|
Reichsrat (Austria)
The Imperial Council was the legislature of the Austrian Empire from 1861 until 1918. It was a bicameral body: the upper house was the House of Lords (Austria), House of Lords (), and the lower house was the House of Deputies (Austria), House of Deputies (). To become law, bills had to be passed by both houses, signed by the government minister responsible, and then granted royal assent by the Emperor of Austria, Emperor. After having been passed, laws were published in the ''Reichsgesetzblatt'' (lit. Reich Law Government gazette, Gazette). In addition to the Imperial Council, the fifteen individual Cisleithania#Crown lands, crown lands of Cisleithania had their own Landtag, diets (). The seat of the Imperial Council from 4 December 1883 was in the Austrian Parliament Building, Parliament Building on Vienna Ring Road, Ringstraße in Vienna. Prior to the completion of this building, the House of Lords met in the Estates House of Lower Austria, and the House of Deputies met in a temp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bicameral
Bicameralism is a type of legislature that is divided into two separate Deliberative assembly, assemblies, chambers, or houses, known as a bicameral legislature. Bicameralism is distinguished from unicameralism, in which all members deliberate and vote as a single group. , roughly 40% of the world's national legislatures are bicameral, while unicameralism represents 60% nationally and much more at the subnational level. Often, the members of the two chambers are elected or selected by different methods, which vary from Jurisdiction (area), jurisdiction to jurisdiction. This can often lead to the two chambers having very different compositions of members. Enactment of a bill, Enactment of primary legislation often requires a concurrent majority—the approval of a majority of members in each of the chambers of the legislature. When this is the case, the legislature may be called an example of perfect bicameralism. However, in many parliamentary and semi-presidential systems, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Gazette
A government gazette (also known as an official gazette, official journal, official newspaper, official monitor or official bulletin) is a periodical publication that has been authorised to publish public or legal notices. It is usually established by statute or official action, and publication of notices within it, whether by the government or a private party, is usually considered sufficient to comply with legal requirements for public notice. Gazettes are published either in print, electronically or both. Publication within privately owned periodicals In some jurisdictions, privately owned newspapers may also register with the public authorities in order to publish public and legal notices. Likewise, a private newspaper may be designated by the courts for publication of legal notices. These are referred to as "legally adjudicated newspapers". See also *List of government gazettes *List of British colonial gazettes *Journals of legislative bodies *Annals *Newspaper of record ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constitutional Monarchy
Constitutional monarchy, also known as limited monarchy, parliamentary monarchy or democratic monarchy, is a form of monarchy in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution and is not alone in making decisions. Constitutional monarchies differ from absolute monarchies (in which a monarch is the only decision-maker) in that they are bound to exercise powers and authorities within limits prescribed by an established legal framework. A constitutional monarch in a parliamentary democracy is a hereditary symbolic head of state (who may be an emperor, king or queen, prince or grand duke) who mainly performs representative and civic roles but does not exercise executive or policy-making power. Constitutional monarchies range from countries such as Liechtenstein, Monaco, Morocco, Jordan, Kuwait, Bahrain and Bhutan, where the constitution grants substantial discretionary powers to the sovereign, to countries such as the United Kingdom and other Com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serfdom
Serfdom was the status of many peasants under feudalism, specifically relating to manorialism and similar systems. It was a condition of debt bondage and indentured servitude with similarities to and differences from slavery. It developed during late antiquity and the Early Middle Ages in Europe and lasted in some countries until the mid-19th century. Unlike slaves, serfs could not be bought, sold, or traded individually, though they could, depending on the area, be sold together with land. Actual slaves, such as the kholops in Russia, could, by contrast, be traded like regular slaves, abused with no rights over their own bodies, could not leave the land they were bound to, and marry only with their lord's permission. Serfs who occupied a plot of land were required to work for the lord of the manor who owned that land. In return, they were entitled to protection, justice, and the right to cultivate certain fields within the manor to maintain their own subsistence. Serfs wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kroměříž
Kroměříž (; ) is a town in the Zlín Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 28,000 inhabitants. It is known for Kroměříž Castle with its castle gardens, which are a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The historic town centre with the castle complex is well preserved and is protected as an urban monument reservation. Administrative division Kroměříž consists of ten municipal parts (in brackets population according to the 2021 census): *Kroměříž (24,415) *Bílany (323) *Drahlov (155) *Hradisko (226) *Kotojedy (221) *Postoupky (598) *Těšnovice (419) *Trávník (601) *Vážany (1,174) *Zlámanka (148) Etymology The name is derived from the personal name Kroměžir, meaning "Kroměžir's (property)". Geography Kroměříž is located about northwest of Zlín. About two thirds of the municipal territory lies in the Litenčice Hills, the eastern part lies in the Upper Morava Valley. A small southern part extends into the Chřiby range. The highest point of the ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
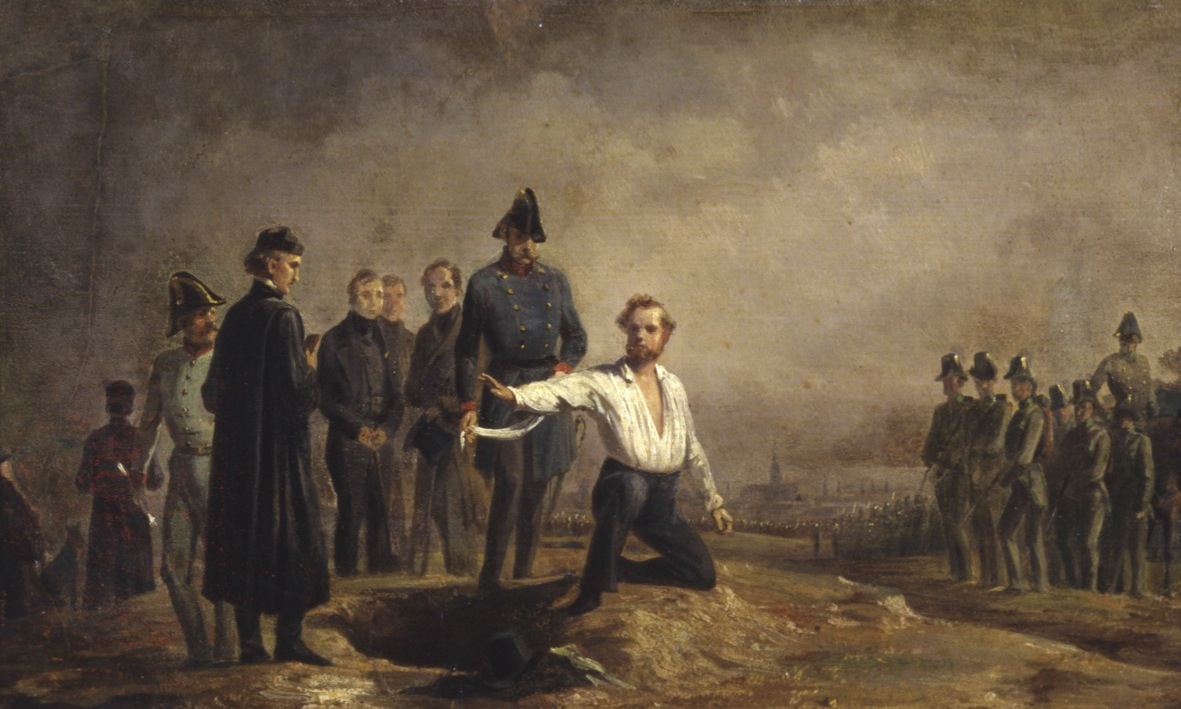
Vienna Uprising
The Vienna Uprising or October Revolution (, or ) of October 1848 was the last uprising in the Austrian Revolution of 1848. On 6 October 1848, as the troops of the Austrian Empire were preparing to leave Vienna to suppress the Hungarian Revolution, a crowd sympathetic to the Hungarian cause (of workers, students and mutinous soldiers) tried to prevent them from leaving. The incident escalated into violent street battles; blood was spilt in Saint Stephen's Cathedral and Count Baillet von Latour, the Austrian Minister of War, was lynched by the crowd. The commander of the Vienna garrison, Count Auersperg, was obliged to evacuate the city, but he entrenched himself in a strong position outside it. The Austrian Empire became familiar with Emperors and Foreign Ministers coming in and out of administration. The first victim to the Revolutions of 1848 was Klemens von Metternich, who resigned as the Foreign Minister on March 13, 1848. On 7 October, Emperor Ferdinand I fled with his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archduke John Of Austria
Archduke John of Austria (, ; (or simply ''Nadvojvoda Janez''); 20 January 1782 – 11 May 1859), a member of the House of Habsburg-Lorraine, was an Austrian field marshal and imperial regent (''Reichsverweser'') of the short-lived German Empire during the Revolutions of 1848. Biography John was born in Florence, the thirteenth child of the Habsburg Grand Duke Leopold I of Tuscany (Archduke of Austria and later Emperor) and Maria Louisa of Spain. He was baptized with the name of John Baptist Joseph Fabian Sebastian, after the patron saint of the Tuscan capital. In 1790, Leopold succeeded his brother Joseph II as the Holy Roman Emperor and his family moved from the Grand Duchy of Tuscany to the Imperial court in Vienna. Only two years later, John's elder brother Francis II ascended the Imperial throne. John's native language was Italian, though he learned to speak French and German fluently. Educated by the Swiss historian Johannes von Müller, he developed wide-rangi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Confederation
The German Confederation ( ) was an association of 39 predominantly German-speaking sovereign states in Central Europe. It was created by the Congress of Vienna in 1815 as a replacement of the former Holy Roman Empire, which had been dissolved in 1806 as a result of the Napoleonic Wars. The Confederation had only one organ, the '' Bundesversammlung'', or Federal Convention (also Federal Assembly or Confederate Diet). The Convention consisted of the representatives of the member states. The most important issues had to be decided on unanimously. The Convention was presided over by the representative of Austria. This was a formality, however, as the Confederation did not have a head of state, since it was not a state. The Confederation, on the one hand, was a strong alliance between its member states because federal law was superior to state law (the decisions of the Federal Convention were binding for the member states). Additionally, the Confederation had been established for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crown Lands
Crown land, also known as royal domain, is a territorial area belonging to the monarch, who personifies the Crown. It is the equivalent of an entailed estate and passes with the monarchy, being inseparable from it. Today, in Commonwealth realms, crown land is considered public land and is apart from the monarch's private estate. Australia In Australia, public lands without a specific tenure (e.g. National Park or State Forest) are referred to as Crown land or State Land, which is described as being held in the "right of the Crown" of either an individual State or the Commonwealth of Australia (as Australia is a federation, there is no single "Crown" as legal entity). Most Crown lands in Australia are held by the Crown in the right of a State. The only land held by the Commonwealth consists of land in the Northern Territory (surrendered by South Australia), the Australian Capital Territory, Jervis Bay Territory, and small areas acquired for airports, defence and other governmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revolutions Of 1848 In The Habsburg Areas
The revolutions of 1848 in the Austrian Empire took place from March 1848 to November 1849. Much of the revolutionary activity had a nationalist character: the Austrian Empire, ruled from Vienna, included ethnic Germans, Hungarians, Poles, Bohemians (Czechs), Ruthenians (Ukrainians), Slovenes, Slovaks, Romanians, Croats, Italians, and Serbs; all of whom attempted in the course of the revolution to either achieve autonomy, independence, or even hegemony over other nationalities. The nationalist picture was further complicated by the simultaneous events in the German states, which moved toward greater German national unity. Besides these nationalists, liberal and socialist currents resisted the Empire's longstanding conservatism. Background The events of 1848 were the product of mounting social and political tensions after the Congress of Vienna of 1815. During the "pre-March" period, the already conservative Austrian Empire moved further away from ideas of the Age of Enlight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferdinand Fellner
Ferdinand Fellner (19 April 1847 – 22 March 1916) was an Austrian architect. Biography Fellner joined his ailing father's architecture firm at the age of nineteen. After his father's death he founded the architecture studio Fellner & Helmer with Hermann Helmer in 1873. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Fellner, Ferdinand 1847 births 1916 deaths Architects from Vienna Baroque Revival architects TU Wien alumni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estates House Of Lower Austria
Estate or The Estate may refer to: Law * Estate (law), a term in common law for a person's property, entitlements and obligations * Estates of the realm, a broad social category in the histories of certain countries. ** The Estates, representative bodies of the estates of the realm *** Estates General, a supra-regional gathering of representatives of the estates of the realm * Estate in land * Estate (land), the grounds and tenancies (such as farms, housing, woodland, parkland) associated with a very large property ** Fortified estate, a housing estate surrounded by a wall with gate entrance/checkpoint. ** Housing estate, a group of houses built as a single development. ** Industrial estate (office park) and trading estate; property planned and sub-let for industrial and commercial use. ** Real estate or real property ***Estate agent or real estate agent * Literary estate, the intellectual property of a deceased author, or the executor thereof Automobiles and technology * Estate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |