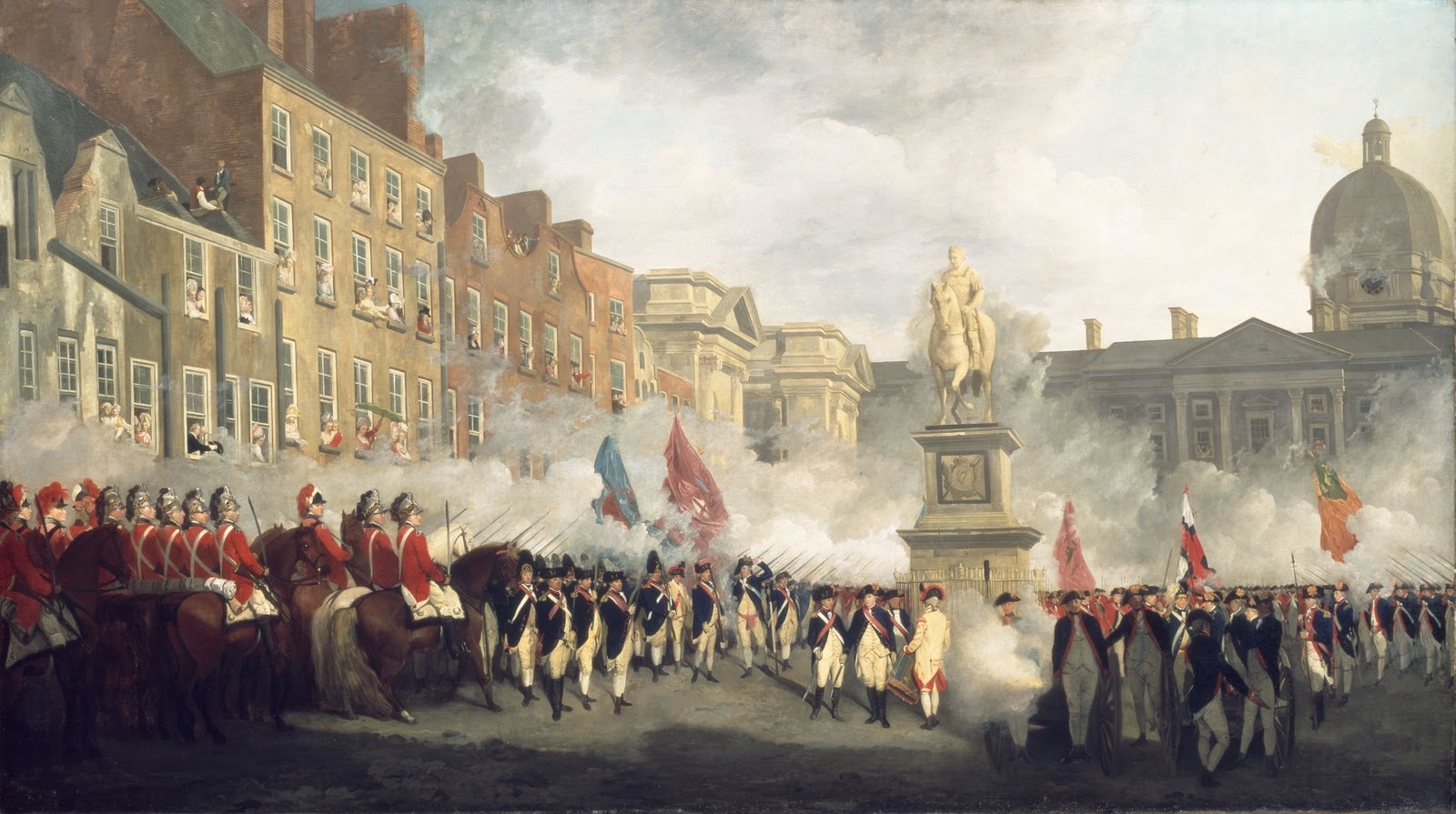|
Richard Boyle, 2nd Earl Of Shannon
Richard Boyle, 2nd Earl of Shannon KP, PC (Ire) (30 January 1727 – 20 May 1807), was an Irish peer and Member of Parliament. He represented Dungarvan and County Cork, and succeeded his father as Earl of Shannon.Listing of the Earls of Shannon and their descendants in Wombat's Family Forest Family He was the elder surviving son of , and his second wife, Lady Henrietta Boyle (1700–1746). His maternal grandparents were |
William Cavendish, 5th Duke Of Devonshire
William Cavendish, 5th Duke of Devonshire, (14 December 1748 – 29 July 1811), was a British nobleman, aristocrat, and politician. He was the eldest son of William Cavendish, 4th Duke of Devonshire, by his wife, the heiress Charlotte Cavendish, Marchioness of Hartington, Lady Charlotte Boyle, ''suo jure'' Baroness Clifford, who brought in considerable money and estates to the Cavendish family. He was invited to join the Cabinet on three occasions, but declined each offer.Michael Durban, 'Cavendish, William, fifth duke of Devonshire (1748–1811)’, Oxford Dictionary of National Biography, Oxford University Press, 200accessed 30 April 2010/ref> He was Lord High Treasurer of Ireland and Governor of Cork, and Lord Lieutenant of Derbyshire. In 1782, he was made a Knight of the Order of the Garter. The 5th Duke is best known for his marriage to his first wife Georgiana Spencer, Georgiana, Duchess of Devonshire. At the age of about twenty, Devonshire toured Italy with Sir William ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Opening Of Parliament
The State Opening of Parliament is a ceremonial event which formally marks the beginning of each Legislative session, session of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. At its core is His or Her Majesty's "Speech from the throne, gracious speech from the throne" (also known as the King's or Queen's Speech), which is read by the Monarchy of the United Kingdom, monarch but written by HM Government. In the speech the monarch gives notice of forthcoming state visits, before setting out the government's legislative programme for the new parliamentary session. No business of either House of Parliament (the House of Lords or the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons) can proceed until the Sovereign’s speech has been delivered. The State Opening takes place in the House of Lords chamber within the Palace of Westminster on the first day of the new parliamentary session. This traditionally tends to fall in November, but can occur at any time of year (depending on the ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speech From The Throne
A speech from the throne, or throne speech, is an event in certain monarchies in which the reigning sovereign, or their representative, reads a prepared speech to members of the nation's legislature when a Legislative session, session is opened. The address sets forth the government's priorities for its legislative agenda, for which the cooperation of the legislature is sought. The speech is often accompanied by formal ceremony. It is often held annually, although in some places it may occur more or less frequently, whenever a new session of the legislature is opened. Historically, when monarchs exercised personal influence and overall decision-making in government, a speech from the throne would outline the policies and objectives of the monarch; the speech was usually prepared by the monarch's advisers, but the monarch supervised the drafting of the speech at least to some extent and exercised final discretion as to its content. In modern constitutional monarchies, whether by l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legislative Session
A legislative session is the period of time in which a legislature, in both parliamentary and presidential systems, is convened for purpose of lawmaking, usually being one of two or more smaller divisions of the entire time between two elections. A session may last for the full term of the legislature or the term may consist of a number of sessions. These may be of fixed duration, such as a year, or may be determined by the party in power. In some countries, a session of the legislature is brought to an end by an official act of prorogation, in others by a motion to adjourn ''sine die''. In either event, the close of a session generally brings an end to all unpassed bills in the legislature, which would have to be introduced anew to continue debate in the following session. Common procedure Historically, each session of a parliament would last less than one year, ceasing with a prorogation during which legislators could return to their constituencies. In more recent times, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George IV Of The United Kingdom
George IV (George Augustus Frederick; 12 August 1762 – 26 June 1830) was King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and King of Hanover from 29 January 1820 until his death in 1830. At the time of his accession to the throne, he was acting as prince regent for his father, King George III, having done so since 5 February 1811 during his father's final mental illness. George IV was the eldest child of King George III and Queen Charlotte. He led an extravagant lifestyle that contributed to the fashions of the Regency era. He was a patron of new forms of leisure, style and taste. He commissioned John Nash to build the Royal Pavilion in Brighton and remodel Buckingham Palace, and commissioned Jeffry Wyatville to rebuild Windsor Castle. George's charm and culture earned him the title "the first gentleman of England", but his dissolute way of life and poor relationships with his parents and his wife, Caroline of Brunswick, earned him the contempt of the pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constitution Of 1782
The Constitution of 1782 was a group of Acts passed by the Parliament of Ireland and the Parliament of Great Britain in 1782–83 which increased the legislative and judicial independence of the Kingdom of Ireland by reducing the ability of the Kingdom of Great Britain to make laws and hear court cases relating to Ireland. These changes were promoted, under the name legislative independence, by the Irish Patriot Party, a loose alliance with Henry Grattan as its leading orator. The Parliament of Ireland as it existed after 1782 is often called Grattan's Parliament in his honour. The constitution did not create a responsible executive, as the Dublin Castle administration remained under the control of a Lord Lieutenant acting as a representative of the British government. Under the terms of Poynings' Law of 1495, no law could be passed by the Parliament of Ireland that was not first approved by the Privy Council of England. In 1719, the Parliament of Great Britain passed the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Volunteers (18th Century)
The Volunteers (also known as the Irish Volunteers) were militia units raised by local initiative in Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland in 1778. Their original purpose was to guard against invasion and to preserve law and order after much of the Irish Army (1661–1801), Irish Army was sent to fight abroad as part of the American Revolutionary War, American War of Independence and the Dublin Castle administration failed to expand the militia. Taking advantage of the Parliament of Great Britain's preoccupation with the American War of Independence, the Volunteers were able to pressure them into conceding legislative independence to the Parliament of Ireland. Members of the Belfast Volunteers laid the foundations for the establishment of the Society of United Irishmen. The majority of the Volunteers, however, were Unionism in Ireland, unionists, and later helped to suppress the Irish Rebellion of 1798.Ulster Museum, History of Belfast exhibition According to historian Thomas Bartlett ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Rule In Ireland
British colonial rule in Ireland built upon the 12th-century Anglo-Norman invasion of Ireland on behalf of the English king and eventually spanned several centuries that involved British control of parts, or the entirety, of the island of Ireland. Most of Ireland gained independence from the United Kingdom following the Anglo-Irish War in the early 20th century. Initially formed as a Dominion called the Irish Free State in 1922, the Republic of Ireland became a fully independent nation state following the passage of the Statute of Westminster in 1931. It effectively became a republic with the passage of a new constitution in 1937, and formally became a republic with the passage of the Republic of Ireland Act in 1949. Northern Ireland remains part of the United Kingdom as a constituent country. Middle Ages From the late 12th century, the Anglo-Norman invasion of Ireland resulted in Anglo-Norman control of much of Ireland, over which the kings of England then claimed sovere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dublin Castle
Dublin Castle () is a major Government of Ireland, Irish government complex, conference centre, and tourist attraction. It is located off Dame Street in central Dublin. It is a former motte-and-bailey castle and was chosen for its position at the highest point of central Dublin. Until 1922 it was the seat of the Dublin Castle administration, British government's administration in Ireland. Many of the current buildings date from the 18th century, though a castle has stood on the site since the days of King John, King of England, John, the first Lordship of Ireland, Lord of Ireland. The Castle served as the seat of English, then later British, government of Ireland under the Lordship of Ireland (1171–1541), the Kingdom of Ireland (1541–1800), and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland (1801–1922). After the signing of the Anglo-Irish Treaty in December 1921, the complex was ceremonially handed over to the newly formed Provisional Government of Ireland (1922), Prov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George III
George III (George William Frederick; 4 June 173829 January 1820) was King of Great Britain and King of Ireland, Ireland from 25 October 1760 until his death in 1820. The Acts of Union 1800 unified Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland into the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, with George as its king. He was concurrently Duke and Prince-elector of Electorate of Hanover, Hanover in the Holy Roman Empire before becoming King of Hanover on 12 October 1814. He was the first monarch of the House of Hanover who was born in Great Britain, spoke English as his first language, and never visited Hanover. George was born during the reign of his paternal grandfather, George II of Great Britain, King George II, as the first son of Frederick, Prince of Wales, and Princess Augusta of Saxe-Gotha. Following his father's death in 1751, Prince George became heir apparent and Prince of Wales. He succeeded to the throne on George II's death in 1760. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peerage Of Great Britain
The Peerage of Great Britain comprises all extant peerages created in the Kingdom of Great Britain between the Acts of Union 1707 and the Acts of Union 1800. It replaced the Peerage of England and the Peerage of Scotland, but was itself replaced by the Peerage of the United Kingdom in 1801. The ranks of the Peerage of Great Britain are Duke, Marquess, Earl, Viscount and Baron. Until the passage of the House of Lords Act 1999, all peers of Great Britain could sit in the House of Lords. Some peerages of Great Britain were created for peers in the Peerage of Scotland and Peerage of Ireland as they did not have an automatic seat in the House of Lords until the Peerage Act 1963 which gave Scottish Peers an automatic right to sit in the Lords. In the following table of peers of Great Britain, holders of higher or equal titles in the other peerages are listed. Those peers who are known by a higher title in one of the other peerages are listed in ''italics''. Ranks The ranks of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |