|
Reinier D'Ozy
Reinier d'Ozy (also Dozy, or d'Ozij) (Steenwijk, 15 April 1773 - at Sea, near Westkapelle, 1 March 1827) was a Dutch colonial administrator who rose to be a member of the High Government of the Dutch East Indies. Life Personal life D'Ozy was the son of Abraham Hendrik d'Ozy, lieutenant of the regiment Hessen-Cassel, and Titia Kiers. He married Maria Philippina Meurs, with whom he had two daughters: Henrietta Maria and Helena Jacoba.Blok and Molhuyzen, pp. 428-429 Career After first having spent some years at the office of his cousin, the Leiden civil-law notary JP Klinkenberg Dozy, d'Ozy accompanied his elder brother Roelof Jacobus in 1791 to China, where he did up the experience that qualified him to be a secretary of the embassy of Isaac Titsingh, Andreas Everardus van Braam Houckgeest, and Chrétien-Louis-Joseph de Guignes to the court of the Qianlong Emperor in 1794–1795. In 1796 he went to the Dutch Cape Colony that was returned to Dutch authority in 1803 after the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
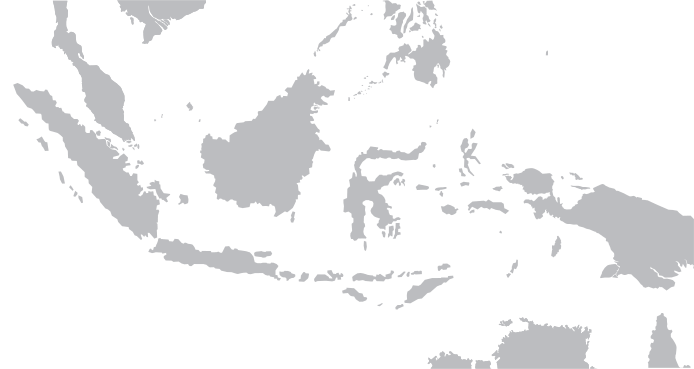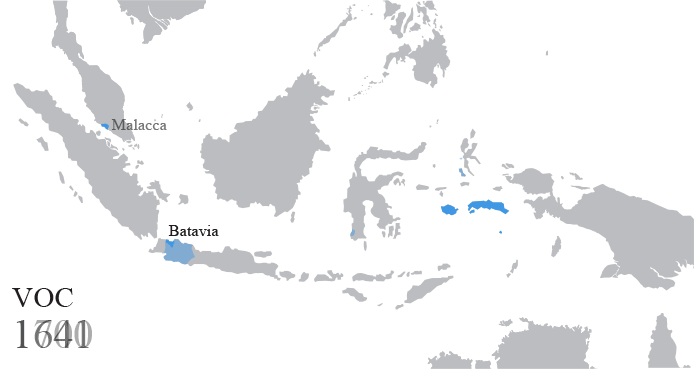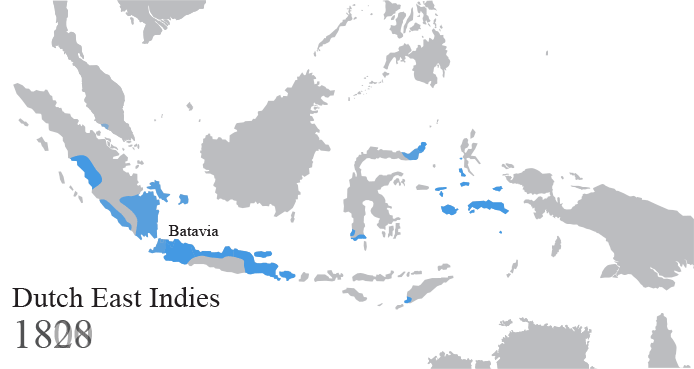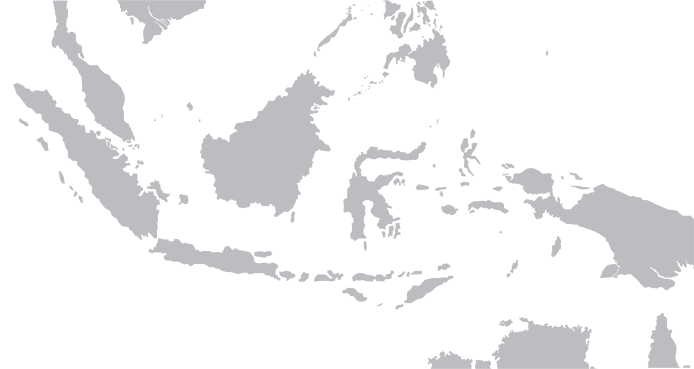
Dutch East Indies
The Dutch East Indies, also known as the Netherlands East Indies ( nl, Nederlands(ch)-Indië; ), was a Dutch colony consisting of what is now Indonesia. It was formed from the nationalised trading posts of the Dutch East India Company, which came under the administration of the Dutch government in 1800. During the 19th century, the Dutch possessions and hegemony expanded, reaching the greatest territorial extent in the early 20th century. The Dutch East Indies was one of the most valuable colonies under European rule, and contributed to Dutch global prominence in spice and cash crop trade in the 19th to early 20th centuries. The colonial social order was based on rigid racial and social structures with a Dutch elite living separate from but linked to their native subjects. The term ''Indonesia'' came into use for the geographical location after 1880. In the early 20th century, local intellectuals began developing the concept of Indonesia as a nation state, and set the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacob Abraham De Mist
Jacob Abraham Uitenhage de Mist (20 April 1749 – 3 August 1823) was a Dutch statesman. He was Head of State of the National Assembly of the Batavian Republic from 17 April 1797 – 1 May 1797, and Commissioner-General of the Cape Colony during the interregnum from 21 February 1803 – 25 September 1804, in accordance with the short-lived Treaty of Amiens. The Cape Colony had been under Dutch control from 1652. In 1795 it was occupied by the British following the Battle of Muizenberg but, under the final terms of peace in 1802 among Great Britain, France and the Netherlands (then known as the Batavian Republic), the colony was restored to the Batavian Republic. Education and career Born in Zaltbommel on 20 April 1749, de Mist was the son of a clergyman, Arnoldus de Mist, and his wife Geertruida Verstrinck. For advanced schooling, he studied Roman Dutch law at the University of Leiden, from 17 September 1766 to 1 July 1768. He practised law in Kampen from 1768 to 1769. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Dutch Treaty Of 1814
The Anglo-Dutch Treaty of 1814 (also known as the Convention of London; nl, Verdrag van Londen) was signed by the United Kingdom and the Netherlands in London on 13 August 1814. The treaty restored most of the territories in Java that Britain had seized in the Napoleonic Wars, but confirmed British possession of the Cape Colony on the southern tip of Africa, as well as portions of South America. It was signed by Robert Stewart, Viscount Castlereagh, on behalf of the British and diplomat Hendrik Fagel, on behalf of the Dutch. Terms Possessions The treaty returned the colonial possessions of the Dutch as they were at 1 January 1803, before the outbreak of the Napoleonic Wars in the Americas, Africa, and Asia, with the exception of the Cape of Good Hope and the South American settlements of Demerara, Essequibo and Berbice, where the Dutch retained trading rights. In addition, the British ceded the island of Banca off the island of Sumatra in exchange for the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arnold Adriaan Buyskes
Arnold Adriaan Buyskess (Enkhuizen 21 January 1771 - Loosduinen 23 January 1838) was a Dutch naval officer, who also served as a Commissioner-General of the Dutch East Indies from 1816 to 1819. Before that he had been Daendels lt.-Governor-General on Java from 1808 to 1809. He successfully led the punitive expedition against the insurgents in the Moluccas in 1817. Life Personal life He was the son of Pieter Buyskes, mayor of Enkhuizen, and Arnoldina Adriana Jordens.Blok and Molhuysen, p. 527 He was on 9 February 1794 in Enkhuizen married to Eva Clasina van Romond. They had a son, Pieter.Blok and Molhuysen, p. 529 Career He became on 15 October 1783 a midshipman, 17 January 1788 lieutenant, left February 1789 to the Dutch East Indies, where he did hydrographic work, and became a first lieutenant in 1792. He returned to the Netherlands on June 21, 1793. From 1793 to 1795 he served with the naval artillery corps in Elburg. After the founding of the Batavian Navy he was charge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commissioners-General Of The Dutch East Indies
The Commissioners-General of the Dutch East Indies (in Dutch ''Commissarissen Generaal over Nederlandsch-Indië'' as they called themselvesOranje, p. 2) was a commission instituted by the Dutch king William I of the Netherlands in 1815 to implement the provisions of the Anglo-Dutch Treaty of 1814 and take over the government of the Dutch Indies from the British lieutenant-governor of Java, John Fendall Jr. The commission consisted of the following three members: Godert van der Capellen, Arnold Adriaan Buyskes, and Cornelis Theodorus Elout. One of their tasks was to implement a new ''Regeringsreglement'' for the colony that they carried in draft-form with them. But instead they promulgated a much-amended version of that draft at the end of their mission in 1818. It embodied a transition from the "Trade Colonialism" of the VOC to an embryonic form of "Imperial Power Colonialism", which would come to full fruition during the 19th century (while retaining aspects of "trade colonial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First French Empire
The First French Empire, officially the French Republic, then the French Empire (; Latin: ) after 1809, also known as Napoleonic France, was the empire ruled by Napoleon Bonaparte, who established French hegemony over much of continental Europe at the beginning of the 19th century. It lasted from 18 May 1804 to 11 April 1814 and again briefly from 20 March 1815 to 7 July 1815. Although France had already established a colonial empire overseas since the early 17th century, the French state had remained a kingdom under the Bourbons and a republic after the French Revolution. Historians refer to Napoleon's regime as the ''First Empire'' to distinguish it from the restorationist '' Second Empire'' (1852–1870) ruled by his nephew Napoleon III. The First French Empire is considered by some to be a " Republican empire." On 18 May 1804, Napoleon was granted the title Emperor of the French (', ) by the French and was crowned on 2 December 1804, signifying the end of the Fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bouches-de-la-Meuse
Bouches-de-la-Meuse (, "Mouths of the Meuse"; , nl, Monden van de Maas) was a department of the First French Empire in the present-day Netherlands. It was named after the mouth of the river Meuse. It was formed in 1810, when the Kingdom of Holland was annexed by France. Its territory corresponded more or less with the present-day Dutch province of South Holland. Its capital was The Hague. The department was subdivided into the following arrondissements and cantons (situation in 1813):Almanach Impérial an bissextil MDCCCXII p. 378-379, accessed in Gallica 24 July 2013 * , cantons: |
Louis Bonaparte
Louis Napoléon Bonaparte (born Luigi Buonaparte; 2 September 1778 – 25 July 1846) was a younger brother of Napoleon I, Emperor of the French. He was a monarch in his own right from 1806 to 1810, ruling over the Kingdom of Holland (a French client state roughly corresponding to the current Netherlands). In that capacity he was known as Louis I ( Dutch: Lodewijk I ). Louis was the fifth surviving child and fourth surviving son of Carlo Buonaparte and Letizia Ramolino, out of eight children who lived past infancy. He and his siblings were all born on Corsica, which had been conquered by France less than a decade before his birth. Louis followed his older brothers into the French Army, where he benefited from Napoleon's patronage. In 1802, he married his step-niece Hortense de Beauharnais, the daughter of Empress Joséphine (Napoleon's wife). In 1806, Napoleon established the Kingdom of Holland in place of the Batavian Republic, appointing Louis as the new king. Napoleon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Holland
The Kingdom of Holland ( nl, Holland (contemporary), (modern); french: Royaume de Hollande) was created by Napoleon Bonaparte, overthrowing the Batavian Republic in March 1806 in order to better control the Netherlands. Since becoming Emperor in 1804, Napoleon sought to extirpate republican tendencies in territories France controlled, and placed his third brother, Louis Bonaparte, on the throne of the puppet kingdom.Jonathan Israel, ''The Dutch Republic: Its Rise, Greatness, and Fall 1477-1806''. Oxford: Oxford University Press 1995, 1128. The name of the leading province, Holland, now designated the whole country. In 1807, East Frisia and Jever were added to the kingdom. In 1809, after the Walcheren Campaign, Holland had to surrender all territories south of the river Rhine to France. Also in 1809, Dutch forces fighting on the French side participated in defeating the anti-Bonapartist German rebellion led by Ferdinand von Schill, at the battle of Stralsund. King Louis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rutger Jan Schimmelpenninck
Rutger Jan Schimmelpenninck (31 October 1761 – 15 February 1825), Lord of Nyenhuis, Peckedam and Gellicum, was a Dutch jurist, ambassador and politician who served as Grand Pensionary of the Batavian Republic from 1805 to 1806. Education Schimmelpenninck was born into a bastard branch of the noble family Schimmelpenninck van der Oye in Deventer, Overijssel on 31 October 1761. His father, Gerrit Schimmelpenninck, was a wine trader who had no rights in the Dutch Republic because of his commitment to the Mennonite Church. Schimmelpenninck attended Athenaeum Illustre of Deventer, and started studying Roman and Contemporary Law at Leiden University in 1781. He received his doctorate in 1784 with his essay ''De imperio populari rite temporato'', in which he defended Rousseau's doctrine of popular sovereignty, although in which this is limited to the wealthy bourgeoisie. He also spoke positively of the Constitution of the United States with its dominating president in this thesis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staatsbewind
{{Unreferenced, date=December 2009 The Staatsbewind (translated into English as "state council" or "state authority") was a governing council of the Batavian Republic between 1801 and 1805. The presidents of the Staatsbewind were acting heads of state of the Batavian Republic. Reign of the Staatsbewind The Staatsbewind came into power after a coup d'état against the Uitvoerend Bewind on 17 October 1801. The reign of the Staatsbewind ended on 29 April 1805, when emperor Napoleon of France appointed Rutger Jan Schimmelpenninck as grand pensionary of the Batavian Republic. Dutch heads of state 1801-1805 *Willem Aernout de Beveren 17 October 1801 - 31 January 1802 *Egbert Sjuck Gerrold Juckema van Burmania Rengers 1 February 1802 - 30 April 1802 *Samuel van Hoogstraten 1 May 1802 - 31 July 1802 *Gerrit Jan Pijman 1 August 1802 - 31 October 1802 *Johannes Baptista Verheyen 1 November 1802 - 31 January 1803 *Jacobus Spoors 1 February 1803 - 30 April 1803 *Campegius Hermannus Gockinga 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |