|
Ronald Coase
Ronald Harry Coase (; 29 December 1910 – 2 September 2013) was a British economist and author. Coase was educated at the London School of Economics, where he was a member of the faculty until 1951. He was the Clifton R. Musser Professor of Economics at the University of Chicago Law School, where he arrived in 1964 and remained for the rest of his life. He received the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences in 1991. Coase believed economists should study real-world wealth creation, in the manner of Adam Smith, stating, "It is suicidal for the field to slide into a hard science of choice, ignoring the influences of society, history, culture, and politics on the working of the economy." He believed economic study should reduce emphasis on Price Theory or theoretical markets and instead focus on real markets. He established the case for the corporation as a means to pay the costs of operating a marketplace. Coase is best known for two articles: "The Nature of the Firm" (1937), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
New Institutional Economics
New Institutional Economics (NIE) is an economic perspective that attempts to extend economics by focusing on the institutions (that is to say the social and legal norms and rules) that underlie economic activity and with analysis beyond earlier institutional economics and neoclassical economics. The NIE assume that individuals are rational and that they seek to maximize their preferences, but that they also have cognitive limitations, lack complete information and have difficulties monitoring and enforcing agreements. As a result, institutions form in large part as an effective way to deal with transaction costs. NIE rejects that the state is a neutral actor (rather, it can hinder or facilitate effective institutions), that there are zero transaction costs, and that actors have fixed preferences. Overview It has its roots in two articles by Ronald Coase, " The Nature of the Firm" (1937) and " The Problem of Social Cost" (1960). In the latter, the Coase theorem (as it was su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nobel Memorial Prize In Economic Sciences
The Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences, officially the Sveriges Riksbank Prize in Economic Sciences in Memory of Alfred Nobel (), commonly referred to as the Nobel Prize in Economics(), is an award in the field of economic sciences administered by the Nobel Foundation, established in 1968 by Sveriges Riksbank (Sweden's central bank) to celebrate its 300th anniversary and in memory of Alfred Nobel. Although the Prize in Economic Sciences was not one of the original five Nobel Prizes established by Alfred Nobel's will, it is considered a member of the Nobel Prize system, and is administered and referred to along with the Nobel Prizes by the Nobel Foundation. Winners of the Prize in Economic Sciences are chosen in a similar manner to and announced alongside the Nobel Prize recipients, and receive the Prize in Economic Sciences at the Nobel Prize Award Ceremony. The laureates of the Prize in Economic Sciences are selected by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
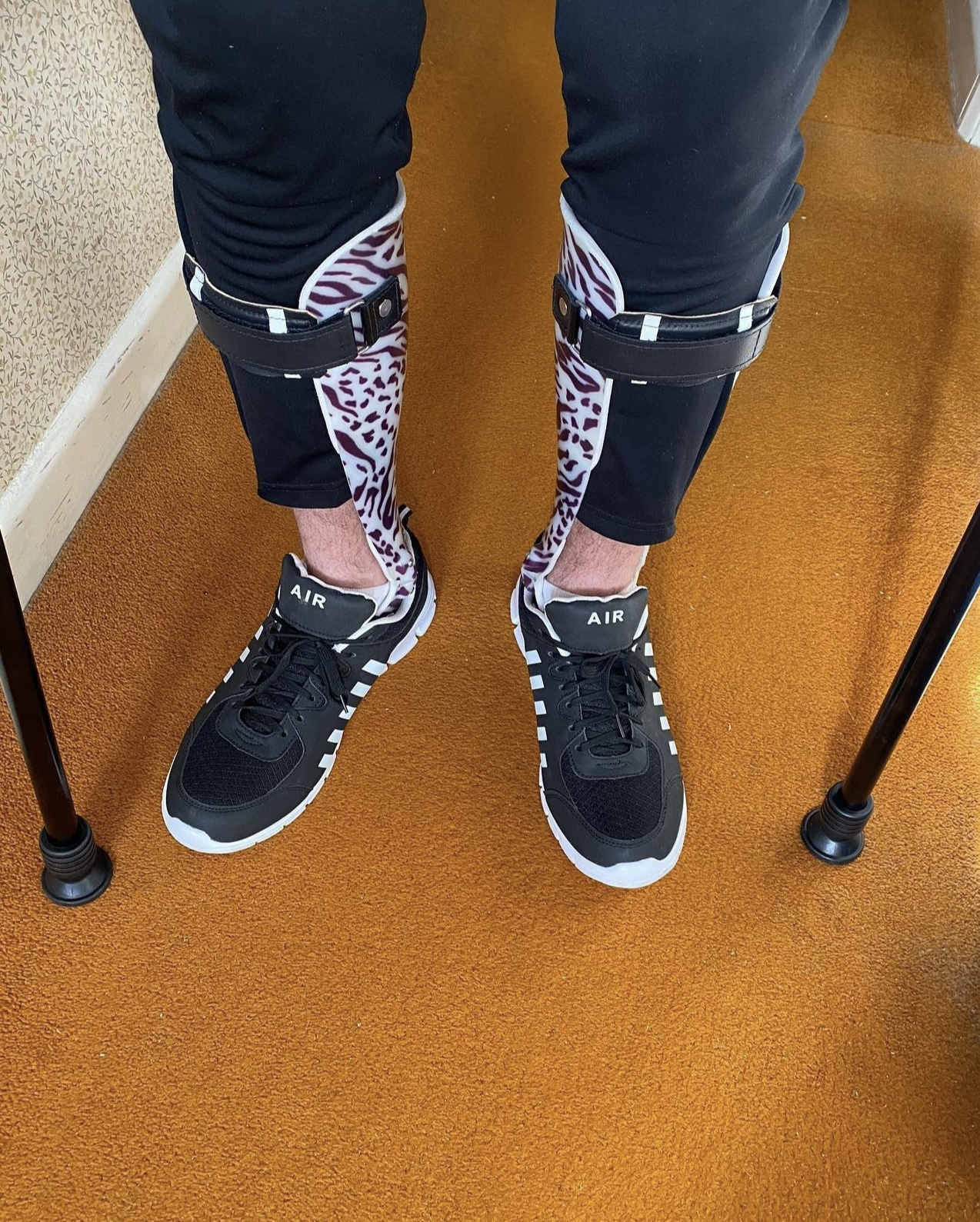
Brace (orthopaedic)
Orthotics () is a medical specialty that focuses on the design and application of orthoses, sometimes known as braces, calipers, or splints. An is "an externally applied device used to influence the structural and functional characteristics of the Neuromuscular junction, neuromuscular and Skeletal muscle, skeletal systems." Orthotists are medical professionals who specialize in designing orthotic devices such as braces or foot orthoses. Classification Orthotic devices are classified into four areas of the body according to the international classification system (ICS): orthotics of the Human leg, lower extremities, orthotics of the Upper limb, upper extremities, orthotics for the Torso, trunk, and orthotics for the head. Orthoses are also classified by function: paralysis orthoses and relief orthoses. Under the International Organization for Standardization, International Standard terminology, orthoses are classified by an acronym describing the anatomical joints they supp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Internet Archive
The Internet Archive is an American 501(c)(3) organization, non-profit organization founded in 1996 by Brewster Kahle that runs a digital library website, archive.org. It provides free access to collections of digitized media including websites, Application software, software applications, music, audiovisual, and print materials. The Archive also advocates a Information wants to be free, free and open Internet. Its mission is committing to provide "universal access to all knowledge". The Internet Archive allows the public to upload and download digital material to its data cluster, but the bulk of its data is collected automatically by its web crawlers, which work to preserve as much of the public web as possible. Its web archiving, web archive, the Wayback Machine, contains hundreds of billions of web captures. The Archive also oversees numerous Internet Archive#Book collections, book digitization projects, collectively one of the world's largest book digitization efforts. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
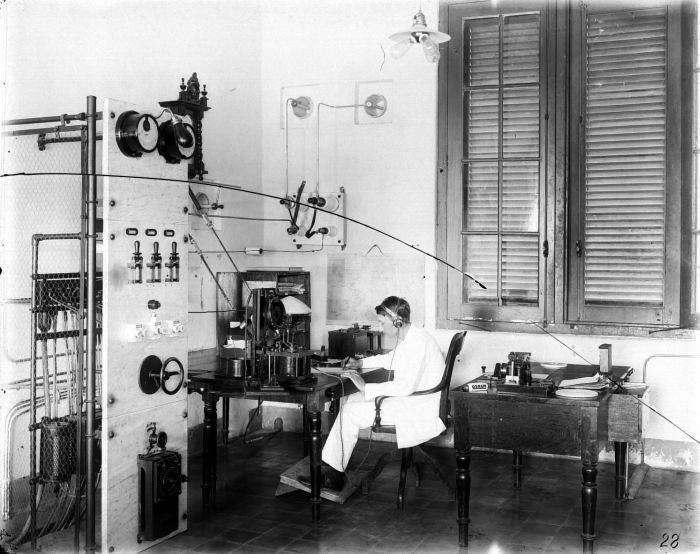
Telegraphist
A telegraphist (British English), telegrapher (American English), or telegraph operator is a person who uses a telegraph key to send and receive Morse code messages in a telegraphy system. These messages, also called telegrams, can be transmitted electronically by land lines, or wirelessly by radio. History During the First World War, the Royal Navy enlisted many volunteers as radio telegraphists. Telegraphists were indispensable at sea in the early days of wireless telegraphy, and many young men were called to sea as professional radiotelegraph operators who were always accorded high-paying officer status at sea. Subsequent to the ''Titanic'' disaster and the Radio Act of 1912, the International Safety of Life at Sea ( SOLAS) conventions established the 500kHz maritime distress frequency monitoring and mandated that all passenger-carrying ships carry licensed radio telegraph operators. Notable telegraphists * Harold Bride * Harold Cottam * Louisa Margaret Dunkley * Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Oliver E
Oliver may refer to: Arts, entertainment and literature Books * ''Oliver the Western Engine'', volume 24 in ''The Railway Series'' by Rev. W. Awdry * ''Oliver Twist'', a novel by Charles Dickens Fictional characters * Ariadne Oliver, in the novels of Agatha Christie * Oliver (Disney character) * Oliver Fish, a gay police officer on the American soap opera ''One Life to Live'' * Oliver Hampton, in the American television series ''How to Get Away with Murder'' * Oliver Jones (''The Bold and the Beautiful''), on the American soap opera ''The Bold and the Beautiful'' * Oliver Lightload, in the movie ''Cars'' * Oliver Oken, from ''Hannah Montana'' * Oliver (paladin), a paladin featured in the Matter of France * Oliver Queen, DC Comic book hero also known as the Green Arrow * Oliver (Thomas and Friends character), a locomotive in the Thomas and Friends franchise * Oliver Trask, a controversial minor character from the first season of ''The O.C.'' * Oliver Twist ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Organizational Economics
Organizational economics (also referred to as ''economics of organization'') involves the use of economic logic and methods to understand the existence, nature, design, and performance of organizations, especially managed ones. Organizational economics is primarily concerned with the obstacles to coordination of activities inside and between organizations (firms, alliances, institutions, and market as a whole). Organizational economics is known for its contribution to and its use of: * Transaction cost theory: costs incurred to organize an activity, especially regarding research of information, bureaucracy, communication etc. * Agency theory: dilemmas connected to making decisions on behalf of, or that impact, another person or entity. * Contract theory: ways economic actors use to construct contractual arrangements, generally in the presence of asymmetric information. Notable theorists and contributors in the field of organizational economics: *Kenneth Arrow * James March * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Externalities
In economics, an externality is an indirect cost (external cost) or indirect benefit (external benefit) to an uninvolved third party that arises as an effect of another party's (or parties') activity. Externalities can be considered as unpriced components that are involved in either consumer or producer consumption. Air pollution from motor vehicles is one example. The cost of air pollution to society is not paid by either the producers or users of motorized transport. Water pollution from mills and factories are another example. All (water) consumers are made worse off by pollution but are not compensated by the market for this damage. The concept of externality was first developed by Alfred Marshall in the 1890s and achieved broader attention in the works of economist Arthur Pigou in the 1920s. The prototypical example of a negative externality is environmental pollution. Pigou argued that a tax, equal to the marginal damage or marginal external cost, (later called a "Pigou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Property Rights (economics)
Property rights are constructs in economics for determining how a resource or economic good is used and owned, which have developed over ancient and modern history, from Abrahamic law to Article 17 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights. Resources can be owned by (and hence be the property of) individuals, associations, collectives, or governments. Property rights can be viewed as an attribute of an economic good. This attribute has three broad components, and is often referred to as a bundle of rights in the United States: # the right to use the good # the right to earn income from the good # the right to transfer the good to others, alter it, abandon it, or destroy it (the right to ownership cessation) Economists such as Adam Smith stress that the expectation of profit from "improving one's stock of capital" rests on the concept of private property rights. Conceptualizing property in economics vs. law The fields of economics and law do not have a general consensus on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
The Problem Of Social Cost
"The Problem of Social Cost" (1960) is a law review article by Ronald Coase, then a faculty member at the University of Virginia, dealing with the economic problem of externalities. It draws from a number of English legal cases and statutes to illustrate Coase's belief that legal rules are only justified by reference to a cost–benefit analysis, and that nuisances that are often regarded as being the fault of one party are more symmetric conflicts between the interests of the two parties. If there are sufficiently low costs of doing a transaction, legal rules would be irrelevant to the maximization of production. Because in the real world there are costs of bargaining and information gathering, legal rules are justified to the extent of their ability to allocate rights to the most efficient right-bearer. Along with an earlier article, “The Nature of the Firm”, "The Problem of Social Cost" was cited by the Nobel committee when Coase was awarded the Nobel Memorial Prize in Econo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Corporation
A corporation or body corporate is an individual or a group of people, such as an association or company, that has been authorized by the State (polity), state to act as a single entity (a legal entity recognized by private and public law as "born out of statute"; a legal person in a legal context) and recognized as such in Corporate law, law for certain purposes. Early incorporated entities were established by charter (i.e., by an ''ad hoc'' act granted by a monarch or passed by a parliament or legislature). Most jurisdictions now allow the creation of new corporations through List of company registers, registration. Corporations come in many different types but are usually divided by the law of the jurisdiction where they are chartered based on two aspects: whether they can issue share capital, stock, or whether they are formed to make a profit (accounting), profit. Depending on the number of owners, a corporation can be classified as ''aggregate'' (the subject of this articl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |