|
Regnal List
A regnal list or king list is, at its simplest, a list of successive monarchs. Some regnal lists may give the relationship between successive monarchs (e.g., son, brother), the length of reign of each monarch or annotations on important reigns. The list may be divided into dynasties marked off by headings. As a distinct genre, the regnal list originates in the ancient Near East. Its purpose was not originally chronological. It originally served to demonstrate the antiquity and legitimacy of the monarchy, but it became an important device for structuring historical narratives (as in Herodotus) and thus a chronological aid. In antiquity, regnal lists were kept in Sumer, Egypt, Israel, Assyria and Babylonia. King lists have made it into sacred religious texts, such as the ''Puranas'' and the Hebrew Bible, which contains an Edomite king list. Regnal lists were kept in early medieval Ireland, Pictland and Anglo-Saxon England. The historian David Dumville regarded them as more reliab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
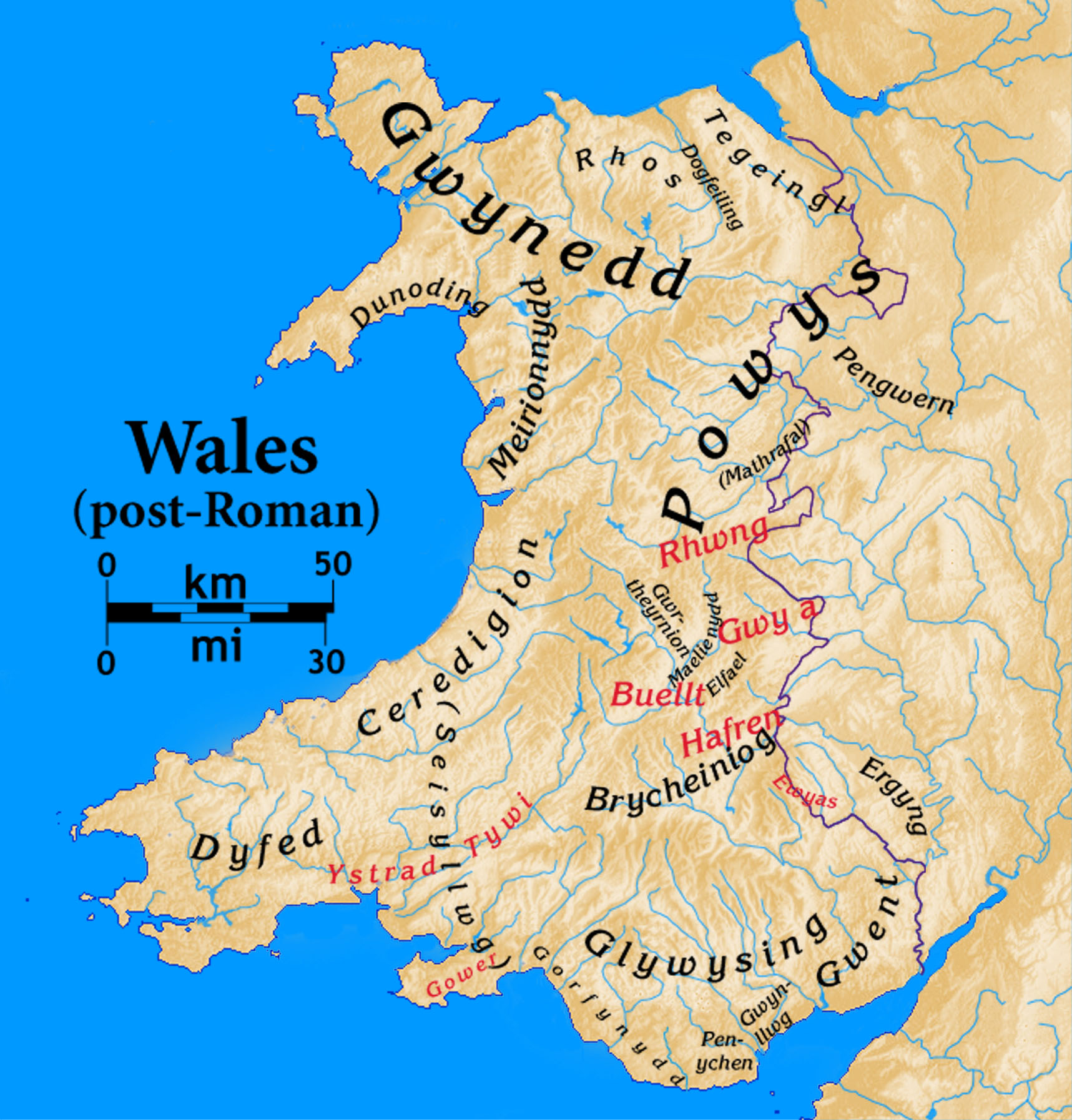
Wales In The Early Middle Ages
Wales in the early Middle Ages covers the time between the Roman departure from Wales c. 383 until the middle of the 11th century. In that time there was a gradual consolidation of power into increasingly hierarchical kingdoms. The end of the early Middle Ages was the time that the Welsh language transitioned from the Primitive Welsh spoken throughout the era into Old Welsh, and the time when the modern England–Wales border would take its near-final form, a line broadly followed by Offa's Dyke, a late eighth-century earthworks (archaeology), earthwork. Successful unification into something recognisable as a Welsh state would come in the next era under the descendants of Merfyn Frych. Wales was Rural area, rural throughout the era, characterised by small settlements called ''trefi''. The local landscape was controlled by a local aristocracy and ruled by a warrior aristocrat. Control was exerted over a piece of land and, by extension, over the people who lived on that land. Many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palermo Stone
The Palermo Stone is one of seven surviving fragments of a stele known as the Royal Annals of the Old Kingdom of Ancient Egypt. The stele contained a list of the kings of Egypt from the First Dynasty (c.3150–2890 BCE) through to the early part of the Fifth Dynasty (c.2498–2345 BCE) and noted significant events in each year of their reigns. It was probably made during the Fifth Dynasty.Dodson, Aidan (2004) ''The Complete Royal Families of Ancient Egypt'', p.62. Thames & Hudson, . The Palermo Stone is held in the Regional Archeological Museum Antonio Salinas in the city of Palermo, Italy, from which it derives its name. The Palermo Stone and other fragments of the Royal Annals preserve what is probably the oldest historical text that has survived from Ancient Egypt and form a key source for Egyptian history in the Old Kingdom.Hsu, Hsu, Shih-Wei (2010) ''The Palermo Stone: the Earliest Royal Inscription from Ancient Egypt'', Altoriental. Forsch., Akademie Verlag, 37 (2010) 1, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nominalia Of The Bulgarian Khans
The ''Nominalia of the Bulgarian Khans'' () is a short text which is presumed to contain the names of some early Bulgar rulers, their clans, the year of their ascending to the throne according to the cyclic Bulgar calendar and the length of their rule, including the times of joint rule and civil war. It is written in Church Slavonic, but contains a large number of Bulgar names and date terms. The manuscript also does not contain any reference that this is a list of rulers of Bulgaria. The ''Nominalia'' was found by the Russian scholar Alexander Popov in 1861, during his research on Russian chronographers. So far, three Russian copies of the document have been found. The earliest of them, the "'' Uvarov transcript''", dates from the 15th century and the other two, the '' Pogodin'' and ''Moscow'' transcripts, from the 16th century. There are certain differences in the names' spellings in the manuscripts. Despite the commonly accepted name of the nominalia, the preserved Slavic t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medinet Habu King List
Medinet Habu (; ; ; ) is an archaeological locality situated near the foot of the Theban Hills on the West Bank of the River Nile opposite the modern city of Luxor, Egypt. Although other structures are located within the area and important discoveries have also been made at these sites, the location is today associated almost synonymously with the largest and best preserved site, the Mortuary Temple of Ramesses III. It was an important New Kingdom period temple structure in the West Bank of Luxor in Egypt. Aside from its size and architectural and artistic importance, the mortuary temple is probably best known as the source of inscribed reliefs depicting the advent and defeat of the "sea peoples" during the reign of Ramesses III (c. 1186–1155 BC), including the Battle of the Delta. Some of the building materials were re-used from earlier monuments including the destroyed mortuary temple of Tausret (c. 1191–1189 BC) the last known ruler and the final pharaoh of the Nineteenth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1922 Regnal List Of Ethiopia
The 1922 regnal list of Ethiopia is an official regnal list used by the Emperor of Ethiopia, Ethiopian monarchy which names over 300 monarchs across six Millennium, millennia. The list is partially inspired by older regnal lists of Ethiopia, Ethiopian regnal lists and chronicles, but is notable for additional monarchs who ruled Nubia, which was known as ''Aethiopia'' in ancient times. Also included are various figures from Greek mythology and the Biblical canon who were known to be "Aethiopian", as well as figures who originated from Egyptian sources (Ancient Egyptian, Coptic literature, Coptic and Arabic literature, Arabic). This list of monarchs was included in Charles Fernand Rey's book ''In the Country of the Blue Nile'' in 1927, and is the longest Ethiopian regnal list published in the Western world. It is the only known regnal list that attempts to provide a timeline of Ethiopian monarchs from the 5th millennium BC, 46th century BC up to modern times without any gaps. Howe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regnal Lists Of Ethiopia
Regnal lists of Ethiopia are recorded lists of monarchs who are claimed by tradition to have ruled Ethiopian Empire, Ethiopia. These lists are often recorded on manuscripts or Oral tradition, orally by Monastery, monasteries and have been passed down over the centuries. Many surviving physical regnal lists, as well as recorded oral lists, chronicle the line of kings beginning with Menelik I to the Solomonic dynasty. In Ethiopian tradition, Menelik is believed to be the son of queen Makeda (the Biblical canon, Biblical Queen of Sheba) and king Solomon. The rulers that followed Menelik were the List of kings of Axum, kings of Axum, the Zagwe dynasty and the Solomonic dynasty. Some monarchs who ruled before Menelik are recorded in different Ethiopian traditions. These regnal lists were used to prove the longevity of the Ethiopian monarchy and to provide legitimacy for the Solomonic dynasty until its 1974 Ethiopian coup d'état, fall from power in 1974. Traditions Ethiopian tradition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Den Seal Impressions
In 1985, the German Archaeological Institute discovered seal impressions of a cylinder seal in the tomb of First Dynasty king Den. They were published by Günter Dreyer the following year. The impressions are the earliest confirmed king list for ancient Egypt.Günter Dreyer: ''Ein Siegel der frühzeitlichen Königsnekropole von Abydos'', in: ''MDAIK'' 43 (1986). 33-43 The names are listed in following order: *Narmer *Hor-Aha *Djer *Djet *Den *Merneith (Den's mother and regent) The list bolsters the argument that Narmer was the founder of the First Dynasty as opposed to being the last of the pre-unification kings of Thinis. Also of importance is the absence of Menes Menes ( ; ; , probably pronounced *; and Μήν) was a pharaoh of the Early Dynastic Period of ancient Egypt, credited by classical tradition with having united Upper and Lower Egypt, and as the founder of the First Dynasty. The identity of M ... as scholarly consensus believe Menes was a later variation of N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canon Of Kings
The Canon of Kings was a dated list of kings used by ancient astronomers as a convenient means to date astronomical phenomena, such as eclipses. For a period, the Canon was preserved by the astronomer Claudius Ptolemy, and is thus known sometimes as Ptolemy's Canon. It is one of the most important bases for modern knowledge of ancient chronology. The Canon derives originally from Babylonian sources. Thus, it lists Kings of Babylon from 747 BC until the conquest of Babylon by Achaemenid Persians in 539 BC, and then Persian kings from 538 to 332 BC. At this point, the Canon was continued by Greek astronomers in Alexandria, and lists the Macedonian kings from 331 to 305 BC, the Ptolemies from 304 BC to 30 BC, and the Roman and Byzantine Emperors, although they are not kings; in some manuscripts the list is continued down to the Fall of Constantinople in 1453.E.J. Bickerman, ''Chronology of the Ancient World'' (Ithaca: Cornell University Press, 1968), pp. 81f The Canon o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
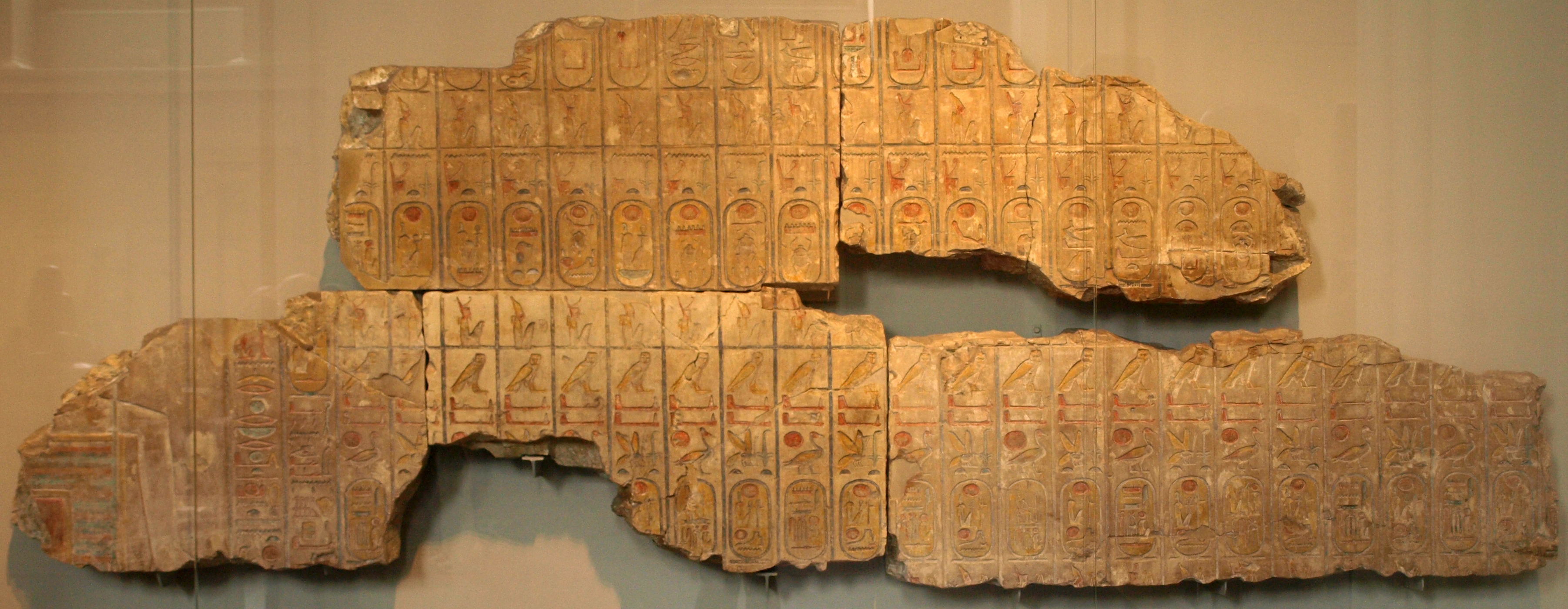
Abydos King List (Ramesses II)
The Abydos King List of Ramesses II, also known as the Fragmentary Abydos King List, the Fragmentary Abydos King Table or the Fragmentary Abydos Tablet, is a list of Ancient Egyptian kings down to Ramesses' own time. Originally located in the temple of Ramesses II at Abydos in Egypt, it was built in the 13th century BC. The list is similar to the one inscribed in the temple built at the site by Ramesses' father and predecessor, Seti I, but with the addition of Ramesses' own throne name and nomen. The list was found by William John Bankes William John Bankes (11 December 1786 – 15 April 1855) was an English politician, explorer, Egyptologist and adventurer. The second, but first surviving, son of Henry Bankes MP, he was a member of the Bankes family of Dorset and he had Sir Ch ... in 1818 and the surviving fragments were removed in 1837 by the French consul in Egypt, dismantled and the blocks sold to the British. Severely damaged, it is now on display at the British Museum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abydos King List
The Abydos King List, also known as the Abydos Table or the Abydos Tablet, is a list of the names of 76 kings of ancient Egypt, found on a wall of the Temple of Seti I at Abydos, Egypt. It consists of three rows of 38 cartouches (borders enclosing the name of a king) in each row. The upper two rows contain names of the kings, while the third row merely repeats Seti I's throne name and nomen. Besides providing the order of the Old Kingdom kings, it is the sole source to date of the names of many of the kings of the Seventh and Eighth Dynasties, so the list is valued greatly for that reason. This list omits the names of many earlier pharaohs. The bulk of these appear to have been left out because although they claimed royal titles and rule over all Egypt, their actual authority was limited to only part of the country. This category includes all the rulers of the Ninth and Tenth Dynasties, the early rulers of the Eleventh Dynasty ( Mentuhotep I, Intef I, Intef II, and In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |