atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice nanostructure. "Carbon nanostructures for electromagnetic shielding applications", Mohammed Arif Poothanari, Sabu Thomas, et al., ''Industrial Applications of Nanomaterials'', 2019. "Carbon nanostructures include various low-dimensional allotropes of carbon including carbon black (CB), carbon fiber, carbon nanotubes (CNTs), fullerene, and graphene." The name is derived from "graphite" and the suffix -ene, reflecting the fact that the allotrope of carbon contains numerous double bonds. Each atom in a graphene sheet is connect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |