|
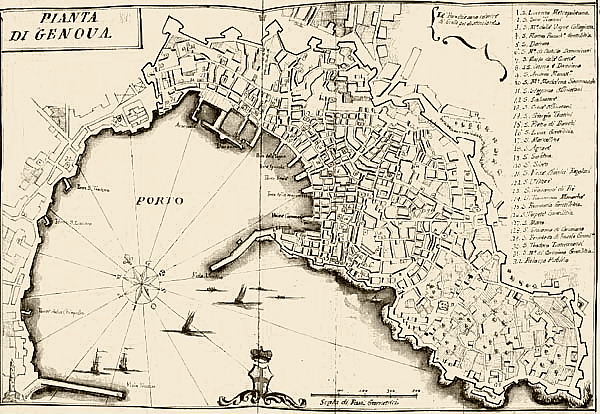
Relief Of Genoa
The Relief of Genoa took place between 28 March 1625 and 24 April 1625, during the Thirty Years' War. It was a major naval expedition launched by Spain against the French-occupied Republic of Genoa, whose capital, Genoa, was being besieged by a joint Franco-Savoyard army composed of 30,000 men and 3,000 cavalry. In 1625, when the Republic of Genoa, traditionally an ally of Spain, was occupied by French troops of the Victor Amadeus I, Duke of Savoy, Duke of Savoy, the city underwent a hard siege. It was known in Genoese governmental circles that one of the reasons why the Dutch government had offered their help to the Franco-Savoyard army was so that they could "hit the bank of the King of Spain". However, the Spanish fleet commanded by General Álvaro de Bazán, 2nd Marquis of Santa Cruz, Álvaro de Bazán, Marquis of Santa Cruz, came to the aid of Genoa and relieved the city. Returning its sovereignty to the Republic of Genoa and forcing the French to raise the siege, they con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War, fought primarily in Central Europe between 1618 and 1648, was one of the most destructive conflicts in History of Europe, European history. An estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died from battle, famine, or disease, while parts of Germany reported population declines of over 50%. Related conflicts include the Eighty Years' War, the War of the Mantuan Succession, the Franco-Spanish War (1635–1659), Franco-Spanish War, the Torstenson War, the Dutch-Portuguese War, and the Portuguese Restoration War. The war had its origins in the 16th-century Reformation, which led to religious conflict within the Holy Roman Empire. The 1555 Peace of Augsburg attempted to resolve this by dividing the Empire into Catholic and Lutheran states, but the settlement was destabilised by the subsequent expansion of Protestantism beyond these boundaries. Combined with differences over the limits of imperial authority, religion was thus an important factor in star ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francesco Barberini (1597–1679)
Francesco Barberini (23 September 1597 – 10 December 1679) was an Italian Catholic Cardinal. The nephew of Pope Urban VIII (reigned 1623–1644), he benefited immensely from the nepotism practiced by his uncle. He was given various roles within the Vatican administration but his personal cultural interests, particularly in literature and the arts, meant that he became a highly significant patron. His secretary was the antiquarian Cassiano dal Pozzo who was also a discerning patron of the arts. Francesco was the elder brother of Cardinal Antonio Barberini and Taddeo Barberini who became Prince of Palestrina. Life He was born in Florence to Carlo Barberini and Costanza Magalotti. Barberinis mother was known for extreme piety. In 1600 his uncle Cardinal Maffeo Barberini invited his brother and his family to join him in Rome. During Barberinis childhood his and his two brothers education was closely supervised by their father and uncle. Barberinis two sisters Camilla and Clar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mansfeld
Mansfeld (), sometimes also unofficially Mansfeld-Lutherstadt, is a town in the district of Mansfeld-Südharz, in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. Protestant reformator Martin Luther grew up in Mansfeld, and in 1993 the town became one of sixteen places in Germany to be designated a '' Lutherstadt'' for this reason. Geography It is situated east of the Harz mountain range on the river Wipper, a left tributary of the Saale, about northwest of Halle. Together with neighbouring Eisleben, it is part of the historic Mansfeld Land region, roughly corresponding to the former district of Mansfelder Land which in 2007 merged into present Mansfeld-Südharz district. Mansfeld station is a stop on the Mansfeldbahn railway line (''Wipperliese''), a branch of the Berlin-Blankenheim railway, running from Klostermansfeld to Wippra. Town districts The township currently comprises 15 districts (''Ortschaften''): [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doge Of Genoa
The Doge of Genoa ( ) was the head of state of the Republic of Genoa, a city-state and soon afterwards a Maritime republics, maritime republic, from 1339 until the state's extinction in 1797. Originally elected for life, after 1528 the Doge (title), doges were elected for terms of two years. The Republic (or Dogate) was ruled by a small group of merchant families, from whom the doges were selected. Form of address The Genoese doge's form of address initially was "''eccelso"'' (exalted), then "''illustrissimo"'' (most illustrious), "''eccellentissimo"'' (most excellent), and finally, "''serenissimo principe"'' (most serene prince), "''signore"'' (lord), or "''altezza serenissima"'' (most serene highness). History The first Doge (title), Doge of Genoa, Simone Boccanegra (Ligurian (Romance language), Ligurian: ''Scimón Boccanéigra''), whose name is kept alive by Giuseppe Verdi, Verdi's Simon Boccanegra, opera, was appointed by public acclaim in 1339. Initially the Doge of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maestre De Campo
''Maestre de campo'' was a rank created in 1534 by the Emperor Charles I of Spain, inferior in rank only to the '' capitán general'' and acted as a chief of staff. He was chosen by the monarch in the Council of State, and commanded a ''tercio''. Their powers were similar to those of the old marshals of the Kingdom of Castile: they had the power to administer justice and to regulate the food supply. Their personal guard consisted of eight German halberdiers, paid by the king, who accompanied them everywhere. Immediately inferior in the chain of command was the '' sargento mayor''. One of the most famous ''maestre de campos'' was Julian Romero, a common soldier who reached that rank and that brought victory to the Spanish ''tercios'' at the battles of San Quintín and Gravelines. In the overseas colonies of the Spanish Empire a governor held the rank of ''capitán general'' over his local forces and would appoint his ''maestre de campo''. Notable Maestres de Campo See also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tommaso Caracciolo, Count Of Roccarainola
Tommaso Caracciolo, Count of Roccarainola (10 March 1572 – 5 December 1631), was among others a Field Marshal who commanded parts of the Spanish forces in the Thirty Years' War. Biography His father, Tristano Caracciolo, was the son of Michele Caracciolo, 2nd Baron of Castelfranco (Cosenza) and ''Signore'' of Lusciano (Terra di lavore) and Ponte Albaneto (Capitanata). Michele had the lordship of these lands from 1530 to his death in 1548, inheriting them from his uncle Berardino Caracciolo, created first baron by privilege signed by the King Fernando I of Aragon at Castelnovo of Naples on 20 June 1598. He seems to have had some military experiences in his youth; he reportedly assisted in the siege of Brichesario (1594). On 25 August 1600 he was made a captain by his relative Camillo Caracciolo (1563–1617), Count of Avellino, who entrusted him a tercio. On 5 September he was made a sergeant major of this tercio. He took part at the Siege of Ostend in Flanders. He is mentio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
François Annibal D'Estrées
François-Annibal d'Estrées, duc d'Estrées (1573 – 5 May 1670) was a French diplomat, soldier and Marshal of France. Biography François-Annibal d'Estrées was born in 1573, to Antoine d'Estrées and Françoise Babou de La Bourdaisière, and the brother of Gabrielle d'Estrées, mistress of Henry IV of France and Julienne-Hypolite-Joséphine, Duchess of Villars, Julienne-Hippolite-Joséphine, Duchess of Villars. His first title was that of a marquis de Cœuvres. He was destined for the church but preferred a military career and joined the army where he became Lieutenant General. In 1624, under Marie de' Medici, he was given supreme command over the troops of France, Venice and Savoy in the conquest of Valtellina. For this, he was given in 1626 the title of a List of Marshals of France, Marshal of France. In 1630, he tried in vain to conquer Mantua. In 1632, he was put in command of the Army of the Rhine and took Trier. After his military career, he became a diplomat. Betw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles I De Blanchefort, Marquis De Créquy
Charles I de Créquy, Prince de Poix and Duc de Lesdiguières (1578–1638), was a leading French soldier of the first half of the 17th century. Life Charles de Créquy, ca. 1575 to 17 March 1638, was the only child of Antoine de Blanchefort (ca. 1545–1575), and Chrétienne d’Aguerre (1556–1611), lady-in-waiting or ''dame d'honneur'' to Louise de Lorraine. The de Créquy family were distributed throughout Northern France, with branches at Fressin, Bernieulles, Auffay and Heilly. They originated from Créquy, in Artois, which formed part of the French-speaking Southern Spanish Netherlands until annexed by France in 1659. Créqui's father Antoine de Blanchefort inherited his titles and lands from his uncle, another Antoine (1531–1574), Roman Catholic Bishop of Amiens and advisor to Charles IX. This background is significant in understanding their importance; Catholic loyalists from a disputed border province, in a period when France was divided by the Wars of Rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultramontanism
Ultramontanism is a clerical political conception within the Catholic Church that places strong emphasis on the prerogatives and powers of the Pope. It contrasts with Gallicanism, the belief that popular civil authority—often represented by the monarch's or state's authority—over the Church is comparable to that of the Pope. History The term descends from the Middle Ages, when a non-Italian pope was said to be ''papa ultramontano –'' a pope from beyond the mountains (the Alps).Benigni, Umberto. "Ultramontanism." The Catholic Encyclopedia Vol. 15. New York: Robert Appleton Company, 1912. 6 January 2019 Foreign students at medieval Italian universities also were referred to as ''ultramontani''. After the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
François De Bonne
François () is a French masculine given name and surname, equivalent to the English name Francis. People with the given name * François Amoudruz (1926–2020), French resistance fighter * François-Marie Arouet (better known as Voltaire; 1694–1778), French Enlightenment writer, historian, and philosopher * François Beauchemin (born 1980), Canadian ice hockey player for the Anaheim Ducks * François Blanc (1806–1877), French entrepreneur and operator of casinos * François Bonlieu (1937–1973), French alpine skier * François Cevert (1944–1973), French racing driver * François Chau (born 1959), Cambodian American actor * François Clemmons (born 1945), American singer and actor * François Corbier (1944–2018), French television presenter and songwriter * François Coty (1874–1934), French perfumer * François Coulomb the Elder (1654–1717), French naval architect * François Coulomb the Younger (1691–1751), French naval architect * François Couperin (1668–1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Savoy
Savoy (; ) is a cultural-historical region in the Western Alps. Situated on the cultural boundary between Occitania and Piedmont, the area extends from Lake Geneva in the north to the Dauphiné in the south and west and to the Aosta Valley in the east. Savoy, formerly a part of the Kingdom of Burgundy, emerged as the feudal County of Savoy ruled by the House of Savoy during the 11th to 14th centuries. The original territory, also known as "ducal Savoy" or "Savoy proper", is largely co-terminous with the modern French Savoie and Haute-Savoie ''départements'' in the region of Rhône-Alpes, but the historical expansion of Savoyard territories, as the Duchy of Savoy (1416–1860), included parts of what is now western Italy and southwestern Switzerland. The current border between France and Italy is due to the Plombières Agreement of 1858, which in preparation for the unification of Italy ceded western Savoy to France, while the eastern territories in Piedmont an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venice
Venice ( ; ; , formerly ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 islands that are separated by expanses of open water and by canals; portions of the city are linked by 438 bridges. The islands are in the shallow Venetian Lagoon, an enclosed bay lying between the mouths of the Po River, Po and the Piave River, Piave rivers (more exactly between the Brenta (river), Brenta and the Sile (river), Sile). As of 2025, 249,466 people resided in greater Venice or the Comune of Venice, of whom about 51,000 live in the historical island city of Venice (''centro storico'') and the rest on the mainland (''terraferma''). Together with the cities of Padua, Italy, Padua and Treviso, Italy, Treviso, Venice is included in the Padua-Treviso-Venice Metropolitan Area (PATREVE), which is considered a statistical metropolitan area, with a total population of 2.6 million. The name is derived from the ancient Adr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |