|
Renal Agenesis
Renal agenesis is a medical condition in which one (unilateral) or both (bilateral) fetal kidneys fail to develop. Unilateral and bilateral renal agenesis in humans, mice and zebra fish has been linked to mutations in the gene GREB1L. It has also been associated with mutations in the genes ''RET proto-oncogene, RET'' or ''UPK3A'' in humans and mice respectively. Type Bilateral Bilateral renal agenesis (BRA) is a condition in which both kidneys of a fetus fail to develop during gestation. It is incompatible with life. It is one causative agent of Potter sequence. This absence of kidneys causes oligohydramnios, a deficiency of amniotic fluid in a pregnancy, which can place extra pressure on the developing baby and cause further malformations. The condition is frequently, but not always the result of a genetic disorder, and is more common in infants born to one or more parents with a malformed or absent kidney. Unilateral This is much more common, but is not usually of any major h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kidney
In humans, the kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped blood-filtering organ (anatomy), organs that are a multilobar, multipapillary form of mammalian kidneys, usually without signs of external lobulation. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal artery, renal arteries; blood exits into the paired renal veins. Each kidney is attached to a ureter, a tube that carries excreted urine to the urinary bladder, bladder. The kidney participates in the control of the volume of various body fluids, fluid osmolality, Acid-base homeostasis, acid-base balance, various electrolyte concentrations, and removal of toxins. Filtration occurs in the glomerulus (kidney), glomerulus: one-fifth of the blood volume that enters the kidneys is filtered. Examples of substances reabsorbed are solute-free water, sodium, bicarbonate, glucose, and amino acids. Examples of substances secreted are hy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
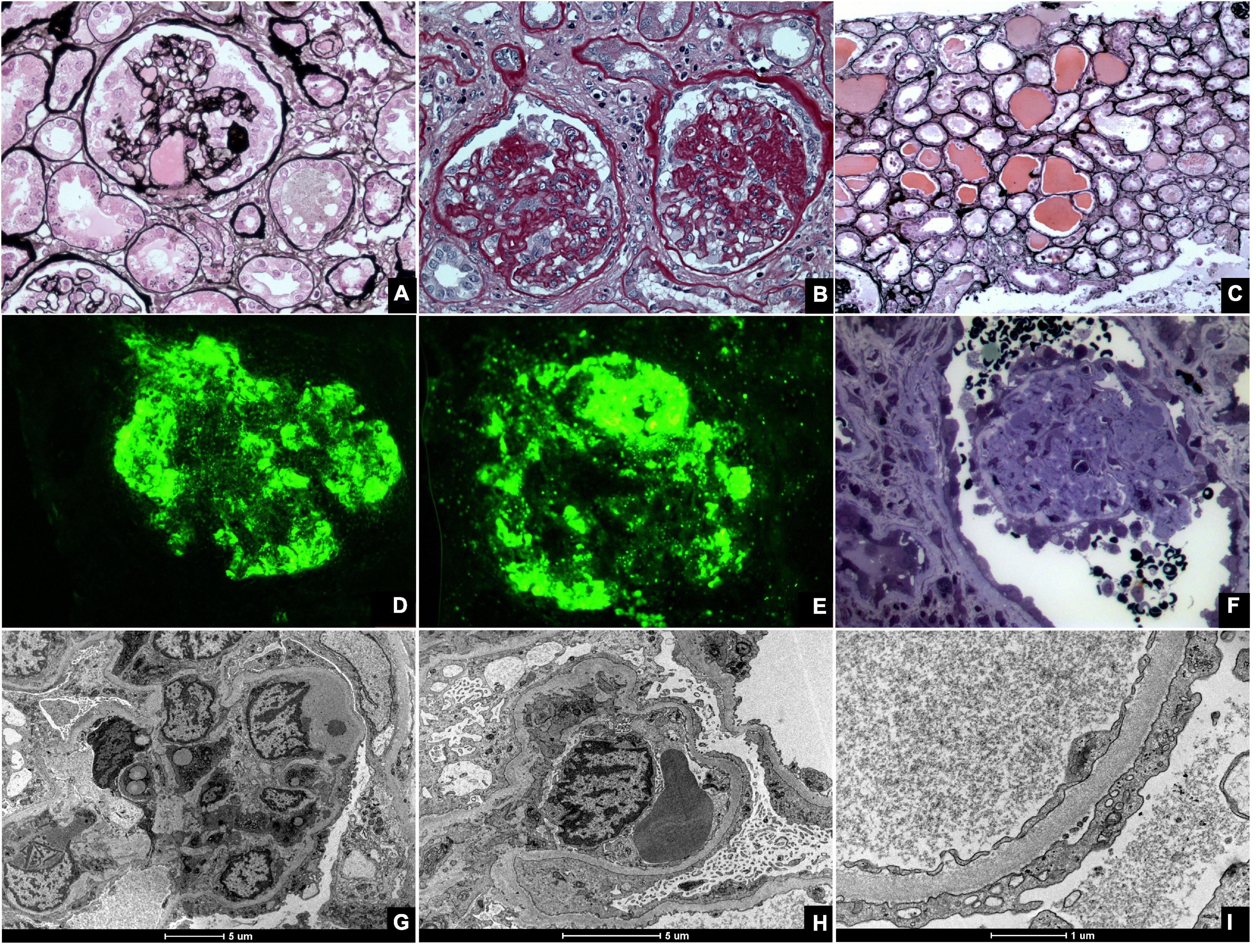
Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis
Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) is a histopathologic finding of scarring (sclerosis) of glomeruli and damage to renal podocytes. This process damages the filtration function of the kidney, resulting in protein presence in the urine due to protein loss. FSGS is a leading cause of excess protein loss—nephrotic syndrome—in children and adults in the US. Signs and symptoms include proteinuria and edema. Kidney failure is a common long-term complication of the disease. FSGS can be classified as primary, secondary, or genetic, depending on whether a particular toxic or pathologic stressor or genetic predisposition can be identified as the cause. Diagnosis is established by renal biopsy, and treatment consists of glucocorticoids and other immune-modulatory drugs. Response to therapy is variable, with a significant portion of patients progressing to end-stage kidney failure. An American epidemiological study 20 years ago demonstrated that FSGS is estimated to occur in 7 pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Branchio-oto-renal Syndrome
Branchio-oto-renal syndrome (BOR) is an autosomal dominant genetic disorder involving the kidneys, ears, and neck. It is also known as Melnick-Fraser syndrome. Signs and symptoms The signs and symptoms of branchio-oto-renal syndrome are consistent with underdeveloped (hypoplastic) or absent kidneys with resultant chronic kidney disease or kidney failure. Ear anomalies include extra openings in front of the ears, extra pieces of skin in front of the ears (preauricular tags), or further malformation or absence of the outer ear ( pinna). Malformation or absence of the middle ear is also possible, individuals can have mild to profound hearing loss. People with BOR may also have cysts or fistulae along the sides of their neck. In some individuals and families, renal features are completely absent. The disease may then be termed "branchio-oto syndrome" (BO syndrome)., updated, 2015, Cause The cause of branchio-oto-renal syndrome are mutations in genes, EYA1, SIX1, and SIX5 (approxi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kallmann Syndrome
Kallmann syndrome (KS) is a hereditary, genetic disorder that prevents a person from starting or fully completing puberty. Kallmann syndrome is a form of a group of conditions termed hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. To distinguish it from other forms of hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, Kallmann syndrome has the additional symptom of a anosmia, total lack of sense of smell (anosmia) or a hyposmia, reduced sense of smell. If left untreated, people will have poorly defined secondary sexual characteristics, show signs of hypogonadism, almost invariably are infertile and are at increased risk of developing osteoporosis. A range of other physical symptoms affecting the face, hands and skeletal system can also occur. Cause & Diagnosis The underlying cause is due to the defective migration of gonadotropin-releasing hormone expressing neurons (GnRH neuron, GNRH neurons) from olfactory placode to hypothalamus, leading to congenital Gonadotropin-releasing hormone, GNRH deficiency. This leads ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consanguineous
Consanguinity (from Latin '' consanguinitas'' 'blood relationship') is the characteristic of having a kinship with a relative who is descended from a common ancestor. Many jurisdictions have laws prohibiting people who are closely related by blood from marrying or having sexual relations with each other. The degree of consanguinity that gives rise to this prohibition varies from place to place. On the other hand, around 20% of the global population lives in areas where some consanguinous marriages are preferred. The degree of relationships are also used to determine heirs of an estate according to statutes that govern intestate succession, which also vary from jurisdiction to jurisdiction. In some communities and time periods, cousin marriage is allowed or even encouraged; in others, it is taboo, and considered to be incest. The degree of relative consanguinity can be illustrated with a ''consanguinity table'' in which each level of lineal consanguinity (''generation'' or ''mei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exome Sequencing
Exome sequencing, also known as whole exome sequencing (WES), is a genomic technique for sequencing all of the protein-coding regions of genes in a genome (known as the exome). It consists of two steps: the first step is to select only the subset of DNA that encodes proteins. These regions are known as exons—humans have about 180,000 exons, constituting about 1% of the human genome, or approximately 30 million base pairs. The second step is to sequence the exonic DNA using any high-throughput DNA sequencing technology. The goal of this approach is to identify genetic variants that alter protein sequences, and to do this at a much lower cost than whole-genome sequencing. Since these variants can be responsible for both Mendelian and common polygenic diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease, whole exome sequencing has been applied both in academic research and as a clinical diagnostic. Motivation and comparison to other approaches Exome sequencing is especially effective in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ITGA8
Integrin alpha-8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ITGA8'' gene In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei .... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * External linksITGA8Info with links in thCell Migration Gateway Integrins {{gene-10-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autosomal Recessive
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the Phenotype, effect of a different variant of the same gene on Homologous chromosome, the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and the second is called recessive. This state of having Heterozygosity, two different variants of the same gene on each chromosome is originally caused by a mutation in one of the genes, either new (''de novo'') or Heredity, inherited. The terms autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive are used to describe gene variants on non-sex chromosomes (autosomes) and their associated traits, while those on sex chromosomes (allosomes) are termed X-linked dominant, X-linked recessive or Y-linked; these have an inheritance and presentation pattern that depends on the sex of both the parent and the child (see Sex linkage). Since there is only one Y chromosome, Y-linked traits cannot be dominant or recessive. Additionally, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GFRA1
GDNF family receptor alpha-1 (GFRα1), also known as the GDNF receptor, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''GFRA1'' gene. Function Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) and neurturin (NTN) are two structurally related, potent neurotrophic factors that play key roles in the control of neuron survival and differentiation. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the GDNF receptor family. It is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol(GPI)-linked cell surface receptor for both GDNF and NTN, and mediates activation of the RET tyrosine kinase receptor. This gene is a candidate gene for Hirschsprung disease. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms A protein isoform, or "protein variant", is a member of a set of highly similar proteins that originate from a single gene and are the result of genetic differences. While many perform the same or similar biological roles, some isoforms have uniqu ... have been described for this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymerase Chain Reaction
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used to make millions to billions of copies of a specific DNA sample rapidly, allowing scientists to amplify a very small sample of DNA (or a part of it) sufficiently to enable detailed study. PCR was invented in 1983 by American biochemist Kary Mullis at Cetus Corporation. Mullis and biochemist Michael Smith (chemist), Michael Smith, who had developed other essential ways of manipulating DNA, were jointly awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1993. PCR is fundamental to many of the procedures used in genetic testing and research, including analysis of Ancient DNA, ancient samples of DNA and identification of infectious agents. Using PCR, copies of very small amounts of DNA sequences are exponentially amplified in a series of cycles of temperature changes. PCR is now a common and often indispensable technique used in medical laboratory research for a broad variety of applications including biomedical research and forensic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GDNF
Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ''GDNF'' gene. GDNF is a small protein that potently promotes the survival of many types of neurons. It signals through GFRα receptors, particularly GFRα1. It is also responsible for the determination of spermatogonia into primary spermatocytes, i.e. it is received by RET proto-oncogene (RET) and by forming gradient with SCF it divides the spermatogonia into two cells. As the result there is retention of spermatogonia and formation of spermatocyte. History GDNF was discovered in 1991 and was the first identified member of the GDNF family of ligands (GFL). Structure GDNF has a structure that is similar to TGF beta 2. GDNF has two finger-like structures that interact with the GFRα1 receptor. N-linked glycosylation, which occurs during the secretion of pro-GDNF, takes place at the tip of one of the finger-like structures. The C-terminal of mature GDNF plays an important ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |