|
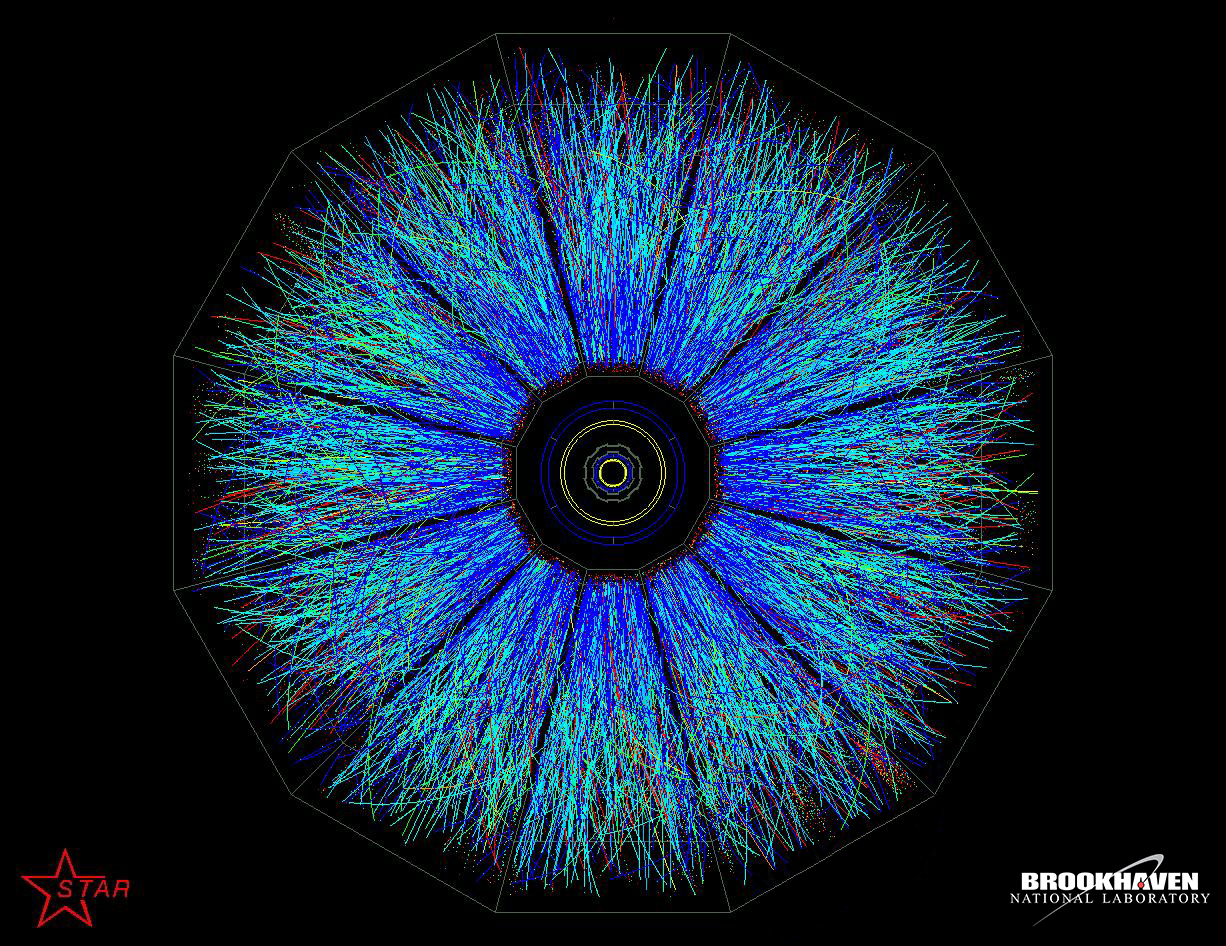
Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider
The Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC ) is the first and one of only two operating heavy- ion colliders, and the only spin-polarized proton collider ever built. Located at Brookhaven National Laboratory (BNL) in Upton, New York, and used by an international team of researchers, it is the only operating particle collider in the US. By using RHIC to collide ions traveling at relativistic speeds, physicists study the primordial form of matter that existed in the universe shortly after the Big Bang. By colliding spin-polarized protons, the spin structure of the proton is explored. RHIC is as of 2019 the second-highest-energy heavy-ion collider in the world, with nucleon energies for collisions reaching 100 GeV for gold ions and 250 GeV for protons. As of November 7, 2010, the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) has collided heavy ions of lead at higher energies than RHIC. The LHC operating time for ions (lead–lead and lead–proton collisions) is limited to about one month per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brookhaven National Laboratory
Brookhaven National Laboratory (BNL) is a United States Department of Energy national laboratories, United States Department of Energy national laboratory located in Upton, New York, a hamlet of the Brookhaven, New York, Town of Brookhaven. It was formally established in 1947 at the site of Camp Upton, a former List of United States Army installations, U.S. Army base on Long Island. Located approximately 60 miles east of New York City, it is managed by Stony Brook University and Battelle Memorial Institute. Research at BNL includes nuclear and high energy physics, energy science and technology, environmental and bioscience, nanoscience, and national security. The 5,300 acre campus contains several large research facilities, including the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider and National Synchrotron Light Source II. Seven Nobel Prizes have been awarded for work conducted at Brookhaven Lab. Overview BNL operations are overseen by a Department of Energy Site office, is staffed by approx ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Storage Ring
A storage ring is a type of circular particle accelerator in which a continuous or pulsed particle beam may be kept circulating, typically for many hours. Storage of a particular particle depends upon the mass, momentum, and usually the charge of the particle to be stored. Storage rings most commonly store electrons, positrons, or protons. Storage rings are most often used to store electrons that radiate synchrotron radiation. Over 50 facilities based on electron storage rings exist and are used for a variety of studies in chemistry and biology. Storage rings can also be used to produce polarized high-energy electron beams through the Sokolov-Ternov effect. The best-known application of storage rings is their use in particle accelerators and in particle colliders, where two counter-rotating beams of stored particles are brought into collision at discrete locations. The resulting subatomic interactions are then studied in a surrounding particle detector. Examples of such faci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aluminum
Aluminium (or aluminum in North American English) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Al and atomic number 13. It has a density lower than that of other common metals, about one-third that of steel. Aluminium has a great affinity towards oxygen, passivation (chemistry), forming a protective layer of aluminium oxide, oxide on the surface when exposed to air. It visually resembles silver, both in its color and in its great ability to reflect light. It is soft, magnetism, nonmagnetic, and ductility, ductile. It has one stable isotope, 27Al, which is highly abundant, making aluminium the abundance of the chemical elements, 12th-most abundant element in the universe. The radioactive decay, radioactivity of aluminium-26, 26Al leads to it being used in radiometric dating. Chemically, aluminium is a post-transition metal in the boron group; as is common for the group, aluminium forms compounds primarily in the +3 oxidation state. The aluminium cation Al3+ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alternating Gradient Synchrotron
The Alternating Gradient Synchrotron (AGS) is a particle accelerator located at the Brookhaven National Laboratory in Long Island, New York, United States. The Alternating Gradient Synchrotron was built on the innovative concept of the alternating gradient, or strong-focusing principle, developed by Brookhaven physicists. This new concept in accelerator design allowed scientists to accelerate protons to energies that were previously unachievable. The AGS became the world's premiere accelerator when it reached its design energy of 33 billion electron volts (GeV) on July 29, 1960. Until 1968, the AGS was the highest energy accelerator in the world, slightly higher than its 28 GeV sister machine, the Proton Synchrotron at CERN, the European laboratory for high-energy physics. While 21st century accelerators can reach energies in the trillion electron volt region, the AGS earned researchers three Nobel Prizes and today serves as the injector for Brookhaven's Relativistic Heavy Ion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinetic Energy
In physics, the kinetic energy of an object is the form of energy that it possesses due to its motion. In classical mechanics, the kinetic energy of a non-rotating object of mass ''m'' traveling at a speed ''v'' is \fracmv^2.Resnick, Robert and Halliday, David (1960) ''Physics'', Section 7-5, Wiley International Edition The kinetic energy of an object is equal to the work, or force ( F) in the direction of motion times its displacement ( s), needed to accelerate the object from rest to its given speed. The same amount of work is done by the object when decelerating from its current speed to a state of rest. The SI unit of energy is the joule, while the English unit of energy is the foot-pound. In relativistic mechanics, \fracmv^2 is a good approximation of kinetic energy only when ''v'' is much less than the speed of light. History and etymology The adjective ''kinetic'' has its roots in the Greek word κίνησις ''kinesis'', meaning "motion". The dichoto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Accelerator
A linear particle accelerator (often shortened to linac) is a type of particle accelerator that accelerates charged subatomic particles or ions to a high speed by subjecting them to a series of oscillating electric potentials along a linear beamline. The principles for such machines were proposed by Gustav Ising in 1924, while the first machine that worked was constructed by Rolf Widerøe in 1928 at the RWTH Aachen University. Linacs have many applications: they generate X-rays and high energy electrons for medicinal purposes in radiation therapy, serve as particle injectors for higher-energy accelerators, and are used directly to achieve the highest kinetic energy for light particles (electrons and positrons) for particle physics. The design of a linac depends on the type of particle that is being accelerated: electrons, protons or ions. Linacs range in size from a cathode-ray tube (which is a type of linac) to the linac at the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Beam Ion Source
An ion source is a device that creates atomic and molecular ions. Ion sources are used to form ions for mass spectrometers, optical emission spectrometers, particle accelerators, ion implanters and ion engines. Electron ionization Electron ionization is widely used in mass spectrometry, particularly for organic molecules. The gas phase reaction producing electron ionization is :M + e^- -> M^ + 2e^- where M is the atom or molecule being ionized, e^- is the electron, and M^ is the resulting ion. The electrons may be created by an arc discharge between a cathode and an anode. An electron beam ion source (EBIS) is used in atomic physics to produce highly charged ions by bombarding atoms with a powerful electron beam. Its principle of operation is shared by the electron beam ion trap. Electron capture ionization Electron capture ionization (ECI) is the ionization of a gas phase atom or molecule by attachment of an electron to create an ion of the form A−•. The reactio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Booster
Booster may refer to: Amusement rides * Booster (Fabbri ride), a pendulum ride * Booster (HUSS ride), an evolution of the Breakdance ride * Booster (KMG ride), a pendulum ride Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional characters * Booster, a character in the animated television series and the pilot episode film '' Buzz Lightyear of Star Command: The Adventure Begins'' and ''Buzz Lightyear of Star Command'' *Booster, the Japanese name for the Pokémon Flareon *Booster, a character in the video game ''Super Mario RPG'' Other uses in arts, entertainment, and media * ''Booster'' (newspaper), a Chicago newspaper *Booster pack, a packaged set of collectable game cards or figurines that supplements the starter packs Science and technology * Booster (electric power), a motor-generator set used for voltage regulation in direct current electrical power circuits * Booster (rocketry), used in space flight to provide or augment the main thrust in the initial phase of the rocket's flight * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dipole Magnet
A dipole magnet is the simplest type of magnet. It has two poles, one north and one south. Its magnetic field lines form simple closed loops which emerge from the north pole, re-enter at the south pole, then pass through the body of the magnet. The simplest example of a dipole magnet is a ''bar magnet''. Bar Magnet" hyperphysics; http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/magnetic/elemag.html/ref> Dipole magnets in accelerators In particle accelerators, a dipole magnet is the electromagnet used to create a homogeneous magnetic field over some distance. Particle motion in that field will be circular in a plane that is perpendicular to the field and collinear to the direction of particle motion, and free in the direction orthogonal to it. Thus, a particle injected into a dipole magnet will travel on a circular or helical trajectory. By adding several dipole sections on the same plane, the bending radial effect of the beam increases. In accelerator physics, dipole magnets are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superconducting Magnet
A superconducting magnet is an electromagnet made from coils of superconducting wire. They must be cooled to cryogenic temperatures during operation. In its superconducting state the wire has no electrical resistance and therefore can conduct much larger electric currents than ordinary wire, creating intense magnetic fields. Superconducting magnets can produce stronger magnetic fields than all but the strongest non-superconducting electromagnets, and large superconducting magnets can be cheaper to operate because no energy is dissipated as heat in the windings. They are used in Magnetic resonance imaging, MRI instruments in hospitals, and in scientific equipment such as Nuclear magnetic resonance, NMR spectrometers, mass spectrometers, Fusion power, fusion reactors and particle accelerators. They are also used for levitation, guidance and propulsion in a SCMaglev, magnetic levitation (maglev) railway system being constructed in Japan. Construction Cooling During operation, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexagon
In geometry, a hexagon (from Greek , , meaning "six", and , , meaning "corner, angle") is a six-sided polygon. The total of the internal angles of any simple (non-self-intersecting) hexagon is 720°. Regular hexagon A regular hexagon is defined as a hexagon that is both equilateral and equiangular. In other words, a hexagon is said to be regular if the edges are all equal in length, and each of its internal angle is equal to 120°. The Schläfli symbol denotes this polygon as \ . However, the regular hexagon can also be considered as the cutting off the vertices of an equilateral triangle, which can also be denoted as \mathrm\ . A regular hexagon is bicentric, meaning that it is both cyclic (has a circumscribed circle) and tangential (has an inscribed circle). The common length of the sides equals the radius of the circumscribed circle or circumcircle, which equals \tfrac times the apothem (radius of the inscribed circle). Measurement The longest diagonals of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |