|
Rosetta (spacecraft)
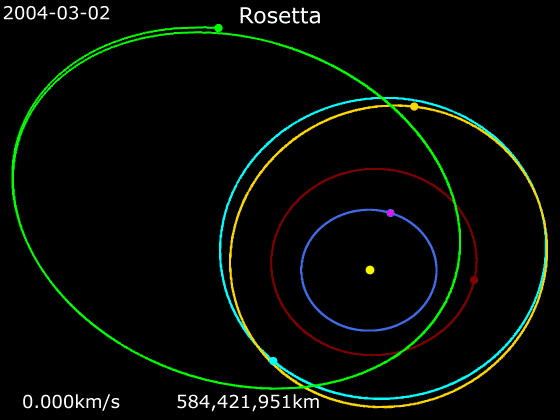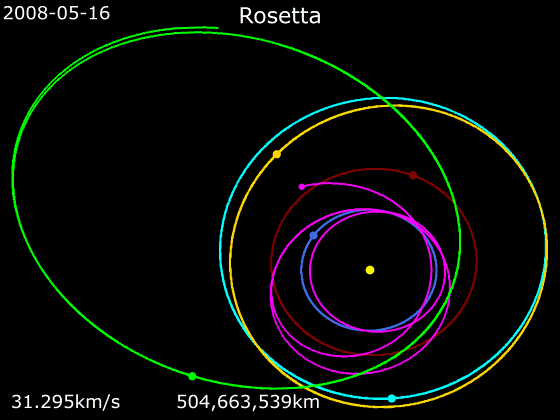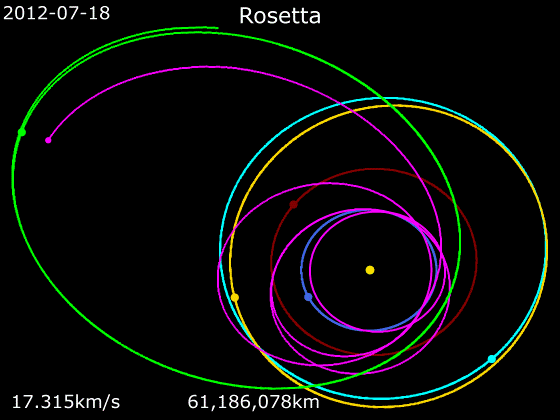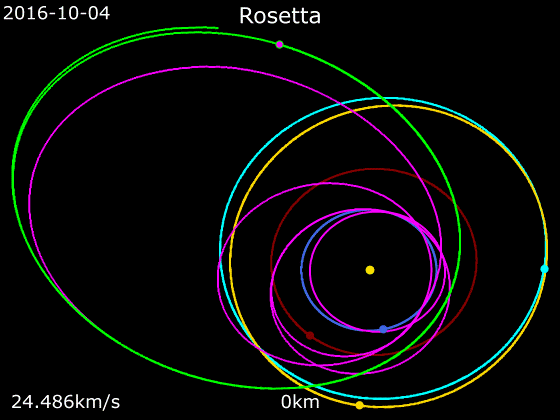
''Rosetta'' was a space probe built by the European Space Agency that launched on 2 March 2004. Along with ''Philae'', its lander module, ''Rosetta'' performed a detailed study of comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko (67P). During its journey to the comet, the spacecraft performed flybys of Earth, Mars, and the asteroids 21 Lutetia and 2867 Šteins. It was launched as the third cornerstone mission of the ESA's Horizon 2000 programme, after ''SOHO' Cluster'' and '' XMM-Newton''. On 6 August 2014, the spacecraft reached the comet and performed a series of manoeuvers to eventually orbit the comet at distances of . On 12 November, its lander module ''Philae'' performed the first successful landing on a comet, though its battery power ran out two days later. Communications with ''Philae'' were briefly restored in June and July 2015, but due to diminishing solar power, ''Rosetta'' communications module with the lander was turned off on 27 July 2016. On 30 September 2016, the ''Rosett ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
European Space Agency
The European Space Agency (ESA) is a 23-member International organization, international organization devoted to space exploration. With its headquarters in Paris and a staff of around 2,547 people globally as of 2023, ESA was founded in 1975 in the context of European integration. Its 2025 annual budget was €7.7 billion. The ESA Human and Robotic Exploration programme includes human spaceflight (mainly through participation in the International Space Station programme); as well as the launch and operation of missions to Mars and Moon. Further activities include science missions to Jupiter, Mercury, the Sun, Earth observation, Asteroid impact avoidance and Telecommunications missions, designing launch vehicles; and maintaining Europe's Spaceport, the Guiana Space Centre at Kourou (French Guiana). Further programmes include space safety, satellite navigation, applications and commercialisation. The main European launch vehicle Ariane 6 is operated through Arianespace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
X Band
The X band is the designation for a band of frequencies in the microwave radio region of the electromagnetic spectrum. In some cases, such as in communication engineering, the frequency range of the X band is set at approximately 7.0–11.2 GHz. In radar engineering, the frequency range is specified by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) as 8.0–12.0 GHz. The X band is used for radar, satellite communication, and wireless computer networks. Radar X band is used in radar applications, including continuous-wave, pulsed, single- polarization, dual-polarization, synthetic aperture radar, and phased arrays. X-band radar frequency sub-bands are used in civil, military, and government institutions for weather monitoring, air traffic control, maritime vessel traffic control, defense tracking, and vehicle speed detection for law enforcement. X band is often used in modern radars. The shorter wavelengths of the X band provide higher-r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Planetary And Space Science
''Planetary and Space Science'' (P&SS), published 15 times per year, is a peer-reviewed scientific journal established in 1959. It publishes original research articles along with short communications (letters). The main topic is Solar System processes which encompasses multiple areas of the natural sciences. Numerical simulations of solar system processes are also conducted at ground-based facilities or on-board space platforms. The editor-in-chief is Maria Cristina De Sanctis (National Institute of Astrophysics, Roma, Italy). It is published by Elsevier. Scope Research that involves planetary and space sciences involves many disciplines, which is reflected by the scope of the journal. Basic science Celestial mechanics is part of these studies, as this science includes understanding the dynamic evolution of the Solar System, relativistic effects, among other areas of analysis and consideration. Cosmochemistry is also part of the published research in this journal. Cosmoch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Asteroid
An asteroid is a minor planet—an object larger than a meteoroid that is neither a planet nor an identified comet—that orbits within the Solar System#Inner Solar System, inner Solar System or is co-orbital with Jupiter (Trojan asteroids). Asteroids are rocky, metallic, or icy bodies with no atmosphere, and are broadly classified into C-type asteroid, C-type (carbonaceous), M-type asteroid, M-type (metallic), or S-type asteroid, S-type (silicaceous). The size and shape of asteroids vary significantly, ranging from small rubble piles under a kilometer across to Ceres (dwarf planet), Ceres, a dwarf planet almost 1000 km in diameter. A body is classified as a comet, not an asteroid, if it shows a coma (tail) when warmed by solar radiation, although recent observations suggest a continuum between these types of bodies. Of the roughly one million known asteroids, the greatest number are located between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter, approximately 2 to 4 astronomical unit, AU ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Planetary Flyby
A planetary flyby is the act of sending a space probe past a planet or a dwarf planet close enough to record scientific data. This is a subset of the overall concept of a flyby in spaceflight. The first flyby of another planet with a functioning spacecraft took place on December 14, 1962, when Mariner 2 zoomed by the planet Venus. Planetary flybys are commonly used as gravity assist maneuvers to "slingshot" a space probe toward its primary target without expending fuel, but in some cases (such as with New Horizons), flybys are the primary objectives of a mission in of themselves. Flybys modify the direction of the probe and adds to its heliocentric velocity. A relatively recent example of a flyby spacecraft is ''New Horizons,'' which performed flyby maneuvers of Jupiter, Pluto and its moons in the 21st century. The flyby of Jupiter, used as a gravity assist, allowed the craft to reach Pluto at high velocity without the complications of slowing down, after which it proceeded f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''NYT'') is an American daily newspaper based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' covers domestic, national, and international news, and publishes opinion pieces, investigative reports, and reviews. As one of the longest-running newspapers in the United States, the ''Times'' serves as one of the country's Newspaper of record, newspapers of record. , ''The New York Times'' had 9.13 million total and 8.83 million online subscribers, both by significant margins the List of newspapers in the United States, highest numbers for any newspaper in the United States; the total also included 296,330 print subscribers, making the ''Times'' the second-largest newspaper by print circulation in the United States, following ''The Wall Street Journal'', also based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' is published by the New York Times Company; since 1896, the company has been chaired by the Ochs-Sulzberger family, whose current chairman and the paper's publ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Comet
A comet is an icy, small Solar System body that warms and begins to release gases when passing close to the Sun, a process called outgassing. This produces an extended, gravitationally unbound atmosphere or Coma (cometary), coma surrounding the nucleus, and sometimes a Comet tail, tail of gas and dust gas blown out from the coma. These phenomena are due to the effects of solar radiation and the outstreaming solar wind plasma acting upon the nucleus of the comet. Comet nuclei range from a few hundred meters to tens of kilometers across and are composed of loose collections of ice, dust, and small rocky particles. The coma may be up to 15 times Earth's diameter, while the tail may stretch beyond one astronomical unit. If sufficiently close and bright, a comet may be seen from Earth without the aid of a telescope and can Subtended angle, subtend an arc of up to 30° (60 Moons) across the sky. Comets have been observed and recorded since ancient times by many cultures and religion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Space Probe
Uncrewed spacecraft or robotic spacecraft are spacecraft without people on board. Uncrewed spacecraft may have varying levels of autonomy from human input, such as remote control, or remote guidance. They may also be autonomous, in which they have a pre-programmed list of operations that will be executed unless otherwise instructed. A robotic spacecraft for scientific measurements is often called a space probe or space observatory. Many space missions are more suited to telerobotic rather than crewed operation, due to lower cost and risk factors. In addition, some planetary destinations such as Venus or the vicinity of Jupiter are too hostile for human survival, given current technology. Outer planets such as Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune are too distant to reach with current crewed spaceflight technology, so telerobotic probes are the only way to explore them. Telerobotics also allows exploration of regions that are vulnerable to contamination by Earth micro-organisms sinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Herschel Space Observatory
The Herschel Space Observatory was a space observatory built and operated by the European Space Agency (ESA). It was active from 2009 to 2013, and was the largest infrared telescope ever launched until the launch of the James Webb Space Telescope in 2021. Herschel carries a mirror and instruments sensitive to the Infrared, far infrared and Submillimetre astronomy, submillimetre wavebands (55–672 μm). Herschel was the fourth and final cornerstone mission in the List of European Space Agency programs and missions#Horizon 2000, Horizon 2000 programme, following ''Solar and Heliospheric Observatory, SOHO''/''Cluster II (spacecraft), Cluster II'', ''XMM-Newton'' and ''Rosetta (spacecraft), Rosetta''. The observatory was carried into orbit by an Ariane 5 in May 2009, reaching the Lagrangian point, second Lagrangian point (L2) of the List of objects at Lagrangian points, Earth–Sun system, from Earth, about two months later. Herschel is named after William Herschel, Sir Will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
INTEGRAL
In mathematics, an integral is the continuous analog of a Summation, sum, which is used to calculate area, areas, volume, volumes, and their generalizations. Integration, the process of computing an integral, is one of the two fundamental operations of calculus,Integral calculus is a very well established mathematical discipline for which there are many sources. See and , for example. the other being Derivative, differentiation. Integration was initially used to solve problems in mathematics and physics, such as finding the area under a curve, or determining displacement from velocity. Usage of integration expanded to a wide variety of scientific fields thereafter. A definite integral computes the signed area of the region in the plane that is bounded by the Graph of a function, graph of a given Function (mathematics), function between two points in the real line. Conventionally, areas above the horizontal Coordinate axis, axis of the plane are positive while areas below are n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
European Space Agency Science Programme
The Science Programme of the European Space Agency is a long-term programme of Outline of space science, space science and space exploration missions. Managed by the agency's Directorate of Science, The programme funds the development, launch, and operation of missions led by European List of government space agencies, space agencies and institutions through generational campaigns. Horizon 2000, the programme's first campaign, facilitated the development of eight missions between 1985 and 1995 including four "cornerstone missions" – Solar and Heliospheric Observatory, SOHO and Cluster II (spacecraft), Cluster II, XMM-Newton, XMM-''Newton'', ''Rosetta (spacecraft), Rosetta'', and ''Herschel Space Observatory, Herschel''. Horizon 2000 Plus, the programme's second campaign, facilitated the development of ''Gaia (spacecraft), Gaia'', LISA Pathfinder, and ''BepiColombo'' between 1995 and 2005. The programme's current campaign since 2005, Cosmic Vision, has so far funded the developm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Optical, Spectroscopic, And Infrared Remote Imaging System
OSIRIS (Optical, Spectroscopic, and Infrared Remote Imaging System) is the main scientific imaging system on the orbiter of the ESA spacecraft '' Rosetta'' for its mission to comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko. It was built by a consortium led by the German Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research. OSIRIS was approved as an instrument for the spacecraft in 1996.Optical, Spectroscopic, and Infrared Remote Imaging System Last Update: 06 September 2013, ESA Science & Technology It was launched in 2004 on ''Rosetta'' and was used until that mission concluded with the deactivation of the ''Rosetta'' spacecraft in September 2016. The OSIRIS had two cameras, each with a different fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |