|
Rover IOE Engine
The intake/inlet over exhaust, or "IOE" engine, known in the US as F-head, is a four-stroke internal combustion engine whose valvetrain comprises OHV inlet valves within the cylinder head and exhaust side-valves within the engine block.V.A.W Hillier: ''Fundamentals of Motor Vehicle Technology'', 4th edition, Standly Thornes, Cheltenham 1991, , p. 39+40 IOE engines were widely used in early motorcycles, initially with the inlet valve being operated by engine suction instead of a cam-activated valvetrain. When the suction-operated inlet valves reached their limits as engine speeds increased, the manufacturers modified the designs by adding a mechanical valvetrain for the inlet valve. A few automobile manufacturers, including Willys, Rolls-Royce and Humber also made IOE engines for both cars and military vehicles. Rover manufactured inline four and six cylinder engines with a particularly efficient version of the IOE induction system. A few designs with the reverse system, exhaust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inlet Over Exhaust
An inlet is a typically long and narrow indentation of a shoreline such as a small arm, cove, bay, sound, fjord, lagoon or marsh, that leads to an enclosed larger body of water such as a lake, estuary, gulf or marginal sea. Overview In marine geography, the term "inlet" usually refers to either the actual channel between an enclosed bay and the open ocean and is often called an "entrance", or a significant recession in the shore of a sea, lake or large river. A certain kind of inlet created by past glaciation is a fjord, typically but not always in mountainous coastlines and also in montane lakes. Multi-arm complexes of large inlets or fjords may be called sounds, e.g., Puget Sound, Howe Sound, Karmsund (''sund'' is Scandinavian for "sound"). Some fjord-type inlets are called canals, e.g., Portland Canal, Lynn Canal, Hood Canal, and some are channels, e.g., Dean Channel and Douglas Channel. Tidal amplitude, wave intensity, and wave direction are all factors that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flathead Engine
A flathead engine, also known as a sidevalve engine''American Rodder'', 6/94, pp.45 & 93. or valve-in-block engine, is an internal combustion engine with its poppet valves contained within the engine block, instead of in the cylinder head, as in an overhead valve engine. Flatheads were widely used internationally by automobile manufacturers from the late 1890s until the mid-1960s but were replaced by more efficient overhead valve and overhead camshaft engines. They are currently experiencing a revival in low-revving aero-engines such as the D-Motor. The side-valve design The valve gear comprises a camshaft sited low in the cylinder block which operates the poppet valves via tappets and short pushrods (or sometimes with no pushrods at all). The flathead system obviates the need for further valvetrain components such as lengthy pushrods, rocker arms, overhead valves or overhead camshafts. The sidevalves are typically adjacent, sited on one side of the cylinder(s), though ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rover P3
The Rover Sixty and Rover Seventy-Five or Rover P3 series were 1.6 and 2.0-litre executive cars announced in the middle of February 1948 and produced by the Rover Company until the summer of 1949. Two months after the announcement of the new cars "a new vehicle for agriculture" was announced, the Land Rover series, Land Rover, with the engine of the new Sixty. Overview For the post-war market Rover had a new engine that had been in preparation since the late 1930s with Rover IOE engine, overhead inlet and side exhaust valves. It was made in two versions for the car, the Rover 60 had a four-cylinder unit of 1595 cc and the Rover 75 had a six-cylinder version of 2103 cc. The gearbox and traditional Rover freewheel were kept unchanged from the previous model. To go with the engine a new car was prepared. Although the body was similar in styling to the Rover 12 and 16, many of the body panels were in fact new but the wings and hood (automobile), bonnet from the 12 were car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Straight-six Engine
A straight-six engine (also referred to as an inline-six engine; abbreviated I6 or L6) is a piston engine with six cylinders arranged in a straight line along the crankshaft. A straight-six engine has perfect primary and secondary engine balance, resulting in fewer vibrations than other designs of six or fewer cylinders. Until the mid-20th century, the straight-six layout was the most common design for engines with six cylinders. However, V6 engines gradually became more common in the 1970s and by the 2000s, V6 engines had replaced straight-six engines in most light automotive applications. Characteristics In terms of packaging, straight-six engines are almost always narrower than a V6 engine or V8 engine, but longer than straight-four engines, V6s, and most V8s. Compared to V-configuration engines with similar power and displacement, the straight configuration has fewer injectors, a single head, and a single exhaust manifold, all contributing to better reliability and perfor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inline-four Engine
A straight-four engine (also referred to as an inline-four engine) is a four-cylinder piston engine where cylinders are arranged in a line along a common crankshaft. The majority of automotive four-cylinder engines use a straight-four layout (with the exceptions of the flat-four engines produced by Subaru and Porsche) and the layout is also very common in motorcycles and other machinery. Therefore the term "four-cylinder engine" is usually synonymous with straight-four engines. When a straight-four engine is installed at an inclined angle (instead of with the cylinders oriented vertically), it is sometimes called a slant-four. Between 2005 and 2008, the proportion of new vehicles sold in the United States with four-cylinder engines rose from 30% to 47%. By the 2020 model year, the share for light-duty vehicles had risen to 59%. Design A four-stroke straight-four engine always has a cylinder on its power stroke, unlike engines with fewer cylinders where there is no power st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tax Horsepower
The tax horsepower or taxable horsepower was an early system by which taxation rates for automobiles were reckoned in some European countries such as the UK, Belgium, Germany, France and Italy; some US states like Illinois charged license plate purchase and renewal fees for passenger automobiles based on taxable horsepower. The tax horsepower rating was computed not from actual engine power but by a mathematical formula based on cylinder dimensions. At the beginning of the twentieth century, tax power was reasonably close to real power; as the internal combustion engine developed, real power became larger than nominal taxable power by a factor of ten or more. Britain The so-called RAC horsepower rating was devised in 1910 by the RAC at the invitation of the British government. The formula is: : \frac where: : D is the diameter (or bore) of the cylinder in inches, : n is the number of cylinders The formula was calculated from total piston surface area (i.e., "bore" only). The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
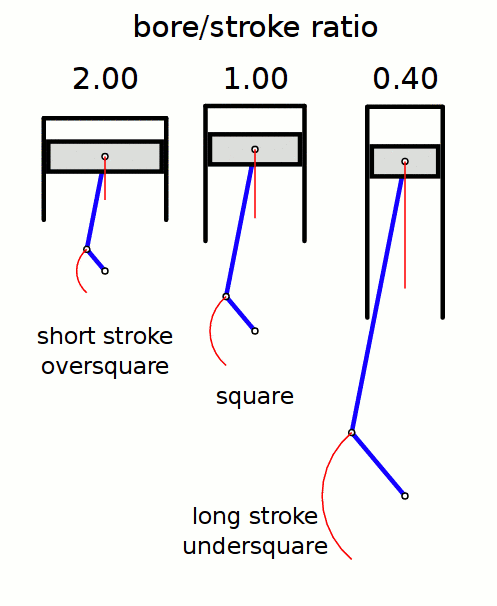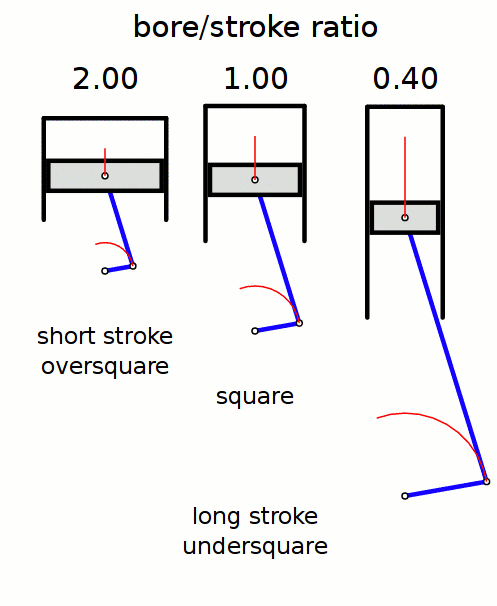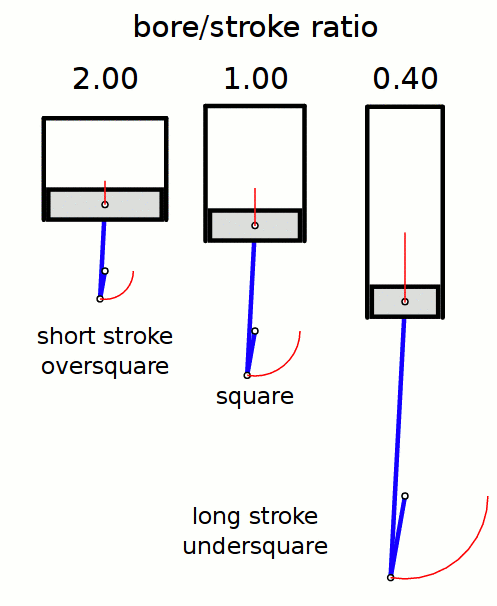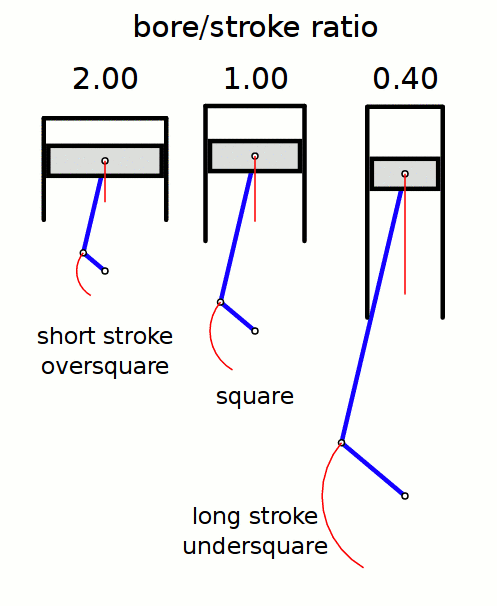
Stroke Ratio
Stroke ratio, today universally defined as bore/stroke ratio, is a term to describe the ratio between cylinder bore diameter and piston stroke length in a reciprocating piston engine. This can be used for either an internal combustion engine, where the fuel is burned within the cylinders of the engine, or external combustion engine, such as a steam engine, where the combustion of the fuel takes place ''outside'' the working cylinders of the engine. Conventions The contemporary convention for describing the ''stroke ratio'' of a piston engine‘s cylinders is its ''bore/stroke'' ratio. ''Stroke/bore'' ratio is an obsolete expression dating to the early era of reciprocating engine development. Bore/stroke ratio The diameter of the cylinder bore is divided by the length of the piston stroke to give the ratio. Square, oversquare and undersquare engines The following terms describe the naming conventions for the configurations of the various bore/stroke ratio: Square A square ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pool Petrol
Rationing was introduced temporarily by the British government several times during the 20th century, during and immediately after a war. At the start of the Timeline of the United Kingdom home front during World War II, Second World War in 1939, the United Kingdom was importing 20 million long tons of food per year, including about 70% of its cheese and sugar, almost 80% of fruit and about 70% of cereals and fats. The UK also imported more than half of its meat and relied on imported feed to support its domestic meat production. The civilian population of the country was about 50 million. It was one of the principal strategies of the Germans in the Battle of the Atlantic to attack shipping bound for Britain, restricting British industry and potentially starving the nation into submission. To deal with sometimes extreme shortages, the Minister of Food (United Kingdom), Ministry of Food instituted a system of rationing. To buy most rationed items, each person had to register ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octane
Octane is a hydrocarbon and also an alkane with the chemical formula C8H18, and the condensed structural formula CH3(CH2)6CH3. Octane has many structural isomers that differ by the location of branching in the carbon chain. One of these isomers, 2,2,4-Trimethylpentane, 2,2,4-trimethylpentane (commonly called iso-octane), is used as one of the standard values in the octane rating scale. Octane is a component of gasoline and petroleum. Under standard temperature and pressure, octane is an odorless, colorless liquid. Like other short-chained alkanes with a low molecular weight, it is Volatility (chemistry), volatile, flammable, and toxic. Octane is 1.2 to 2 times more toxic than heptane. Isomers N-octane has 23 Structural isomers, constitutional isomers. 8 of these isomers have one stereocenter; 3 of them have two stereocenters. Achiral isomers: * 2-Methylheptane * 4-Methylheptane * 3-Ethylhexane * 2,2-Dimethylhexane * 2,5-Dimethylhexane * 3,4-Dimethylhexane, (''meso'')-3,4-Dime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squish (piston Engine)
Squish is an effect in internal combustion engines which creates sudden turbulence of the air-fuel mixture as the piston approaches top dead centre (TDC)."The Combustion Chamber" Retrieved 16 June 2013. In an engine designed to use the squish effect, at top dead centre the piston crown comes very close (typically less than 1 mm) to the cylinder head. The gases are suddenly "squished" out within the , creating turbulence which promotes thorough air-fuel mixing, a factor beneficial to efficient . Squish effect may be found in [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |