|
RNA Primer
A primer is a short, single-stranded nucleic acid used by all living organisms in the initiation of DNA synthesis. A synthetic primer is a type of oligo, short for oligonucleotide. DNA polymerases (responsible for DNA replication) are only capable of adding nucleotides to the 3’-end of an existing nucleic acid, requiring a primer be bound to the template before DNA polymerase can begin a complementary strand. DNA polymerase adds nucleotides after binding to the RNA primer and synthesizes the whole strand. Later, the RNA strands must be removed accurately and replaced with DNA nucleotides. This forms a gap region known as a nick that is filled in using a ligase. The removal process of the RNA primer requires several enzymes, such as Fen1, Lig1, and others that work in coordination with DNA polymerase, to ensure the removal of the RNA nucleotides and the addition of DNA nucleotides. Living organisms use solely RNA primers, while laboratory techniques in biochemistry and molecula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Replication En
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a Nucleic acid double helix, double helix. The polymer carries genetics, genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of all known organisms and many viruses. DNA and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are nucleic acids. Alongside proteins, lipids and complex carbohydrates (polysaccharides), nucleic acids are one of the four major types of macromolecules that are essential for all known forms of life. The two DNA strands are known as polynucleotides as they are composed of simpler monomeric units called nucleotides. Each nucleotide is composed of one of four nitrogenous base, nitrogen-containing nucleobases (cytosine [C], guanine [G], adenine [A] or thymine [T]), a monosaccharide, sugar called deoxyribose, and a Organophosphate, phosphate group. The nucleotides are joined to one another in a chain by covalent bonds (known as the Phosphod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Novo Synthesis
In chemistry, ''de novo'' synthesis () is the synthesis of complex molecules from simple molecules such as sugars or amino acids, as opposed to recycling after partial degradation. For example, nucleotides are not needed in the diet as they can be constructed from small precursor molecules such as formate and aspartate. Methionine, on the other hand, is needed in the diet because while it can be degraded to and then regenerated from homocysteine, it cannot be synthesized ''de novo''. Nucleotide ''De novo'' pathways of nucleotides do not use free bases: adenine (abbreviated as A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), thymine (T), or uracil (U). The purine ring is built up one atom or a few atoms at a time and attached to ribose throughout the process. Pyrimidine ring is synthesized as orotate and attached to ribose phosphate and later converted to common pyrimidine nucleotides. Cholesterol Cholesterol is an essential structural component of animal cell membranes. Cholesterol a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ribonucleotide
In biochemistry, a ribonucleotide is a nucleotide containing ribose as its pentose component. It is considered a molecular precursor of nucleic acids. Nucleotides are the basic building blocks of DNA and RNA. Ribonucleotides themselves are basic monomeric building blocks for RNA. Deoxyribonucleotides, formed by reducing ribonucleotides with the enzyme ribonucleotide reductase (RNR), are essential building blocks for DNA. There are several differences between DNA deoxyribonucleotides and RNA ribonucleotides. Successive nucleotides are linked together via phosphodiester bonds. Ribonucleotides are also utilized in other cellular functions. These special monomers are utilized in both cell regulation and cell signaling as seen in adenosine-monophosphate ( AMP). Furthermore, ribonucleotides can be converted to adenosine triphosphate ( ATP), the energy currency in organisms. Ribonucleotides can be converted to cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cyclic AMP) to regulate hormones in organisms as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphodiesterase I
Phosphodiesterase 1, PDE1, EC 3.1.4.1, systematic name oligonucleotide 5-nucleotidohydrolase) is a phosphodiesterase enzyme also known as calcium- and calmodulin-dependent phosphodiesterase. It is one of the 11 families of phosphodiesterase (PDE1-PDE11). Phosphodiesterase 1 has three subtypes, PDE1A, PDE1B and PDE1C which divide further into various isoforms. The various isoforms exhibit different affinities for cAMP and cGMP. Discovery The existence of the Ca2+-stimulated Phosphodiesterase 1 was first demonstrated by Cheung (1970), Kakiuchi and Yamazaki (1970) as a result of their research on bovine brain and rat brain respectively. It has since been found to be widely distributed in various mammalian tissues as well as in other eukaryotes. It is now one of the most intensively studied member of the PDE superfamily of enzymes, which today represents 11 gene families, and the best characterized one as well. Further research in the field along with increased availability of mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Ligase
DNA ligase is a type of enzyme that facilitates the joining of DNA strands together by catalyzing the formation of a phosphodiester bond. It plays a role in repairing single-strand breaks in duplex DNA in living organisms, but some forms (such as DNA ligase IV) may specifically repair double-strand breaks (i.e. a break in both complementary strands of DNA). Single-strand breaks are repaired by DNA ligase using the complementary strand of the double helix as a template, with DNA ligase creating the final phosphodiester bond to fully repair the DNA. DNA ligase is used in both DNA repair and DNA replication (see '' Mammalian ligases''). In addition, DNA ligase has extensive use in molecular biology laboratories for recombinant DNA experiments (see '' Research applications''). Purified DNA ligase is used in gene cloning to join DNA molecules together to form recombinant DNA. Enzymatic mechanism The mechanism of DNA ligase is to form two covalent phosphodiester bonds between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deoxyribonucleotides
A deoxyribonucleotide is a nucleotide that contains deoxyribose. They are the monomeric units of the informational biopolymer, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Each deoxyribonucleotide comprises three parts: a deoxyribose sugar (monosaccharide), a nitrogenous base, and one phosphoryl group. The nitrogenous bases are either purines or pyrimidines, heterocycles whose structures support the specific base-pairing interactions that allow nucleic acids to carry information. The base is always bonded to the 1'-carbon of the deoxyribose, an analog of ribose in which the hydroxyl group of the 2'-carbon is replaced with a hydrogen atom. The third component, the phosphoryl group, attaches to the deoxyribose monomer via the hydroxyl group on the 5'-carbon of the sugar. When deoxyribonucleotides polymerize to form DNA, the phosphate group from one nucleotide will bond to the 3' carbon on another nucleotide, forming a phosphodiester bond via dehydration synthesis. New nucleotides are always added to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryote
The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the Domain (biology), domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya, organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a membrane-bound cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, Fungus, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms are eukaryotes. They constitute a major group of Outline of life forms, life forms alongside the two groups of prokaryotes: the Bacteria and the Archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but given their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass is much larger than that of prokaryotes. The eukaryotes emerged within the archaeal Kingdom (biology), kingdom Asgard (Archaea), Promethearchaeati and its sole phylum Promethearchaeota. This implies that there are only Two-domain system, two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among the Archaea. Eukaryotes first emerged during the Paleoproterozoic, likely as Flagellated cell, flagellated cells. The leading evolutiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prokaryote
A prokaryote (; less commonly spelled procaryote) is a unicellular organism, single-celled organism whose cell (biology), cell lacks a cell nucleus, nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Ancient Greek (), meaning 'before', and (), meaning 'nut' or 'kernel'. In the earlier two-empire system arising from the work of Édouard Chatton, prokaryotes were classified within the empire Prokaryota. However, in the three-domain system, based upon molecular phylogenetics, prokaryotes are divided into two domain (biology), domains: Bacteria and Archaea. A third domain, Eukaryote, Eukaryota, consists of organisms with nuclei. Prokaryotes evolution, evolved before eukaryotes, and lack nuclei, mitochondria, and most of the other distinct organelles that characterize the eukaryotic cell. Some unicellular prokaryotes, such as cyanobacteria, form colony (biology), colonies held together by biofilms, and large colonies can create multilayered microbial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reverse Transcriptase
A reverse transcriptase (RT) is an enzyme used to convert RNA genome to DNA, a process termed reverse transcription. Reverse transcriptases are used by viruses such as HIV and hepatitis B to replicate their genomes, by retrotransposon mobile genetic elements to proliferate within the host genome, and by eukaryotic cells to extend the telomeres at the ends of their linear chromosomes. The process does not violate the flows of genetic information as described by the classical central dogma, but rather expands it to include transfers of information from RNA to DNA. Retroviral RT has three sequential biochemical activities: RNA-dependent DNA polymerase activity, ribonuclease H (RNase H), and DNA-dependent DNA polymerase activity. Collectively, these activities enable the enzyme to convert single-stranded RNA into double-stranded cDNA. In retroviruses and retrotransposons, this cDNA can then integrate into the host genome, from which new RNA copies can be made via host-cell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Okazaki Fragments
Okazaki fragments are short sequences of DNA nucleotides (approximately 150 to 200 base pairs long in eukaryotes) which are synthesized discontinuously and later linked together by the enzyme DNA ligase to create the lagging strand during DNA replication. They were discovered in the 1960s by the Japanese molecular biologists Reiji and Tsuneko Okazaki, along with the help of some of their colleagues. During DNA replication, the double helix is unwound and the complementary strands are separated by the enzyme DNA helicase, creating what is known as the DNA replication fork. Following this fork, DNA primase and DNA polymerase begin to act in order to create a new complementary strand. Because these enzymes can only work in the 5’ to 3’ direction, the two unwound template strands are replicated in different ways. One strand, the leading strand, undergoes a continuous replication process since its template strand has 3’ to 5’ directionality, allowing the polymerase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
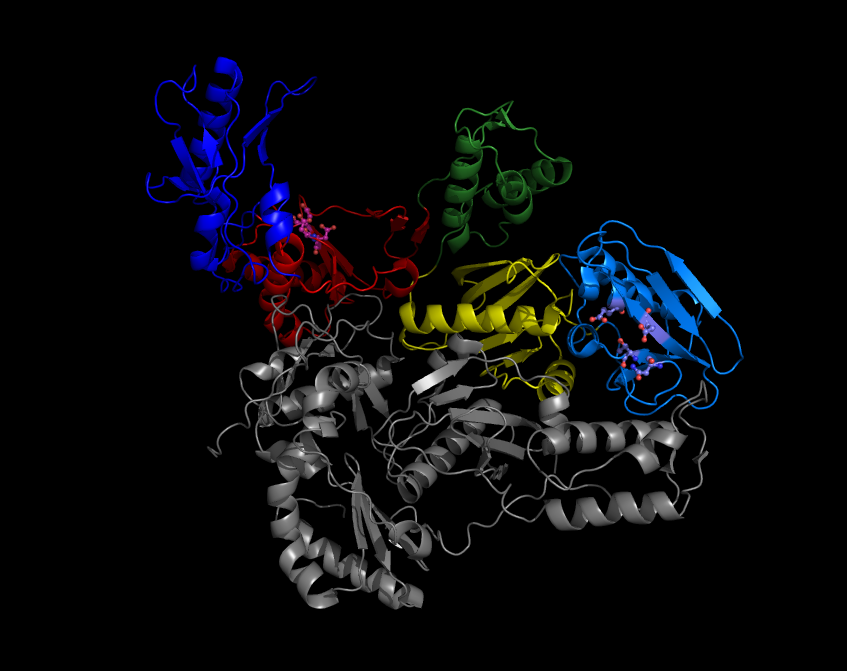
DNA Polymerase
A DNA polymerase is a member of a family of enzymes that catalyze the synthesis of DNA molecules from nucleoside triphosphates, the molecular precursors of DNA. These enzymes are essential for DNA replication and usually work in groups to create two identical DNA duplexes from a single original DNA duplex. During this process, DNA polymerase "reads" the existing DNA strands to create two new strands that match the existing ones. These enzymes catalysis, catalyze the chemical reaction : deoxynucleoside triphosphate + DNAn pyrophosphate + DNAn+1. DNA polymerase adds nucleotides to the Directionality (molecular biology), three prime (3')-end of a DNA strand, one nucleotide at a time. Every time a Cell division, cell divides, DNA polymerases are required to duplicate the cell's DNA, so that a copy of the original DNA molecule can be passed to each daughter cell. In this way, genetic information is passed down from generation to generation. Before replication can take place, an enzy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Replication Fork
In molecular biology, DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. DNA replication occurs in all living organisms, acting as the most essential part of biological inheritance. This is essential for cell division during growth and repair of damaged tissues, while it also ensures that each of the new cells receives its own copy of the DNA. The cell possesses the distinctive property of division, which makes replication of DNA essential. DNA is made up of a double helix of two complementary strands. DNA is often called double helix. The double helix describes the appearance of a double-stranded DNA which is composed of two linear strands that run opposite to each other and twist together. During replication, these strands are separated. Each strand of the original DNA molecule then serves as a template for the production of its counterpart, a process referred to as semiconservative replication. As a result, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |