|
Rock Mechanics
Rock mechanics is a theoretical and applied science of the mechanical behavior of rocks and rock masses. Compared to geology, it is the branch of mechanics concerned with the response of rock and rock masses to the force fields of their physical environment. Background Rock mechanics is part of a much broader subject of geomechanics, which is concerned with the mechanical responses of all geological materials, including soils. Rock mechanics is concerned with the application of the principles of Engineering Mechanics, engineering mechanics to the design of structures built in or on rock. The structure could include many objects such as a drilling well, a mine shaft, a tunnel, a reservoir dam, a repository component, or a building. Rock mechanics is used in many engineering disciplines, but is primarily used in Mining, Civil, Geotechnical, Transportation, and Petroleum Engineering. Rock mechanics answers questions such as, "is reinforcement necessary for a rock, or will it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanics
Mechanics () is the area of physics concerned with the relationships between force, matter, and motion among Physical object, physical objects. Forces applied to objects may result in Displacement (vector), displacements, which are changes of an object's position relative to its environment. Theoretical expositions of this branch of physics has its origins in Ancient Greece, for instance, in the writings of Aristotle and Archimedes (see History of classical mechanics and Timeline of classical mechanics). During the early modern period, scientists such as Galileo Galilei, Johannes Kepler, Christiaan Huygens, and Isaac Newton laid the foundation for what is now known as classical mechanics. As a branch of classical physics, mechanics deals with bodies that are either at rest or are moving with velocities significantly less than the speed of light. It can also be defined as the physical science that deals with the motion of and forces on bodies not in the quantum realm. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Creep (deformation)
In materials science, creep (sometimes called cold flow) is the tendency of a solid material to undergo slow deformation while subject to persistent mechanical stresses. It can occur as a result of long-term exposure to high levels of stress that are still below the yield strength of the material. Creep is more severe in materials that are subjected to heat for long periods and generally increases as they near their melting point. The rate of deformation is a function of the material's properties, exposure time, exposure temperature and the applied structural load. Depending on the magnitude of the applied stress and its duration, the deformation may become so large that a component can no longer perform its function – for example creep of a turbine blade could cause the blade to contact the casing, resulting in the failure of the blade. Creep is usually of concern to engineers and metallurgists when evaluating components that operate under high stresses or high temperatures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petrology
Petrology () is the branch of geology that studies rocks, their mineralogy, composition, texture, structure and the conditions under which they form. Petrology has three subdivisions: igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary petrology. Igneous and metamorphic petrology are commonly taught together because both make heavy use of chemistry, chemical methods, and phase diagrams. Sedimentary petrology is commonly taught together with stratigraphy because it deals with the processes that form sedimentary rock. Modern sedimentary petrology is making increasing use of chemistry. Background Lithology was once approximately synonymous with petrography, but in current usage, lithology focuses on macroscopic hand-sample or outcrop-scale description of rocks while petrography is the speciality that deals with microscopic details. In the petroleum industry, lithology, or more specifically mud logging, is the graphic representation of geological formations being drilled through and drawn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rock Mechanics
Rock mechanics is a theoretical and applied science of the mechanical behavior of rocks and rock masses. Compared to geology, it is the branch of mechanics concerned with the response of rock and rock masses to the force fields of their physical environment. Background Rock mechanics is part of a much broader subject of geomechanics, which is concerned with the mechanical responses of all geological materials, including soils. Rock mechanics is concerned with the application of the principles of Engineering Mechanics, engineering mechanics to the design of structures built in or on rock. The structure could include many objects such as a drilling well, a mine shaft, a tunnel, a reservoir dam, a repository component, or a building. Rock mechanics is used in many engineering disciplines, but is primarily used in Mining, Civil, Geotechnical, Transportation, and Petroleum Engineering. Rock mechanics answers questions such as, "is reinforcement necessary for a rock, or will it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rock Mass Plasticity
300px, sinistral shear sense'', Starlight Pit, Fortnum Gold Mine, Western Australia In geotechnical engineering, rock mass plasticity is the study of the response of Rock (geology), rocks to loads beyond the elastic limit. Historically, conventional wisdom has it that rock is brittle and fails by fracture, while plasticity (irreversible deformation without fracture) is identified with ductile materials such as metals. In field-scale rock masses, structural discontinuities exist in the rock indicating that failure has taken place. Since the rock has not fallen apart, contrary to expectation of brittle behavior, clearly elasticity theory is not the last word.Pariseau (1988). Theoretically, the concept of rock plasticity is based on soil plasticity which is different from metal plasticity. In metal plasticity, for example in steel, the size of a dislocation is sub-grain size while for soil it is the relative movement of microscopic grains. The theory of soil plasticity was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
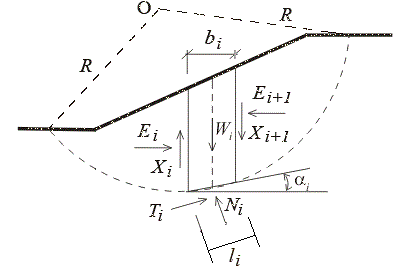
Slope Stability Analysis
Slope stability analysis is a static or dynamic, analytical or empirical method to evaluate the ''stability of slopes'' of soil- and rock-fill dams, embankments, excavated slopes, and natural slopes in soil and rock. It is performed to assess the safe design of a human-made or natural slopes (e.g. Embankment (transportation), embankments, road cuts, open-pit mining, excavations, landfills etc.) and the equilibrium conditions. Slope stability is the resistance of inclined surface to failure by Landslide, sliding or collapsing. The main objectives of slope stability analysis are finding endangered areas, investigation of potential failure mechanisms, determination of the slope sensitivity to different triggering mechanisms, designing of optimal slopes with regard to safety, Reliability engineering, reliability and economics, and designing possible remedial measures, e.g. barriers and Stabilization (architecture), stabilization. Successful design of the slope requires geological in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rock Mass Classification
Rock mass classification systems are used for various engineering design and stability analysis. These are based on empirical relations between rock mass parameters and engineering applications, such as tunnels, slopes, foundations, and excavatability. The first rock mass classification system in geotechnical engineering was proposed in 1946 for tunnels with steel set support. Design methods In engineering in rock, three design strategies can be distinguished: analytical, empirical, and numerical. Empirical, i.e. rock mass classification, methods are extensively used for feasibility and pre-design studies, and often also for the final design. Objectives The objectives of rock mass classifications are (after Bieniawski 1989): # Identify the most significant parameters influencing the behaviour of a rock mass. # Divide a particular rock mass formulation into groups of similar behaviour – rock mass classes of varying quality. # Provide a basis of understanding the characteristics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geotechnical Engineering
Geotechnical engineering, also known as geotechnics, is the branch of civil engineering concerned with the engineering behavior of earth materials. It uses the principles of soil mechanics and rock mechanics to solve its engineering problems. It also relies on knowledge of geology, hydrology, geophysics, and other related sciences. Geotechnical engineering has applications in military engineering, mining engineering, petroleum engineering, coastal engineering, and offshore construction. The fields of geotechnical engineering and engineering geology have overlapping knowledge areas. However, while geotechnical engineering is a specialty of civil engineering, engineering geology is a specialty of geology. History Humans have historically used soil as a material for flood control, irrigation purposes, burial sites, building foundations, and construction materials for buildings. Dykes, dams, and canals dating back to at least 2000 BCE—found in parts of ancient Egypt, ancient Mes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engineering Geology
Engineering geology is the application of geology to engineering study for the purpose of assuring that the geological factors regarding the location, design, construction, operation and maintenance of engineering works are recognized and accounted for. Engineering geologists provide geological and geotechnical recommendations, analysis, and design associated with human development and various types of structures. The realm of the engineering geologist is essentially in the area of earth-structure interactions, or investigation of how the earth or earth processes impact human made structures and human activities. Engineering geology studies may be performed during the planning, environmental impact analysis, civil or structural engineering design, value engineering and construction phases of public and private works projects, and during post-construction and forensic phases of projects. Works completed by engineering geologists include; geologic hazards assessment, geotechnica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tensile Strength
Ultimate tensile strength (also called UTS, tensile strength, TS, ultimate strength or F_\text in notation) is the maximum stress that a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before breaking. In brittle materials, the ultimate tensile strength is close to the yield point, whereas in ductile materials, the ultimate tensile strength can be higher. The ultimate tensile strength is usually found by performing a tensile test and recording the engineering stress versus strain. The highest point of the stress–strain curve is the ultimate tensile strength and has units of stress. The equivalent point for the case of compression, instead of tension, is called the compressive strength. Tensile strengths are rarely of any consequence in the design of ductile members, but they are important with brittle members. They are tabulated for common materials such as alloys, composite materials, ceramics, plastics, and wood. Definition The ultimate tensile strength ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sound Velocity
The speed of sound is the distance travelled per unit of time by a sound wave as it propagates through an elastic medium. More simply, the speed of sound is how fast vibrations travel. At , the speed of sound in air is about , or in or one mile in . It depends strongly on temperature as well as the medium through which a sound wave is propagating. At , the speed of sound in dry air (sea level 14.7 psi) is about . The speed of sound in an ideal gas depends only on its temperature and composition. The speed has a weak dependence on frequency and pressure in dry air, deviating slightly from ideal behavior. In colloquial speech, ''speed of sound'' refers to the speed of sound waves in air. However, the speed of sound varies from substance to substance: typically, sound travels most slowly in gases, faster in liquids, and fastest in solids. For example, while sound travels at in air, it travels at in water (almost 4.3 times as fast) and at in iron (almost 15 times as fast). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |