|
Rincón Bomba Massacre
The Rincón Bomba Massacre, also known as the Pilagá Massacre, La Bomba Massacre, Pilagá Genocide, or Rincón Bomba, was a genocide and Crimes against humanity, crime against humanity committed by the Government of Argentina, Argentine state against Indigenous peoples in Argentina, indigenous peoples in 1947. The Argentine National Gendarmerie, National Gendarmerie, with support from an Argentine Air Force aircraft and National Territories Police, targeted the Pilagá people in La Bomba Hamlet, near Las Lomitas, in what was then the (now Formosa Province), between October 10 and 30, 1947, during the first presidency of Juan Perón. The atrocities included Execution by firing squad, executions, Enforced disappearance, disappearances, torture, rape, kidnappings, and forced labor, with an estimated 750 to 1,000 deaths. In 2019, the event was judicially recognized as a crime against humanity, and in 2020, it was classified as a genocide. The massacre was largely unaddressed by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pilagá
fThe Pilagá (in Pilagá language, Pilagá language: ''pit'laxá'') are an Indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous people of the Guaycuru peoples, Guaycuru group that inhabits the center of the province of Formosa Province, Formosa, in Argentina. Some migrant groups also live in the provinces of Chaco Province, Chaco and Santa Fe Province, Santa Fe. Their language is part of the Mataco–Guaicuru languages, Mataco-Guaicurú linguistic family. They are closely related to the Toba people, Toba people, and about 2000 of them speak their own language, along with the Spanish language, Spanish language. Since 1996, they have been writing Pilagá in a Latin alphabet of 4 vowels and 19 consonants. They have been able to preserve much of their native culture. They are of tall stature and strong build. In ancient times, they were hunters and gatherers. Among the fruits they gathered were those of the Prosopis nigra, carob tree, Geoffroea decorticans, chañar, Sarcomphalus mistol, mis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
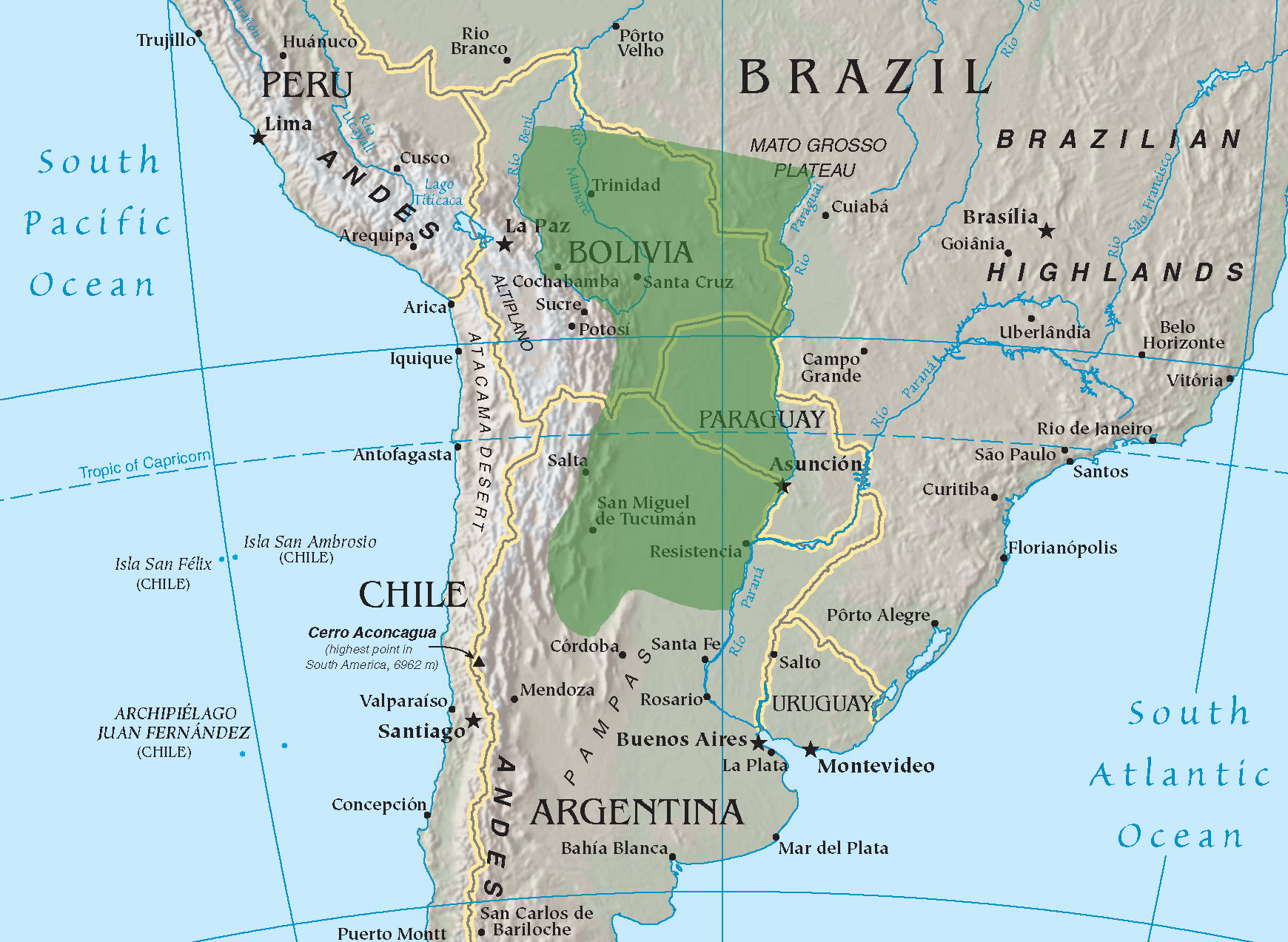
Gran Chaco
The Gran Chaco or simply Chaco is a sparsely populated, hot and semiarid lowland tropical dry broadleaf forest natural region of the Río de la Plata basin, divided among eastern Bolivia, western Paraguay, northern Argentina, and a portion of the Brazilian states of Mato Grosso and Mato Grosso do Sul, where it is connected with the Pantanal region. This land is sometimes called the Chaco Plain. The ecoregion has an estimated population of 3,985,000. Toponymy The name Chaco comes from the Quechua word meaning "hunting land", an indigenous language from the Andes and highlands of South America, and comes probably from the rich variety of animal life present throughout the entire region. Geography The Gran Chaco is about 647,500km2 (250,000 sq mi) in size, though estimates differ. It is located west of the Paraguay River and east of the Andes, and is mostly an alluvial sedimentary plain shared among Paraguay, Bolivia, and Argentina. It stretches from about 17 to 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Misiones Province
Misiones (, ''Missions'') is one of the Provinces of Argentina, 23 provinces of Argentina, located in the northeastern corner of the country in the Mesopotamia, Argentina, Mesopotamia region. It is surrounded by Paraguay to the northwest, Brazil to the north, east and south, and Corrientes Province of Argentina to the southwest. This was an early area of Roman Catholic missionary activity by the Jesuits in what was then called the province of Paraguay, beginning in the early 17th century. In 1984, the ruins of four mission sites in Argentina were designated World Heritage Sites by UNESCO. History Indigenous peoples of various tribes lived in the area of the future province for thousands of years. At the time of European encounter, the area was occupied by the Kaingang and Xokleng people, Xokleng tribes, later followed by the Guarani people, Guarani tribe. The first European to visit the region, Sebastian Cabot (explorer), Sebastian Cabot, discovered Apipé Falls while navigat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1994 Amendment Of The Constitution Of Argentina
The 1994 amendment to the Constitution of Argentina was approved on 22 August 1994 by a Constitutional Assembly that met in the twin cities of Santa Fe and Paraná. The calling for elections for the Constitutional Convention and the main issues to be decided were agreed in 1993 between President Carlos Menem, and former president and leader of the opposition, Raúl Alfonsín. Constitutional Assembly election On April 10, 1994 the conventional constituent elections were held. The Justicialist Party led by President Menem won the elections with 38.50% of the votes. Radical Civic Union came second with 19.74% votes, while two newly born forces each obtained 13%: the progressive peronist Broad Front, led by Carlos Álvarez, and the rightist Movement for Dignity and Independence, led by the carapintada military man Aldo Rico. Out of a total of 305 constituents, the Justicialist Party obtained 137 representatives, Radical Civic Union 74, Broad Front 31, Movement for Dign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mocoví
The Mocoví ( Mocoví: ''moqoit'') are an Indigenous people of the Gran Chaco region of South America. They speak the Mocoví language and are one of the ethnic groups belonging to the Guaycuru peoples. In the 2010 Argentine census, 22,439 people self-identified as Mocoví. Not much is known about them before the Spanish arrived. They were nomadic and lived off of their fishing, hunting and gathering. They hunted deer and rhea and slept on animal skins and flimsy shelters. They did not farm because the soil conditions were poor where they roamed and there was flooding. Trade routes were discovered in the Chaco forest, indicating trading and it was assumed they traded skins and feathers for gold, silver and copper objects. When the Jesuits arrived, they taught the Mocoví to farm with cattle and they became sedentary. In 1924, at least 200 Mocoví and Toba people The Toba people, also known as the Qom people, are one of the largest Indigenous groups in Argentina who historical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toba People
The Toba people, also known as the Qom people, are one of the largest Indigenous groups in Argentina who historically inhabited the region known today as the Gran Chaco, Pampas of the Central Chaco. During the 16th century, the Qom inhabited a large part of what is today northern Argentina, in the current provinces of Salta Province, Salta, Chaco Province, Chaco, Santiago del Estero Province, Santiago del Estero, Formosa Province, Formosa and the province of Gran Chaco Province, Gran Chaco in the southeast of the Tarija Department, Department of Tarija in Bolivia (which the Qom have inhabited since the 20th century). Currently, many Toba, due to persecution in their rural ancestral regions, live in the suburbs of Orán, Salta, San Ramón de la Nueva Orán, Salta, Tartagal, Salta, Tartagal, Resistencia, Chaco, Resistencia, Charata, Formosa, Rosario, Santa Fe, Rosario and Santa Fe, Argentina, Santa Fe and in Greater Buenos Aires. Nearly 130,000 people currently identify themselves as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcelo Torcuato De Alvear
Máximo Marcelo Torcuato de Alvear y Pacheco (4 October 1868 – 23 March 1942) served as president of Argentina between from 1922 to 1928. His period of government coincided precisely with the end of the Post-war, postwar world crisis, which allowed him to improve the economy and finances of the country without major setbacks. He also stood out in the development of the automotive industry and the successful Extraction of petroleum, oil exploitation, with which he achieved an economic prosperity unknown until then for Argentina, and that was demonstrated with the great increase achieved in the Gross domestic product, GDP per inhabitant. In 1928, he had reached the sixth position among the highest in the world. In the labor and social sphere, this period was characterized by a process of urban concentration in the Argentine Littoral, Litoral and Greater Buenos Aires, in addition to the establishment of half a million immigrants; there was an increase in the middle class, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napalpí Massacre
The Napalpí massacre occurred on 19 July 1924, in Napalpí a rural village in the Chaco Province of Northeast Argentina. It involved the massacre of 400 Indigenous people of the Toba and Mocoví ethnicity by the Argentine Police and ranchers. Historical context Forty years earlier, the Argentine Army had been involved in a military campaign to subjugate the Indigenous people, mostly Guaycuru of several different ethnic groups, of the Argentine Chaco called the Conquest of Chaco. The campaign resulted in the death of thousands of Indigenous people, the displacement of many more, and the social and cultural destruction of numerous ethnic groups from the provinces of Chaco and Formosa. The Argentine forces established a line of fortresses in order to gain lands for European settlers. The land was mainly used by the settlers to grow cotton. The native people were confined in compounds, where they were subjected to a regime of exploitation bordering on slavery. One of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaco Province
Chaco (; Wichi languages, Wichi: ''To-kós-wet''), officially the Province of Chaco ( ) is one of the 23 provinces of Argentina, provinces of Argentina. Its capital and largest city is Resistencia, Chaco, Resistencia. It is located in the north-east of the country. It is bordered by Salta Province, Salta and Santiago del Estero Province, Santiago del Estero to the west, Formosa Province, Formosa to the north, Corrientes Province, Corrientes to the east, and Santa Fe Province, Santa Fe to the south. It also has an international border with the Paraguayan Departments of Paraguay, department of Ñeembucú. With an area of and a population of 1,142,963 as of 2022, it is the twelfth most extensive, and the eleventh most populated, of Argentina's provinces. In 2010, Chaco became the second province in Argentina to adopt more than one official language. These are the Toba Qom language, Kom, Mocoví language, Moqoit and Wichí languages, Wichí languages, spoken by the Toba people, Tob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radical Civic Union
The Radical Civic Union (, UCR) is a major political party in Argentina. It has reached the national government on ten occasions, making it one of the most historically important parties in the country. Ideologically, the party has stood for radicalism, secularism and universal suffrage. Especially during the 1970s and 1980s, it was perceived as a strong advocate for human rights. Its factions however, have been more heterogeneous, ranging from conservative liberalism to social democracy. Founded in 1891 by Leandro N. Alem, it is the second oldest political party active in Argentina. The party's main support has long come from the middle class. On many occasions, the UCR was in opposition to Peronist governments and declared illegal during military rule. Since 1995 it has been a member of the Socialist International (an international organisation of social democrat political parties). The UCR had different fractures, conformations, incarnations and factions, through w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hipólito Yrigoyen
Juan Hipólito del Sagrado Corazón de Jesús Yrigoyen (12 July 1852 – 3 July 1933) was an Argentine politician of the Radical Civic Union who served as President of Argentina from 1916 to 1922 and again from 1928 until his overthrow in 1930. He was the first president elected democratically by means of the secret and mandatory male suffrage established by the Sáenz Peña Law of 1912. His activism was the prime impetus behind the passage of that law in Argentina. Known as "the father of the poor", Yrigoyen presided over a rise in the standard of living of Argentina's working class together with the passage of a number of progressive social reforms, including improvements in factory conditions, regulation of working hours, compulsory pensions, and the introduction of a universally accessible public education system. Yrigoyen was the first nationalist president, convinced that the country had to manage its own currency and, above all, it should have control of its transp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |