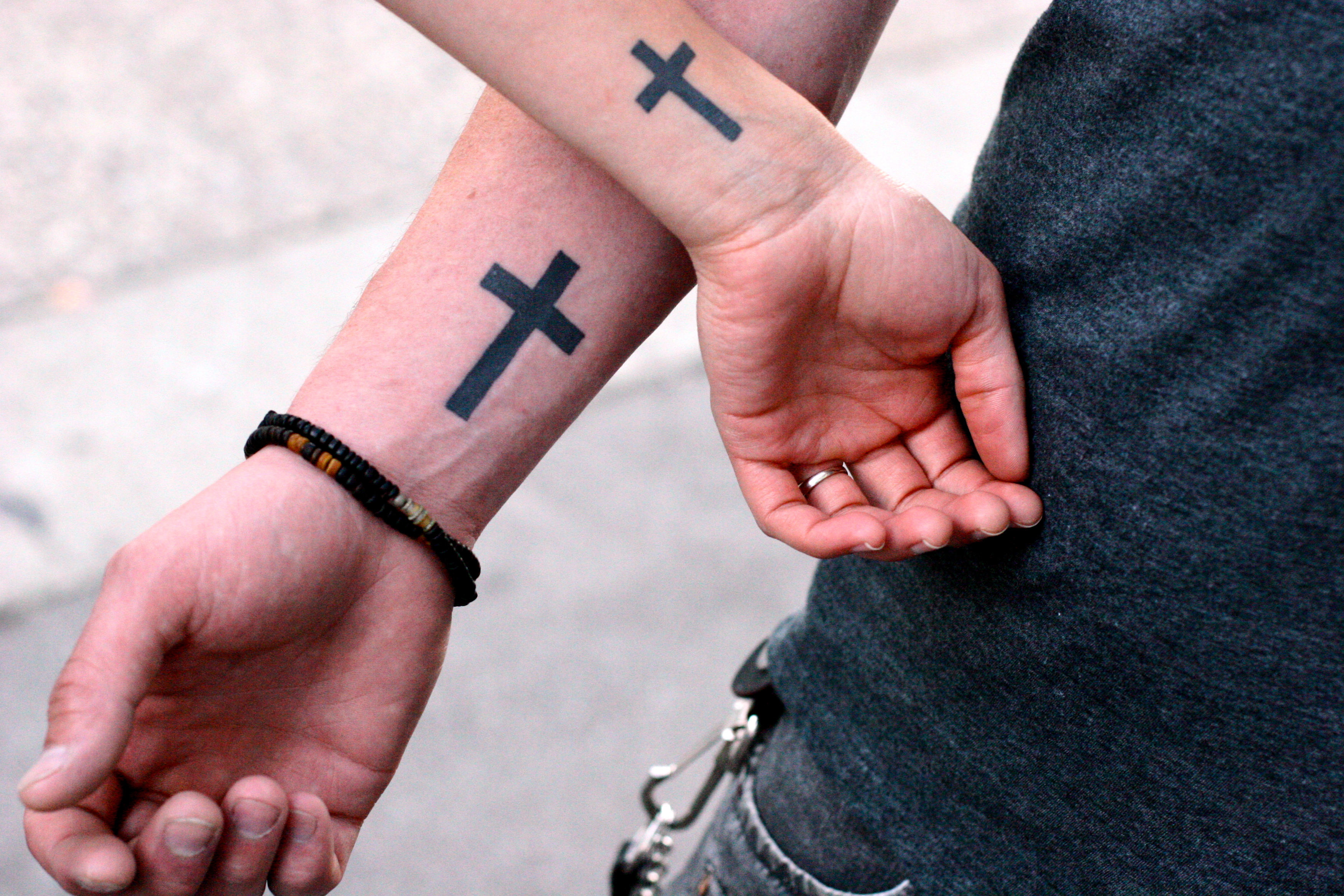|
Religious Perspectives On Tattooing
Tattoos hold rich historical and cultural significance as permanent markings on the body, conveying personal, social, and spiritual meanings. However, religious interpretations of tattooing vary widely, from acceptance and endorsement to strict prohibitions associating it with the desecration of the sacred body. In Christianity, opinions range from discouragement based on the sanctity of the body as a temple, to acceptance. Judaism traditionally prohibits tattooing as self-mutilation but modern interpretations have become more lenient. Islam generally discourages tattoos as altering the natural state of the body, though there are differing opinions among scholars. In Hinduism there is a varying acceptance among sects and communities. Buddhism also has a varied perspective on tattooing, with a tradition of protective tattoos in Southeast Asia incorporating Buddhist symbols, but the display of tattoos not adhering to traditional norms can be a cause of controversy. Buddhism South ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Jesus Is So Cool
Jesus (AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ, Jesus of Nazareth, and many Names and titles of Jesus in the New Testament, other names and titles, was a 1st-century Jewish preacher and religious leader. He is the Jesus in Christianity, central figure of Christianity, the Major religious groups, world's largest religion. Most Christians consider Jesus to be the Incarnation (Christianity), incarnation of God the Son and awaited Messiah#Christianity, messiah, or Christ (title), Christ, a descendant from the Davidic line that is prophesied in the Old Testament. Virtually all modern scholars of classical antiquity, antiquity agree that Historicity of Jesus, Jesus existed historically. Accounts of Life of Jesus, Jesus's life are contained in the Gospels, especially the four canonical Gospels in the New Testament. Since the Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment, Quest for the historical Jesus, academic research has yielded various views on the historical reliability of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Croats Of Bosnia And Herzegovina
The Croats of Bosnia and Herzegovina (), often referred to as Bosnian Croats () or Herzegovinian Croats (), are native to Bosnia and Herzegovina and constitute the third most populous ethnic group, after Bosniaks and Serbs of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Serbs. They are also one of the constitutive nations of Bosnia and Herzegovina. Croats of Bosnia and Herzegovina have made significant contributions to the culture of Bosnia and Herzegovina. Most Croats identify themselves as Catholic Church in Bosnia and Herzegovina, Catholics and speak the Croatian language. Between the 15th and 19th centuries, Christianity in the Ottoman Empire, Catholics in Ottoman Bosnia and Herzegovina were often persecuted by the Ottoman Empire, causing many of them to flee the area. In the 20th century, political turmoil and poor economic conditions led to increased emigration. Ethnic cleansing in the Bosnian War, Ethnic cleansing within Bosnia and Herzegovina in the 1990s saw Croats forced to go to different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
David A
David (; , "beloved one") was a king of ancient Israel and Judah and the third king of the United Monarchy, according to the Hebrew Bible and Old Testament. The Tel Dan stele, an Aramaic-inscribed stone erected by a king of Aram-Damascus in the late 9th/early 8th centuries BCE to commemorate a victory over two enemy kings, contains the phrase (), which is translated as " House of David" by most scholars. The Mesha Stele, erected by King Mesha of Moab in the 9th century BCE, may also refer to the "House of David", although this is disputed. According to Jewish works such as the '' Seder Olam Rabbah'', '' Seder Olam Zutta'', and '' Sefer ha-Qabbalah'' (all written over a thousand years later), David ascended the throne as the king of Judah in 885 BCE. Apart from this, all that is known of David comes from biblical literature, the historicity of which has been extensively challenged,Writing and Rewriting the Story of Solomon in Ancient Israel; by Isaac Kalimi; page 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gordon B
Gordon may refer to: People * Gordon (given name), a masculine given name, including list of persons and fictional characters * Gordon (surname), the surname * Gordon (slave), escaped to a Union Army camp during the U.S. Civil War * Gordon Heuckeroth (born 1968), Dutch performer and radio and television personality, known professionally by the mononym Gordon * Clan Gordon, a Scottish clan Education * Gordon State College, a public college in Barnesville, Georgia * Gordon College (Massachusetts), a Christian college in Wenham, Massachusetts * Gordon College (Pakistan), a Christian college in Rawalpindi, Pakistan * Gordon College (Philippines), a public university in Subic, Zambales * Gordon College of Education, a public college in Haifa, Israel Places Australia * Gordon, Australian Capital Territory * Gordon, New South Wales * Gordon, South Australia * Gordon, Victoria * Gordon River, Tasmania * Gordon River (Western Australia) Canada * Gordon Parish, New Brunswick * Gordon, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
The Church Of Jesus Christ Of Latter-day Saints
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, informally known as the LDS Church or Mormon Church, is a Nontrinitarianism, nontrinitarian Restorationism, restorationist Christianity, Christian Christian denomination, denomination and the largest List of denominations in the Latter Day Saint movement, denomination in the Latter Day Saint movement. Founded during the Second Great Awakening, the church is headquartered in Salt Lake City, Utah, and has established congregations and built Temple (LDS Church), temples worldwide. According to the church, , it has over 17.5 million The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints membership statistics, members, of which Membership statistics of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (United States), over 6.8 million live in the U.S. The church also reports over 109,000 Missionary (LDS Church), volunteer missionaries and 202 dedicated List of temples of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, temples. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Apostatize
Apostasy (; ) is the formal disaffiliation from, abandonment of, or renunciation of a religion by a person. It can also be defined within the broader context of embracing an opinion that is contrary to one's previous religious beliefs. One who undertakes apostasy is known as an apostate. Undertaking apostasy is called apostatizing (or apostasizing – also spelled apostacizing). The term ''apostasy'' is used by sociologists to mean the renunciation ''and'' criticism of, or opposition to, a person's former religion, in a technical sense, with no pejorative connotation. Occasionally, the term is also used metaphorically to refer to the renunciation of a non-religious belief or cause, such as a political party, social movement, or sports team. Apostasy is generally not a self-definition: few former believers call themselves apostates due to the term's negative connotation. Many religious groups and some states punish apostates; this may be the official policy of a particular reli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Christianity In Ethiopia
Christianity in Ethiopia is the country's largest religion with members making up 68% of the population. Christianity in Ethiopia dates back to the ancient Kingdom of Aksum, when the Ezana of Aksum, King Ezana first adopted the faith in the 4th century AD. This makes Ethiopia one of the first regions in the world to officially adopt Christianity. Various Christian denominations are now followed in the country. Of these, the largest and oldest is the Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church, an Oriental Orthodox church centered in Ethiopia. The Orthodox Tewahedo Church was part of the Coptic Orthodox Church until 1959 when it was granted its own patriarch by the Coptic Orthodox Pope of Alexandria and Patriarch of All Africa Pope Cyril VI of Alexandria, Cyril VI. The Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church is one of the largest and oldest Christian churches in Africa; only surpassed in age by the Church of the East, the Armenian Apostolic Church, the Syriac Orthodox Church, the Greek Or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pope Alexander II Of Alexandria
Pope Alexander II of Alexandria ( Coptic: ⲁⲗⲉⲝⲁⲛⲇⲣⲟⲥ; died 14 February 729) was the 43rd Pope of Alexandria and Patriarch of the See of St. Mark. He presided over his church during an era of great hardship and oppression. Consecration There is little information available on Alexander's early life as a layman prior to becoming a monk at the monastery of the Enaton west of Alexandria. However, at the Enaton he became well known for his chastity, sanctity, and religious scholarship. Upon the death of Simeon of Alexandria in 701, the Patriarchate of Alexdandria remained vacant for approximately four years, while the members of the church sought an appropriate successor. The lack of a patriarch, though, created economic problems for the church, so the secretary of state, or ''mutawallī al-diwān'' in Alexandria, a Copt named Athanasius, asked the governor to allow the bishop of al-Qays, Anbā Gregorius, to assume authority over the church's finances until ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Coptic Christianity
Copts (; ) are a Christian ethnoreligious group native to Northeast Africa who have primarily inhabited the area of modern Egypt since antiquity. They are, like the broader Egyptian population, descended from the ancient Egyptians. Copts predominantly follow the Coptic Orthodox Church in Alexandria. They are the largest Christian denomination in Egypt and the Middle East, as well as in Sudan and Libya.Coptic Orthodox Church Listings for Libya, p. 136 account for roughly 5 to 15 percent of the population of Egypt. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Università Degli Studi Del Molise
The University of Molise (), also known as UNIMOL, is an Italian public university located in Campobasso, Italy. It was founded in 1982 by the Law n.590 according to the plan for the development and institution of new universities; the campuses of this university are all set in the region of Molise and they are: in Campobasso (Headquarter), Pesche and Termoli. History In the years 1982-1983 the University opened, but the only faculty was Agricultural Science, then with the opening of the faculties of Economics and especially of Law, the number of students grew. In 1993 new structures were opened in Isernia, including the faculty of Natural Sciences. Later on, Campobasso opened the Colozza Center, which has improved the quality and organization of the courses becoming nowadays a school for master's degrees in Secondary Education. Since 2000 the University increased the number of students and courses, establishing in 2006 the faculty of Medicine and Surgery, the youngest faculty of UN ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Centre Of Albanological Studies
The Academy of Albanological Studies (AAS; ; stylised asa) is the main institution of albanology in Albania. History The Academy of Albanological Studies started as part of the reconstruction and modernization of the Albanian academical and university system. The decision was taken by the Albanian Government in August 2007. It derived from joining the four existing institutions: Institute of Archaeology, Institute of Linguistics and Literature, Institute of History, and Institute of Cultural Anthropology and Art Studies, with two research units: Art Studies and Albanian Encyclopedia which used to belong Albanian Academy of Sciences. The centre was reorganised on 10 March 2008 as a scientific research institute and received the status of the inter-university organ. It inherited the staff of specialist and a rich archive of a high importance. Along with the research in the fields of history, archaeology, cultural anthropology, art study, linguistics, literature, etc., part of it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kultura Popullore
''Kultura Popullore'' (Folkloric Culture) is a quarterly magazine published in Tirana, Albania by the Centre of Albanological Studies. It publishes scientific articles on different fields of Albanian ethnography and folklore. The magazine started in 1980, as one of scientific magazines of the Albanian Academy of Sciences, specifically the Institute of Folkloric Culture, established in 1979 by merging the former Institute of Folklore with the Ethnography Section of the Institute of History, both branches of the Academy of Science.With the creation of the Centre of Albanological Studies The Academy of Albanological Studies (AAS; ; stylised asa) is the main institution of albanology in Albania. History The Academy of Albanological Studies started as part of the reconstruction and modernization of the Albanian academical and uni ... in 1980, the Institute of Folkloric Culture merged into it and disaffiliated with the Academy, carrying over all its periodicals. See also *'' Studi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |