|
Rosalia (festival)
In the Roman Empire, Rosalia or Rosaria was a festival of roses celebrated on various dates, primarily in May, but scattered through mid-July. The observance is sometimes called a ''rosatio'' ("rose-adornment") or the ''dies rosationis'', "day of rose-adornment," and could be celebrated also with violets ''(violatio'', an adorning with violets, also ''dies violae'' or ''dies violationis'', "day of the "). As a commemoration of the dead, the ''rosatio'' developed from the custom of placing flowers at burial sites. It was among the extensive private religious practices by means of which the Romans cared for their dead, reflecting the value placed on tradition ''(mos maiorum'', "the way of the ancestors"), family lineage, and memorials ranging from simple inscriptions to grand public works. Several dates on the Roman calendar were set aside as public holidays or memorial days devoted to the dead. As a religious expression, a ''rosatio'' might also be offered to the cult statue o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Roman Festival
Festivals in ancient Rome were a very important part of Roman religious life during both the Republican and Imperial eras, and one of the primary features of the Roman calendar. ''Feriae'' ("holidays" in the sense of "holy days"; singular also ''feriae'' or ''dies ferialis'') were either public ''(publicae)'' or private ''( privatae)''. State holidays were celebrated by the Roman people and received public funding. Games ''( ludi)'', such as the Ludi Apollinares, were not technically ''feriae'', but the days on which they were celebrated were '' dies festi'', holidays in the modern sense of days off work. Although ''feriae'' were paid for by the state, ''ludi'' were often funded by wealthy individuals. ''Feriae privatae'' were holidays celebrated in honor of private individuals or by families. This article deals only with public holidays, including rites celebrated by the state priests of Rome at temples, as well as celebrations by neighborhoods, families, and friends held ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Corpus Inscriptionum Latinarum
The ''Corpus Inscriptionum Latinarum'' (''CIL'') is a comprehensive collection of ancient Latin inscriptions. It forms an authoritative source for documenting the surviving epigraphy of classical antiquity. Public and personal inscriptions throw light on all aspects of Roman life and history. The ''Corpus'' continues to be updated in new editions and supplements. CIL also refers to the organization within the Berlin-Brandenburg Academy of Sciences and Humanities responsible for collecting data on and publishing the Latin inscriptions. It was founded in 1853 by Theodor Mommsen and is the first and major organization aiming at a comprehensive survey. Aim The ''CIL'' collects all Latin inscriptions from the whole territory of the Roman Empire, ordering them geographically and systematically. The earlier volumes collected and published authoritative versions of all inscriptions known at the time—most of these had been previously published in a wide range of publications. The desc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dionysus
In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, myth, Dionysus (; ) is the god of wine-making, orchards and fruit, vegetation, fertility, festivity, insanity, ritual madness, religious ecstasy, and theatre. He was also known as Bacchus ( or ; ) by the Greeks (a name later adopted by the Ancient Rome, Romans) for a frenzy he is said to induce called ''baccheia''. His wine, music, and ecstatic dance were considered to free his followers from self-conscious fear and care, and subvert the oppressive restraints of the powerful. His ''thyrsus'', a fennel-stem sceptre, sometimes wound with ivy and dripping with honey, is both a beneficent wand and a weapon used to destroy those who oppose his Cult of Dionysus, cult and the freedoms he represents. Those who partake of his mysteries are believed to become possessed and empowered by the god himself. His origins are uncertain, and his cults took many forms; some are described by ancient sources as Thrace, Thracian, others as Greek. In O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Syncretism
Syncretism () is the practice of combining different beliefs and various school of thought, schools of thought. Syncretism involves the merging or religious assimilation, assimilation of several originally discrete traditions, especially in the theology and mythology of religion, thus asserting an underlying unity and allowing for an Inclusivism, inclusive approach to other faiths. While syncretism in art and culture is sometimes likened to eclecticism, in the realm of religion, it specifically denotes a more integrated merging of beliefs into a unified system, distinct from eclecticism, which implies a selective adoption of elements from different traditions without necessarily blending them into a new, cohesive belief system. Etymology The English word is first attested in the early 17th century. It is from Neo-Latin, Modern Latin , drawing on the (), supposedly meaning "Cretan federation". However, this is a spurious etymology derived from the naive idea in Plutarch's 1st- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Martial
Marcus Valerius Martialis (known in English as Martial ; March, between 38 and 41 AD – between 102 and 104 AD) was a Roman and Celtiberian poet born in Bilbilis, Hispania (modern Spain) best known for his twelve books of '' Epigrams'', published in Rome between AD 86 and 103, during the reigns of the emperors Domitian, Nerva and Trajan. In these poems he satirises city life and the scandalous activities of his acquaintances, and romanticises his provincial upbringing. He wrote a total of 1,561 epigrams, of which 1,235 are in elegiac couplets. Martial has been called the greatest Latin epigrammatist, and is considered the creator of the modern epigram. He also coined the term plagiarism. Early life Knowledge of his origins and early life are derived almost entirely from his works, which can be more or less dated according to the well-known events to which they refer. In Book X of his ''Epigrams'', composed between 95 and 98, he mentions celebrating his fifty-sevent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pliny The Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/24 79), known in English as Pliny the Elder ( ), was a Roman Empire, Roman author, Natural history, naturalist, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the Roman emperor, emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic (''Natural History''), a comprehensive thirty-seven-volume work covering a vast array of topics on human knowledge and the natural world, which became an editorial model for encyclopedias. He spent most of his spare time studying, writing, and investigating natural and geographic phenomena in the field. Among Pliny's greatest works was the twenty-volume ''Bella Germaniae'' ("The History of the German Wars"), which is Lost literary work, no longer extant. ''Bella Germaniae'', which began where Aufidius Bassus' ''Libri Belli Germanici'' ("The War with the Germans") left off, was used as a source by other prominent Roman historians, including Plutarch, Tacitus, and Suetonius. Tacitus may have used ''Bella Ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Glosses
A gloss is a brief notation, especially a marginal or interlinear one, of the meaning of a word or wording in a text. It may be in the language of the text or in the reader's language if that is different. A collection of glosses is a ''glossary.'' A collection of medieval legal glosses, made by glossators, is called an ''apparatus''. The compilation of glosses into glossaries was the beginning of lexicography, and the glossaries so compiled were in fact the first dictionaries. In modern times a glossary, as opposed to a dictionary, is typically found in a text as an appendix of specialized terms that the typical reader may find unfamiliar. Also, satirical explanations of words and events are called glosses. The German Romantic movement used the expression of gloss for poems commenting on a given other piece of poetry, often in the Spanish style. Glosses were originally notes made in the margin or between the lines of a text in a classical language; the meaning of a word or pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Garland
A garland is a decorative braid, knot or wreath of flowers, leaves, or other material. Garlands can be worn on the head or around the neck, hung on an inanimate object, or laid in a place of cultural or religious importance. In contemporary times, Garlands are used to decorate, especially around holidays Etymology From the French language, French , itself from the Italian language, Italian , a braid. Types *Bead garland *Flower garland **Lei (garland), Lei – The traditional garland of Hawaiʻi. **Daisy chain – A garland created from the Bellis, daisy flower (generally as a children's game) is called a daisy chain. One method of creating a daisy chain is to pick daisies and create a hole towards the base of the stem (such as with fingernails or by tying a Overhand knot, knot). The stem of the next flower can be threaded through until stopped by the head of the flower. By repeating this with many daisies, it is possible to build up long chains and to form them into simple bra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
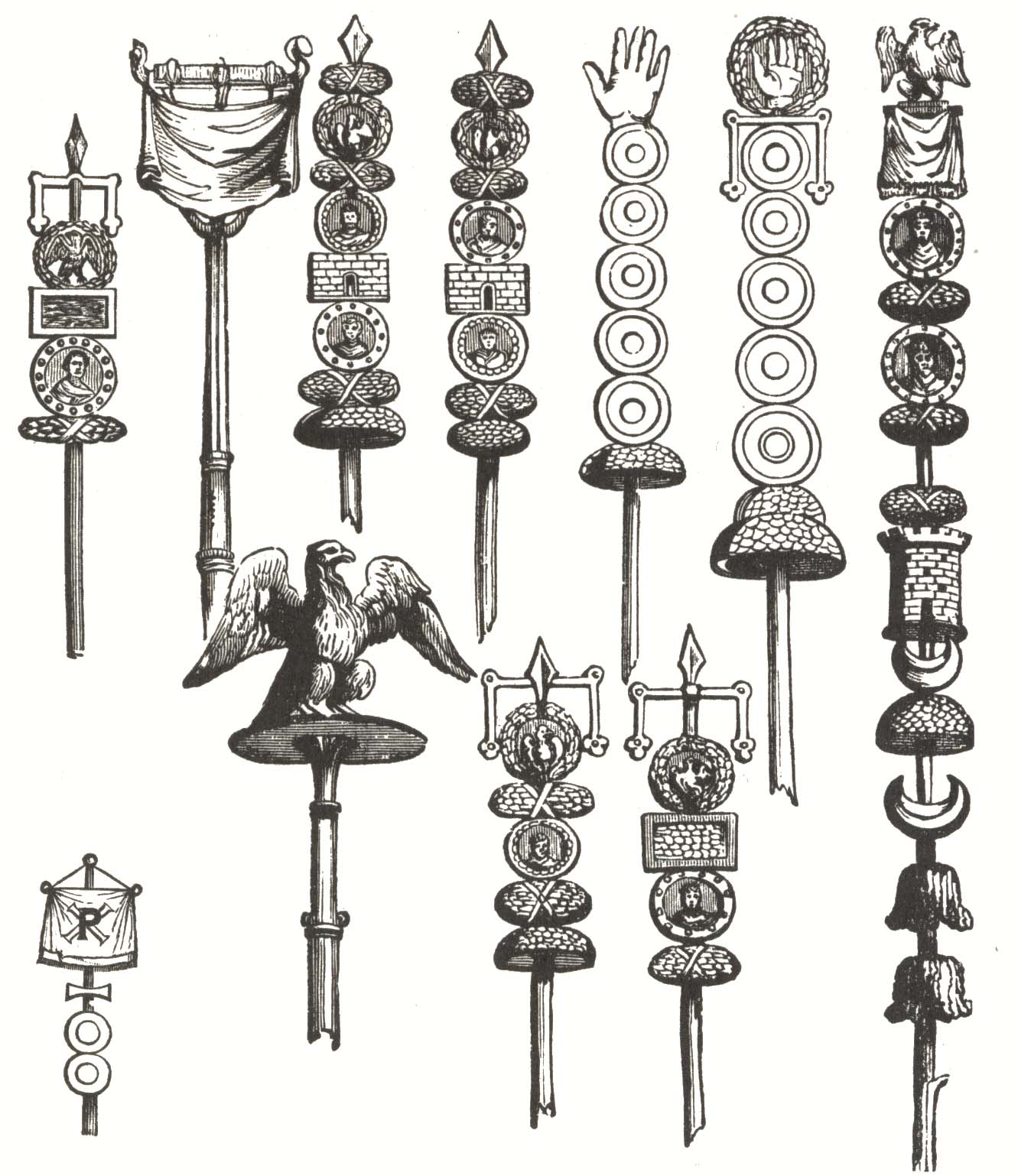
Roman Military Standard
Roman military standards were emblems adopted by units of the Roman army. There were three main types of standard (Aquila, Vexillum, Signum). Several throughout its history include: * ''Aquila'', the emblem of the Roman legion whose adoption Pliny the Elder attributes to the general Gaius Marius. Each legion had an eagle, or aquila, carried by an aquilifer; * ''Vexillum'', the emblem of a legion, cohors, numerus or detachments of such units. This was a flag attached to the top of the pole. One type had the name and number of the legion on it. Others were used by detachments serving away from the legion; * ''Draco'', a cavalry standard later adopted also by infantry units; * ''Labarum'', personal ensign of emperor Constantine I, later adopted as army standard. * '' Signum'', Each century (80 men) had its own standard, called a signum. Signa had lots of symbols attached to the pole (Many were discs with indented circles). * ''Imago In biology, the imago (Latin for "image") is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Imperial Roman Army
The Imperial Roman Army was the military land force of the Roman Empire from 27 BC to 476 AD, and the final incarnation in the long history of the Roman army. This period is sometimes split into the Principate (27 BC – 284 AD) and the Dominate (284–476) periods. Under Augustus (), the army consisted of Roman legion, legions, eventually and also ''Numerus (Roman military unit), numeri''. By the end of Augustus' reign, the imperial army numbered some 250,000 men, equally split between 25 legions and 250 units of auxiliaries. The numbers grew to a peak of about 450,000 by 211, in 33 legions and about 400 auxiliary units. By then, auxiliaries outnumbered legionaries substantially. From this peak, numbers probably underwent a steep decline by 270 due to plague and losses during multiple major invasions by the Germanic Tribal Folk. Numbers were restored to their early 2nd-century level of c. 400,000 (but probably not to their 211 peak) under Diocletian (r. 284–305). After the E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Roman Calendar
The Roman calendar was the calendar used by the Roman Kingdom and Roman Republic. Although the term is primarily used for Rome's pre-Julian calendars, it is often used inclusively of the Julian calendar established by Julius Caesar in 46 BC. According to most Roman accounts, #Romulus, their original calendar was established by their Roman legend, legendary list of kings of Rome, first king Romulus. It consisted of ten months, beginning in spring with March and leaving winter as an unassigned span of days before the next year. These months each had 30 or 31 days and ran for 38 nundinal cycles, each forming a kind of eight-day weeknine days inclusive counting, counted inclusively in the Roman mannerand ending with religious rituals and a Roman commerce, public market. This fixed calendar bore traces of its origin as an observational calendar, observational lunar calendar, lunar one. In particular, the most important days of each monthits kalends, nones (calendar), nones, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |