|
Remnant Cholesterol
Remnant cholesterol, also known as remnant lipoprotein and triglyceride-rich lipoprotein cholesterol is an atherogenic lipoprotein composed primarily of very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) and intermediate-density lipoprotein (IDL) with chylomicron remnants. Elevated remnant cholesterol is associated with increased risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and stroke. Definition Remnant cholesterol is the cholesterol content of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins, which consist of very low-density lipoproteins and intermediate-density lipoproteins with chylomicron remnants. Remnant cholesterol is primarily chylomicron and VLDL, and each remnant particle contains about 40 times more cholesterol than LDL. Remnant cholesterol corresponds to all cholesterol not found in high-density lipoprotein (HDL-C) and low-density lipoprotein (LDL-C). It is calculated as total cholesterol minus HDL-C and LDL-C. Health effects Elevated remnant cholesterol is associated with an increased risk of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypertriglyceridemia
Hypertriglyceridemia is the presence of high amounts of triglycerides in the blood. Triglycerides are the most abundant fatty molecule in most organisms. Hypertriglyceridemia occurs in various physiologic conditions and in various diseases, and high triglyceride levels are associated with atherosclerosis, even in the absence of hypercholesterolemia (high cholesterol levels) and predispose to cardiovascular disease. Chronically elevated serum triglyceride levels are a component of metabolic syndrome and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease, both of which typically involve obesity and contribute significantly to cardiovascular mortality in industrialised countries as of 2021. Extreme triglyceride levels also increase the risk of acute pancreatitis. Hypertriglyceridemia itself is usually symptomless, although high levels may be associated with skin lesions known as '' xanthomas''. Signs and symptoms Most people with elevated triglycerides experience no sympt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiology
Cardiology () is the study of the heart. Cardiology is a branch of medicine that deals with disorders of the heart and the cardiovascular system. The field includes medical diagnosis and treatment of congenital heart defects, coronary artery disease, heart failure, valvular heart disease, and electrophysiology. Physicians who specialize in this field of medicine are called cardiologists, a sub-specialty of internal medicine. Pediatric cardiologists are pediatricians who specialize in cardiology. Physicians who specialize in cardiac surgery are called cardiothoracic surgeons or cardiac surgeons, a specialty of general surgery. Specializations All cardiologists in the branch of medicine study the disorders of the heart, but the study of adult and child heart disorders each require different training pathways. Therefore, an adult cardiologist (often simply called "cardiologist") is inadequately trained to take care of children, and pediatric cardiologists are not trained to treat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipid Profile
A lipid profile or lipid panel is a Test panel, panel of blood tests used to find abnormalities in blood lipid ( such as cholesterol and triglycerides) concentrations. The results of this test can identify certain Inborn error of lipid metabolism, genetic diseases and can determine approximate risks for cardiovascular disease, certain forms of pancreatitis, and other diseases. Lipid panels are usually ordered as part of a physical exam, along with other panels such as the complete blood count (CBC) and basic metabolic panel (BMP). Components A lipid profile report typically includes: * Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) * High-density lipoprotein (HDL) * Total triglycerides * Total cholesterol LDL is not usually actually measured, but calculated from the other three using the ''Friedewald equation''. A laboratory can optionally calculate the two extra values from the report: * Very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) * Cholesterol:HDL ratio Procedure and indication Recommendations f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
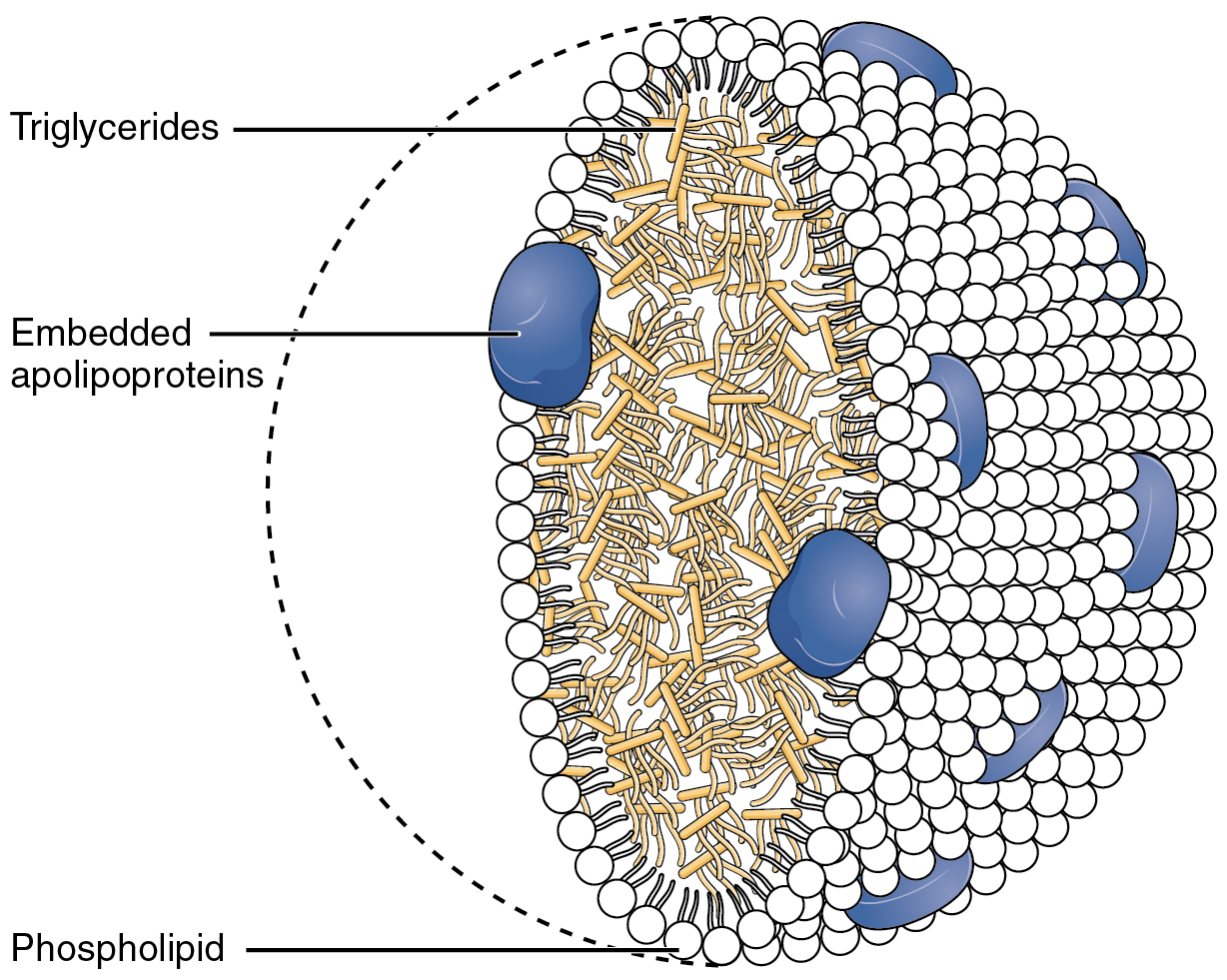
Chylomicron
Chylomicrons (from the Greek χυλός, chylos, meaning ''juice'' (of plants or animals), and micron, meaning ''small''), also known as ultra low-density lipoproteins (ULDL), are lipoprotein particles that consist of triglycerides (85–92%), phospholipids (6–12%), cholesterol (1–3%), and proteins (1–2%). They transport dietary lipids, such as fats and cholesterol, from the intestines to other locations in the body, within the water-based solution of the bloodstream. ULDLs are one of the five major groups lipoproteins are divided into based on their density. A protein specific to chylomicrons is ApoB48. There is an inverse relationship in the density and size of lipoprotein particles: fats have a lower density than water or smaller protein molecules, and the larger particles have a higher ratio of internal fat molecules with respect to the outer emulsifying protein molecules in the shell. ULDLs, if in the region of 1,000 nm or more, are the only lipoprotein particl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ANGPTL3
Angiopoietin-like 3, also known as ANGPTL3, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ANGPTL3'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the angiopoietin-like family of secreted factors. It is expressed predominantly in the liver, and has the characteristic structure of angiopoietins, consisting of a signal peptide, N-terminal coiled-coil domain, and the C-terminal fibrinogen (FBN)-like domain. The FBN-like domain in angiopoietin-like 3 protein was shown to bind alpha-5/beta-3 integrins, and this binding induced endothelial cell adhesion and migration. This protein may also play a role in the regulation of angiogenesis. Angptl3 also acts as dual inhibitor of lipoprotein lipase (LPL) and endothelial lipase (EL), thereby increasing plasma triglyceride, LDL cholesterol and HDL cholesterol in mice and humans. ANGPTL3 inhibits endothelial lipase hydrolysis Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clinical Chemistry (journal)
''Clinical Chemistry'' is a peer-reviewed medical journal covering the field of clinical chemistry. It is the official journal of the American Association for Clinical Chemistry. The journal was first published in 1955 on a bi-monthly basis "to raise the level at which chemistry is practiced in the clinical laboratory"; monthly publication commenced in 1964.Rej, R. Clin Chem 50:2415-58 (2004) The editor-in-chief is Nader Rifai ( Harvard Medical School). Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in PubMed/ MEDLINE and the Science Citation Index. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. The Impact Factor of a journa ... of 8.327. References External links * {{Official website, http://intl. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Body Mass Index
Body mass index (BMI) is a value derived from the mass (Mass versus weight, weight) and height of a person. The BMI is defined as the human body weight, body mass divided by the square (algebra), square of the human height, body height, and is expressed in Units of measurement, units of kg/m2, resulting from mass in kilograms (kg) and height in metres (m). The BMI may be determined first by measuring its components by means of a weighing scale and a stadiometer. The multiplication and division may be carried out directly, by hand or using a calculator, or indirectly using a lookup table (or chart). The table displays BMI as a function of mass and height and may show other units of measurement (converted to Metric system, metric units for the calculation). The table may also show contour lines or colours for different BMI categories. The BMI is a convenient rule of thumb used to broadly categorize a person as based on tissue mass (muscle, fat, and bone) and height. Major adult B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of The American College Of Cardiology
The ''Journal of the American College of Cardiology'' is a peer-reviewed medical journal covering all aspects of cardiovascular disease, including original clinical studies, translational investigations with clear clinical relevance, state-of-the-art papers, review articles, and editorials interpreting and commenting on the research presented, published by the American College of Cardiology. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in Current Contents, EMBASE, MEDLINE, Science Citation Index, and Scopus. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor of 24.094, ranking it 4th out of 141 journals in the category "Cardiac & Cardiovascular Systems". Associated journals * ''JACC: Basic to Translational Science'' (Impact Factor: 8.4) * ''JACC: CardioOncology'' (Impact Factor: 12) * '' JACC: Cardiovascular Imaging'' (Impact Factor: 12.8) * '' JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions'' (Impact Factor: 11.7) * ''JACC: Clinical Ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
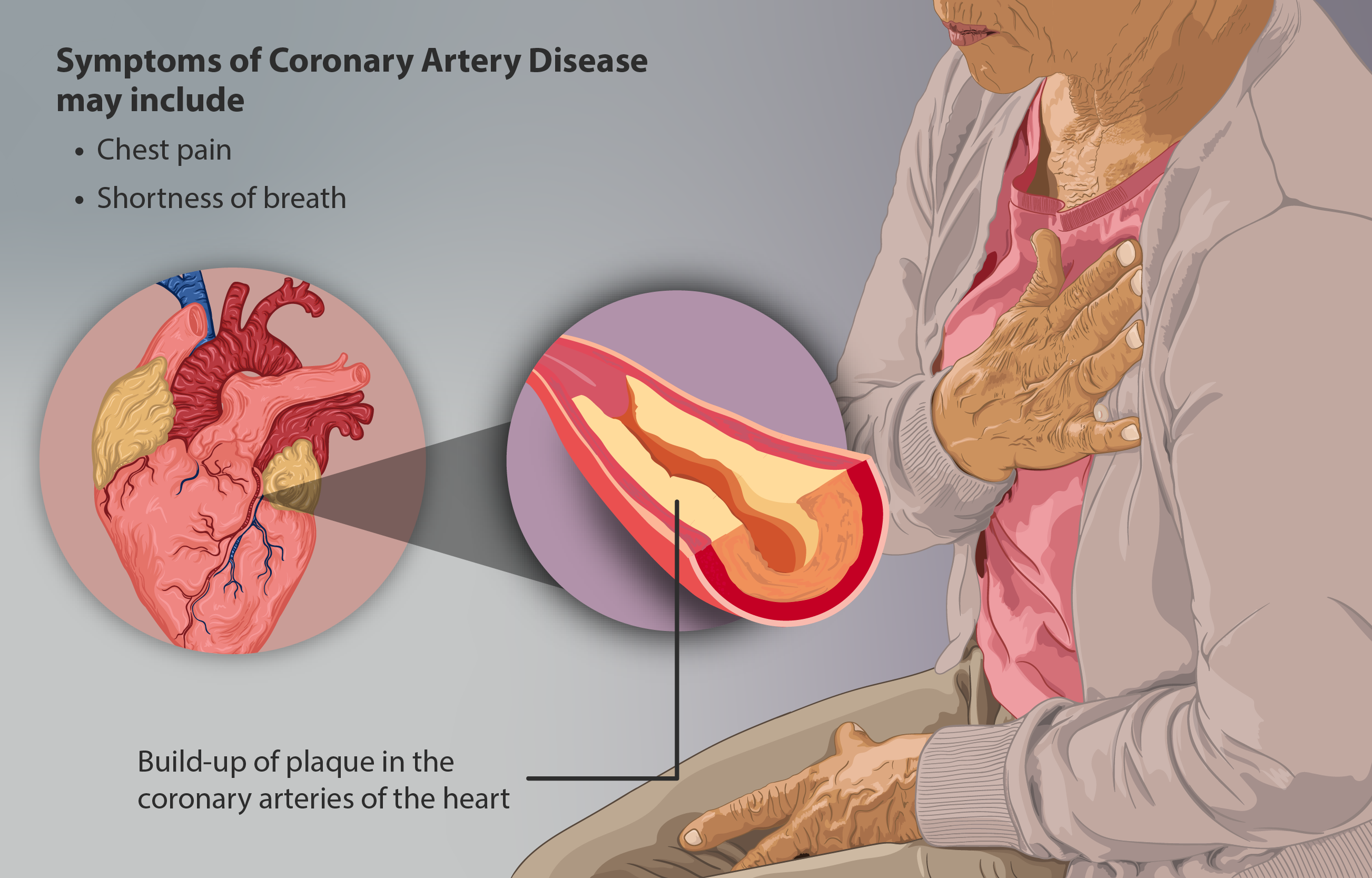
Coronary Artery Disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), or ischemic heart disease (IHD), is a type of cardiovascular disease, heart disease involving Ischemia, the reduction of blood flow to the cardiac muscle due to a build-up of atheromatous plaque in the Coronary arteries, arteries of the heart. It is the most common of the cardiovascular diseases. CAD can cause stable angina, unstable angina, myocardial ischemia, and myocardial infarction. A common symptom is angina, which is chest pain or discomfort that may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck, or jaw. Occasionally it may feel like heartburn. In stable angina, symptoms occur with exercise or emotional Psychological stress, stress, last less than a few minutes, and improve with rest. Shortness of breath may also occur and sometimes no symptoms are present. In many cases, the first sign is a Myocardial infarction, heart attack. Other complications include heart failure or an Heart arrhythmia, abnormal h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Current Atherosclerosis Reports
''Current Atherosclerosis Reports'' is a bimonthly peer-reviewed medical journal publishing review articles pertaining to atherosclerosis. It was established in 1999 and is published by Springer Science+Business Media. The editor-in-chief is Antonio Gotto (Weill Cornell Medical College). According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2014 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. The Impact Factor of a journa ... of 3.417. References External links * Cardiology journals Springer Science+Business Media academic journals Academic journals established in 1999 Bimonthly journals Review journals English-language journals {{Cardiology-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a pattern of the disease arteriosclerosis, characterized by development of abnormalities called lesions in walls of arteries. This is a chronic inflammatory disease involving many different cell types and is driven by elevated blood levels of cholesterol. These lesions may lead to narrowing of the arterial walls due to buildup of atheromatous plaques. At the onset, there are usually no symptoms, but if they develop, symptoms generally begin around middle age. In severe cases, it can result in coronary artery disease, stroke, peripheral artery disease, or kidney disorders, depending on which body part(s) the affected arteries are located in the body. The exact cause of atherosclerosis is unknown and is proposed to be multifactorial. Risk factors include dyslipidemia, abnormal cholesterol levels, elevated levels of inflammatory biomarkers, high blood pressure, diabetes, smoking (both active and passive smoking), obesity, genetic factors, family history, lifes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |