|
Russian Monitor Rusalka
''Rusalka'' (, ''Mermaid''), was one of two s built for the Imperial Russian Navy in the 1860s. She served for her entire career with the Baltic Fleet. Aside from hitting an uncharted rock not long after she was completed in 1869, she had an uneventful career. ''Rusalka'' sank in a storm in 1893 with the loss of all hands in the Gulf of Finland. In 1902, a memorial was built in Reval (Tallinn) to commemorate her loss. Her wreck was rediscovered in 2003, bow-down in the mud, which has prompted a new theory regarding her loss. Design and description ''Rusalka'' was long at the waterline. She had a beam of and a maximum draft of . The ship was designed to displace , but turned out to be overweight and actually displaced . Her crew numbered 13 officers and 171 crewmen in 1877.McLaughlin, p. 156 The ship had two simple horizontal direct-acting steam engines, each driving a single propeller. The engines were designed to produce a total of using steam provided by two coal-fired r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Drydock
A dry dock (sometimes drydock or dry-dock) is a narrow basin or vessel that can be flooded to allow a load to be floated in, then drained to allow that load to come to rest on a dry platform. Dry docks are used for the construction, maintenance, and repair of ships, boats, and other watercraft. History China The use of dry docks in China goes at least as far back as the 10th century A.D. In 1088, Song dynasty scientist and statesman Shen Kuo (1031–1095) wrote in his '' Dream Pool Essays'': Europe Greco-Roman world The Greek author Athenaeus of Naucratis (V 204c-d) reports something that may have been a dry dock in Ptolemaic Egypt in the reign of Ptolemy IV Philopator (221-204 BC) on the occasion of the launch of the enormous '' Tessarakonteres'' rowing ship. However a more recent survey by Goodchild and Forbes does not substantiate its existence. It has been calculated that a dock for a vessel of such a size might have had a volume of 750,000 gallons of water. Renaissa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Imperial Russian Navy
The Imperial Russian Navy () operated as the navy of the Russian Tsardom and later the Russian Empire from 1696 to 1917. Formally established in 1696, it lasted until being dissolved in the wake of the February Revolution and the declaration of the Russian Republic in 1917. It developed from a smaller force that had existed prior to Tsar Peter the Great's founding of the modern Russian navy during the Azov campaigns (1695–1696), Second Azov campaign in 1696, and expanded in the second half of the 18th century before reaching its peak strength by the early part of the 19th century, behind only the British and French fleets in terms of size. The Imperial Navy drew its officers from the aristocracy of the Empire, who belonged to the state Russian Orthodox Church. Young aristocrats began to be trained for leadership at a national naval boarding school, the Naval Cadet Corps (Russia), Naval Cadet Corps. From 1818 on, only officers of the Imperial Russian Navy were appointed to the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Quick-firing Gun
A quick-firing or rapid-firing gun is an artillery piece, typically a gun or howitzer, that has several characteristics which taken together mean the weapon can fire at a fast rate. Quick-firing was introduced worldwide in the 1880s and 1890s and had a marked impact on war both on land and at sea. Characteristics The characteristics of a quick-firing artillery piece are: *A breechloader, breech-loading weapon with a breech mechanism that allows rapid reloading *Single-part casing (ammunition), cased ammunition, i.e. a cartridge (firearms), cartridge containing both shell and propellant *Recoil buffers to limit recoil, so the barrel can quickly return to the same position after firing *The use of smokeless powder – nitrocellulose, nitroglycerine, or cordite – which create far less smoke than gunpowder, meaning that gun crews could still see their target These innovations, taken together, meant that the quick-firer could fire aimed shells much more rapidly than an older weapon. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Torpedo Boat
A torpedo boat is a relatively small and fast naval ship designed to carry torpedoes into battle. The first designs were steam-powered craft dedicated to ramming enemy ships with explosive spar torpedoes. Later evolutions launched variants of self-propelled Whitehead torpedoes. These were inshore craft created to counter both the threat of battleships and other slow and heavily armed ships by using speed, agility, and powerful torpedoes, and the overwhelming expense of building a like number of capital ships to counter an enemy. A swarm of expendable torpedo boats attacking en masse could overwhelm a larger ship's ability to fight them off using its large but cumbersome guns. A fleet of torpedo boats could pose a similar threat to an adversary's capital ships, albeit only in the coastal areas to which their small size and limited fuel load restricted them. The introduction of fast torpedo boats in the late 19th century was a serious concern to the era's naval strategists, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Obukhov State Plant
Obukhov State Plant (also known Obukhovski Plant, ) is a major Russian metallurgy and heavy machine-building Factory, plant in St. Petersburg, Russia. Predecessors In 1854, the mining engineer P.M. Obukhov invented a new procedure to make crucible steel. In combination with the work of metallurgist P.P. Anosov, this crucible steel proved very useful for making cannons. In 1859, this led to the founding of the Prince Michael Artillery Works in Zlatoust. In 1860, this factory delivered its first steel cannon. A reason for the failure of this company was the problematic transport of the guns from this factory to the end users. In 1863, the state would therefore sponsor the establishment of two new artillery factories: The Motovilikhinsk works on the navigable Kama (river), Kama River near Perm, Russia, Perm; and the Obukhov-Putilov-Kudryavzev factory in St. Petersburg, later known as Obukhov. History in Tsarist Russia (1863-1917) Foundation Colonel Putilov acquired a lic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Smoothbore
A smoothbore weapon is one that has a barrel without rifling. Smoothbores range from handheld firearms to powerful tank guns and large artillery mortars. Some examples of smoothbore weapons are muskets, blunderbusses, and flintlock pistols. The opposite of smoothbore is rifling. History Early firearms had smoothly bored barrels that fired projectiles without significant spin. To minimize inaccuracy-inducing tumbling during flight, their projectiles required an aerodynamically uniform shape, such as a sphere. However, surface imperfections on the projectile and/or the barrel will cause even a sphere to rotate randomly during flight, and the Magnus effect will curve it off the intended trajectory when spinning on any axis not parallel to the direction of travel. Rifling the bore surface with spiral grooves or polygonal valleys imparts a stabilizing gyroscopic spin to a projectile that prevents tumbling in flight. Not only does this more than counter Magnus-induced drift, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Rifling
Rifling is the term for helical grooves machined into the internal surface of a firearms's barrel for imparting a spin to a projectile to improve its aerodynamic stability and accuracy. It is also the term (as a verb) for creating such grooves. The opposite of rifling is smoothbore. Rifling is measured in ''twist rate'', the distance the rifling takes to complete one full revolution, expressed as a ratio with 1 as its base (e.g., 1:). A shorter distance/lower ratio indicates a faster twist, generating a higher spin rate (and greater projectile stability). The combination of length, weight, and shape of a projectile determines the twist rate needed to gyroscopically stabilize it: barrels intended for short, large-diameter projectiles such as spherical lead balls require a very low twist rate, such as 1 turn in 48 inches (122 cm). Barrels intended for long, small-diameter projectiles, such as the ultra-low-drag 80-grain 0.223 inch bullets (5.2 g, 5.56&nb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sea Trial
A sea trial or trial trip is the testing phase of a watercraft (including boats, ships, and submarines). It is also referred to as a "shakedown cruise" by many naval personnel. It is usually the last phase of construction and takes place on open water, and it can last from a few hours to many days. Sea trials are conducted to measure a vessel's performance and general seaworthiness. Testing of a vessel's speed, maneuverability, equipment and safety features are usually conducted. Usually in attendance are technical representatives from the builder (and from builders of major systems), governing and certification officials, and representatives of the owners. Successful sea trials subsequently lead to a vessel's certification for commissioning and acceptance by its owner. Although sea trials are commonly thought to be conducted only on new-built vessels (referred by shipbuilders as 'builders trials'), they are regularly conducted on commissioned vessels as well. In new vessels, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
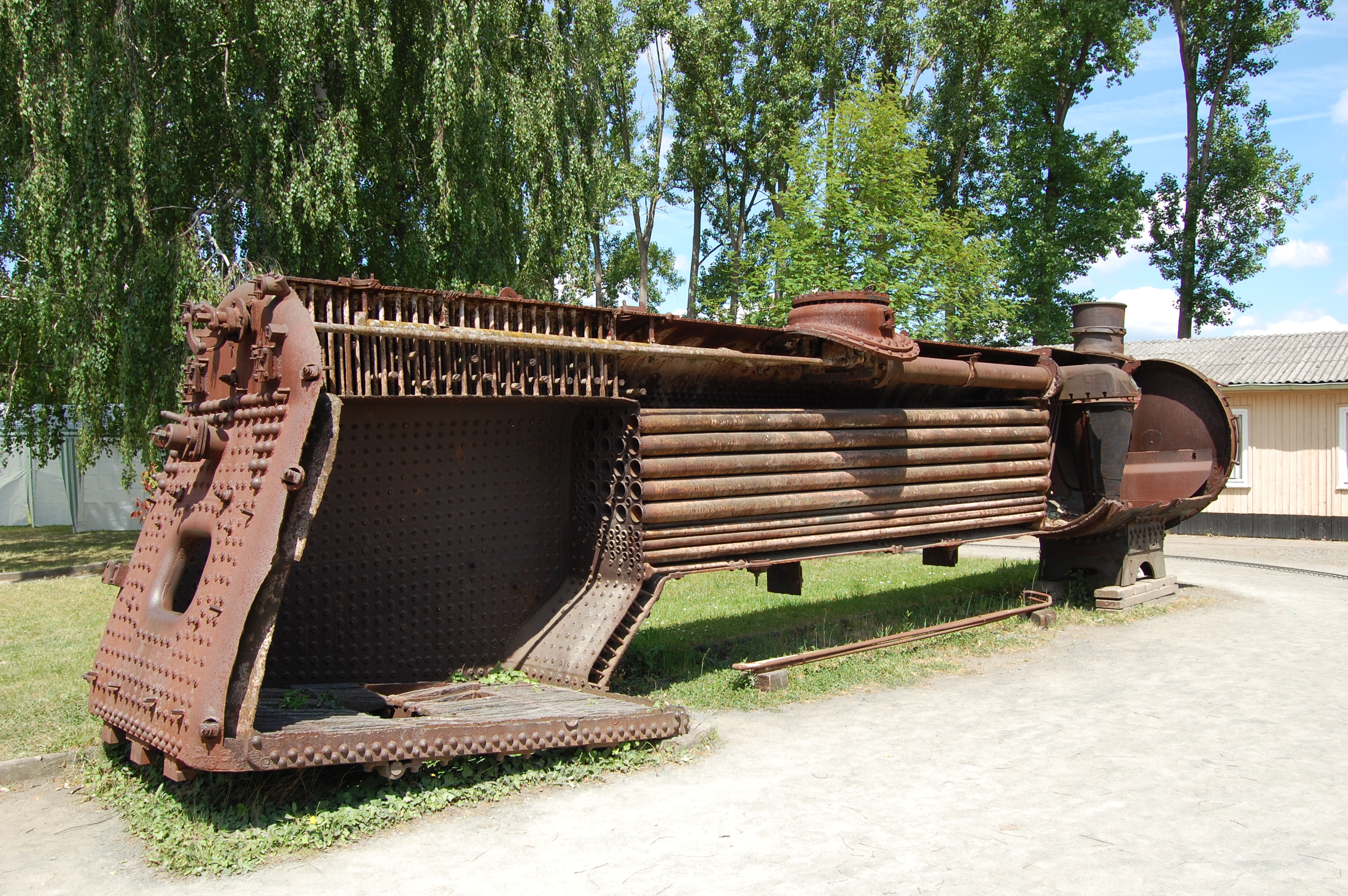
Fire-tube Boiler
A fire-tube boiler is a type of boiler invented in 1828 by Marc Seguin, in which hot gases pass from a fire through one or more tubes running through a sealed container of water. The heat of the gases is transferred through the walls of the tubes by thermal conduction, heating the water and ultimately creating steam. The fire-tube boiler developed as the third of the four major historical types of boilers: low-pressure tank or " haystack" boilers, flued boilers with one or two large flues, fire-tube boilers with many small tubes, and high-pressure water-tube boilers. Their advantage over flued boilers with a single large flue is that the many small tubes offer far greater heating surface area for the same overall boiler volume. The general construction is as a tank of water penetrated by tubes that carry the hot flue gases from the fire. The tank is usually cylindrical for the most part—being the strongest practical shape for a pressurized container—and this cylindrical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
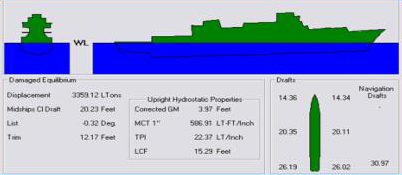
Displacement (ship)
The displacement or displacement tonnage of a ship is its weight. As the term indicates, it is measured indirectly, using Archimedes' principle, by first calculating the volume of water displaced by the ship, then converting that value into weight. Traditionally, various measurement rules have been in use, giving various measures in long tons. Today, tonnes are more commonly used. Ship displacement varies by a vessel's degree of load, from its empty weight as designed (known as "lightweight tonnage") to its maximum load. Numerous specific terms are used to describe varying levels of load and trim, detailed below. Ship displacement should not be confused with measurements of volume or capacity typically used for commercial vessels and measured by tonnage: net tonnage and gross tonnage. Calculation The process of determining a vessel's displacement begins with measuring its draft.George, 2005. p. 5. This is accomplished by means of its "draft marks". A merchant vessel has t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Draft (hull)
The draft or draught of a ship is a determined depth of the vessel below the waterline, measured vertically to its hull's lowest—its propellers, or keel, or other reference point. Draft varies according to the loaded condition of the ship. A deeper draft means the ship will have greater vertical depth below the waterline. Draft is used in under keel clearance calculations, where the draft is calculated with the available depth of water (from Electronic navigational charts) to ensure the ship can navigate safely, without grounding. Navigators can determine their draught by calculation or by visual observation (of the ship's painted load lines). Related terminology A ship's draft/draught is the "depth of the vessel below the waterline measured vertically to the lowest part of the hull, propellers, or other reference point". That is, the draft or draught is the maximum depth of any part of the vessel, including appendages such as rudders, propellers and drop keels if de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Beam (nautical)
The beam of a ship is its width at its widest point. The maximum beam (BMAX) is the distance between planes passing through the outer sides of the ship, beam of the hull (BH) only includes permanently fixed parts of the hull, and beam at waterline (BWL) is the maximum width where the hull intersects the surface of the water. Generally speaking, the wider the beam of a ship (or boat), the more initial stability it has, at the expense of secondary stability in the event of a capsize, where more energy is required to right the vessel from its inverted position. A ship that heels on her ''beam ends'' has her deck beams nearly vertical. Typical values Typical length-to-beam ratios ( aspect ratios) for small sailboats are from 2:1 (dinghies to trailerable sailboats around ) to 5:1 (racing sailboats over ). Large ships have widely varying beam ratios, some as large as 20:1. Rowing shells designed for flatwater racing may have length to beam ratios as high as 30:1, while a cora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |