|
River Walbrook
The Walbrook is a subterranean river in London. It gives its name to the Walbrook City ward and to a nearby street. It played an important role in the Roman settlement of Londinium. Name The usual interpretation is that the brook's name comes from ''weala broc'' meaning "brook of the foreigners" (usually taken to mean the native Britons, who were also referred to as the Welsh). This suggests that there was a British speaking quarter in the city in the Anglo-Saxon period, and this possibility has been linked to the division of the city by the Walbrook, with claims that the Britons lived on Cornhill to the east, while the Saxons lived on Ludgate Hill to the west. Another theory is that it was so named because it ran through or under the London Wall. Geoffrey of Monmouth linked it to the phenomena of the '' Walbrook Skulls'' (below); recounting, or inventing an explanation where the name ''Gallobroc''Geoffrey of Monmouth, ''Historia Regum Britanniae'' 5.4 derived from the na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forgotten Streams Along The Walbrook
Forgotten or The Forgotten may refer to: Places and fictional locations * Forgotten River, New Zealand * Forgotten Hills, Victoria Land, Antarctica People and fictional characters * Bolesław the Forgotten (before 1016–1038 or 1039), a semi-legendary Duke of Poland Film * ''Forgotten'' (1933 film), an American film directed by Richard Thorpe * ''The Forgotten'' (1973 film), a psychological horror film * ''The Forgotten'', a 1989 television action film directed by James Keach * ''The Forgotten'' (2003 film), a Korean War film * ''The Forgotten'' (2004 film), a psychological thriller * ''Forgotten'' (2012 film), a Taiwanese/Chinese television film * ''Forgotten'' (2013 film), a Bolivian film * ''The Forgotten'' (2014 film), a British horror film * ''Forgotten'' (2017 film), a South Korean mystery thriller Literature * ''The Forgotten'' (Applegate novel), a book in the ''Animorphs'' series by K. A. Applegate * ''The Forgotten'' (Baldacci novel), a 2012 novel by D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finsbury
Finsbury is a district of Central London, forming the southeastern part of the London Borough of Islington. It borders the City of London. The Manorialism, Manor of Finsbury is first recorded as ''Vinisbir'' (1231) and means "manor of a man called Finn".Mills, D. (2000). ''Oxford Dictionary of London Place Names''. . Finsbury lay just outside Cripplegate (and on its later construction, Moorgate) in London Wall. At that time, much of the manor was part of the ''"great fen which washed against the London Wall, northern wall of the City of London, City"''. Finsbury gave its name to two larger administrative areas: the Finsbury division, Finsbury Division of the Ossulstone (hundred), Ossulstone Hundred of Middlesex, from the 17th century until 1900, and from 1900 to 1965 the Metropolitan Borough of Finsbury. The Metropolitan Borough included Finsbury (also known as St Luke's, London, St Luke's) and Clerkenwell. The area should not be confused with Finsbury Park, a public space r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Celtic Religion
Ancient Celtic religion, commonly known as Celtic paganism, was the religion of the ancient Celtic peoples of Europe. Because there are no extant native records of their beliefs, evidence about their religion is gleaned from archaeology, Greco-Roman accounts (some of them hostile and probably not well-informed), and literature from the early Christian period. Green, Miranda (2012). "Chapter 25: The Gods and the supernatural", ''The Celtic World''. Routledge. pp.465–485 Celtic paganism was one of a larger group of polytheistic Indo-European religions of Iron Age Europe. While the specific deities worshipped varied by region and over time, underlying this were broad similarities in both deities and "a basic religious homogeneity" among the Celtic peoples. Widely worshipped Celtic gods included Lugus, Toutatis, Taranis, Cernunnos, Epona, Maponos, Belenos, and Sucellos. Sacred springs were often associated with Celtic healing deities. Triplicity is a common theme, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Morris (historian)
John Robert Morris (8 June 1913 – 1 June 1977) was an English historian who specialised in the study of the institutions of the Roman Empire and the history of Sub-Roman Britain. He is best known for his book ''The Age of Arthur'' (1973), which attempted to reconstruct the history of Britain and Ireland during the so-called "Dark Ages (historiography), Dark Ages" (350–650 AD) following the Roman withdrawal, based on scattered archaeology, archaeological and historical records. The book was heavily criticised by other academic historians. Biography Morris read modern history at Jesus College, Oxford, from 1932 to 1935, and served in the British Army, Army during the Second World War. After the war, he held a Leon Fellowship at the University of London and a Junior Fellowship at the Warburg Institute. In 1948 he was appointed Lecturer in Ancient History at University College, London. He worked in India in 1968 and 1969 as a lecturer for the Indian University Grants Commission, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boudica
Boudica or Boudicca (, from Brittonic languages, Brythonic * 'victory, win' + * 'having' suffix, i.e. 'Victorious Woman', known in Latin chronicles as Boadicea or Boudicea, and in Welsh language, Welsh as , ) was a queen of the Iceni, ancient British Iceni tribe, who led a Boudican revolt, failed uprising against the Roman Britain, conquering forces of the Roman Empire in AD 60 or 61. She is considered a British national heroine and a symbol of the struggle for justice and independence. Boudica's husband Prasutagus, with whom she had two daughters, ruled as a nominally independent ally of Rome. He left his kingdom jointly to his daughters and to the Roman emperor in his Will and testament, will. When he died, his will was ignored, and the kingdom was annexed and his property taken. According to the Roman historian Tacitus, Boudica was Flagellation, flogged and her daughters wartime sexual violence, raped. The historian Cassius Dio wrote that previous imperial donations to influ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
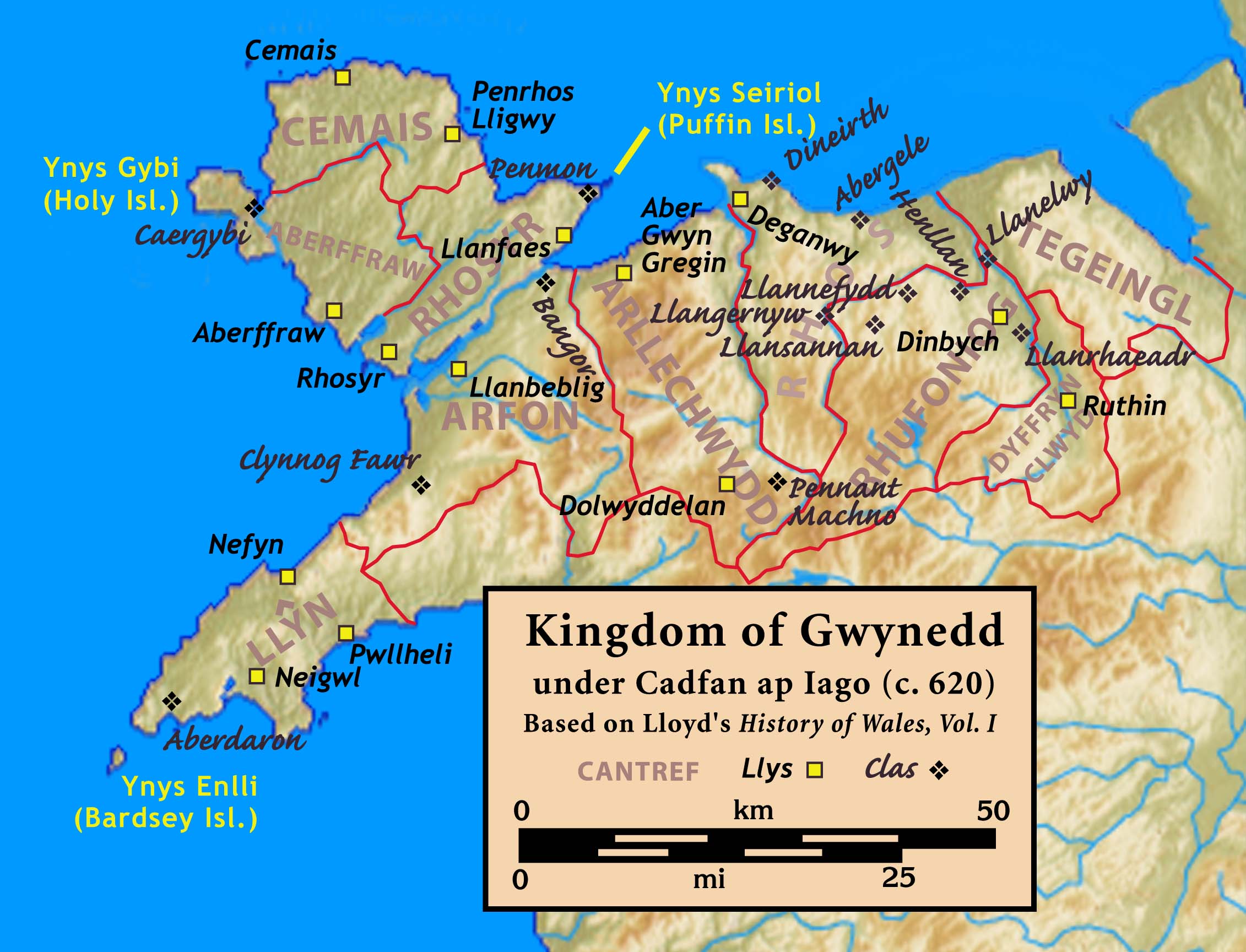
Kingdom Of Gwynedd
The Kingdom of Gwynedd (Medieval Latin: ; Middle Welsh: ) was a Wales in the Early Middle Ages, Welsh kingdom and a Roman Empire Succession of states, successor state that emerged in sub-Roman Britain in the 5th century during the Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain. Based in northwest Wales, the list of rulers of Gwynedd, rulers of Gwynedd repeatedly rose to dominance and were acclaimed as "King of the Britons" before losing their power in civil wars or invasions. The kingdom of Gruffydd ap Llywelynthe King of Wales from 1055 to 1063was shattered by a Timeline of conflict in Anglo-Saxon Britain, Saxon invasion in 1063 just prior to the Norman invasion of Wales, but the House of Aberffraw restored by Gruffudd ap Cynan slowly recovered and Llywelyn the Great of Gwynedd was able to proclaim the Principality of Wales at the Aberdyfi gathering of Welsh princes in 1216. In 1277, the Treaty of Aberconwy between Edward I of England and Llywelyn's grandson Llywelyn ap Gruffudd granted pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julius Asclepiodotus
Julius Asclepiodotus was a Roman praetorian prefect who, according to the ''Historia Augusta'', served under the emperors Aurelian, Probus and Diocletian, and was consul in 292. In 296, he assisted the western Caesar Constantius Chlorus in re-establishing Roman rule in Britain, following the illegal rules of Carausius and Allectus. Historical Life Allectus, having assassinated Carausius in 293, remained in control of Britain until 296, when Constantius staged an invasion to retake the island. While Constantius sailed from Boulogne, Asclepiodotus took a section of the fleet and the legions from San Dun Sandouville and the oppidum near Le Havre, slipping past Allectus's fleet at the Isle of Wight under cover of fog, and landed presumably in the vicinity of Southampton or Chichester, where he burned his ships. Allectus attempted to retreat from the coast, but was cut off by Constantius's forces and defeated. Some of Constantius's troops, who had been separated from the main body by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Legion
The Roman legion (, ) was the largest military List of military legions, unit of the Roman army, composed of Roman citizenship, Roman citizens serving as legionary, legionaries. During the Roman Republic the manipular legion comprised 4,200 infantry and 300 cavalry. After the Marian reforms in 107 BC, the legions were formed of 5,200 men and were restructured around 10 cohorts, the first cohort being double strength. This structure persisted throughout the Principate and Roman Empire, middle Empire, before further changes in the fourth century resulted in new formations of around 1,000 men. Size The size of a typical legion varied throughout the history of ancient Rome, with complements ranging from 4,200 legionaries and 300 ''equites'' (drawn from the wealthier classes – in early Rome all troops provided their own equipment) in the Republic, to 5,500 in the Imperial period, when most legions were led by a Roman Imperial Legate. A legion had 4,800 Legionary, legionaries ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blomfield Street
Blomfield Street is a road in the City of London, close to Liverpool Street railway station. It was known as Broker Row, until 1860. The street was built along the course of a part of the River Walbrook known as the ''Deepditch''. Although the Walbrook is now culverted and runs beneath the street, the land on each side observably dips towards the course of the river. Setting The street extends in a SSW-NNE direction from its junction with the road ''London Wall'' in the south to ''Broad Street Place'' in the north. The street forms the boundary between the Bishopsgate#Bishopsgate Without, Bishopsgate Without (to the east) and Coleman Street Ward (to the west) areas of the City of London. The side streets are ''Liverpool Street'' and ''New Broad Street'' on the eastern side, and Finsbury Circus to the west. The western side of the street is in the Finsbury Circus Conservation area and includes a number of listed buildings. History Walbrook The street covers a section of the Rive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moorfields
Moorfields was an open space, partly in the City of London, lying adjacent to – and outside – its London Wall, northern wall, near the eponymous Moorgate. It was known for its marshy conditions, the result of the defensive wall acting as a dam, impeding the flow of the River Walbrook and its tributaries. Moorfields gives its name to the Moorfields Eye Hospital which occupied a site on the former fields from 1822–1899, and is still based close by, in the St Luke's, London, St Luke's area of the London Borough of Islington. Setting Moorfields is first recorded in the late 12th century, though not by name, as a ''great fen''. The fen was larger than the area subsequently known as Moorfields. Moorfields was contiguous with Finsbury Square, Finsbury Fields, Bunhill Fields and other open spaces, and until its eventual loss in the 19th century, was the innermost part of a green wedge of land which stretched from the London Wall, wall, to the open countryside which lay close ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Stow
John Stow (''also'' Stowe; 1524/25 – 5 April 1605) was an English historian and antiquarian. He wrote a series of chronicles of History of England, English history, published from 1565 onwards under such titles as ''The Summarie of Englyshe Chronicles'', ''The Chronicles of England'', and ''The Annales of England''; and also ''A Survey of London'' (1598; second edition 1603). A. L. Rowse has described him as "one of the best historians of that age; indefatigable in the trouble he took, thorough and conscientious, accurate – above all things devoted to truth". Life John Stow was born in about 1525 in the City of London parish of St Michael, Cornhill, then at the heart of London's metropolis. His father, Thomas Stow, was a Worshipful Company of Tallow Chandlers, tallow chandler. Thomas Stow is recorded as paying rent of 6s 8d per year for the family dwelling, and as a youth Stow would fetch milk every morning from a farm on the land nearby to the east owned by the Poor Clares, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |