|
Red5 (media Server)
Red5 is a free software media streaming server implemented in Java, which provides services similar to those offered by the proprietary Adobe Flash Media Server and Wowza Streaming Engine including: * Streaming Video (FLV, F4V, MP4, 3GP) * Streaming Audio (MP3, F4A, M4A, AAC) * Recording Client Streams (FLV and AVC+AAC in FLV container) * Shared Objects * Live Stream Video Publishing (FLV, VP6) * Live Stream Audio Publishing (MP3, AAC) * Remoting (Action Message Format) * Protocols: RTMP, RTMPT, RTMPS, and RTMPE The Red5 Project originated in the early 2000s with a mission to provide an open-source real time streaming alternative to Adobe’s proprietary Real-Time Messaging Protocol (RTMP). A group of innovative developers set out to reverse-engineer RTMP, enabling wider access to streaming technology and fostering innovation in the field. In September 2005, the Red5 team successfully reverse-engineered RTMP, marking Red5 as the first open-source project to achieve this milest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Java (programming Language)
Java is a High-level programming language, high-level, General-purpose programming language, general-purpose, Memory safety, memory-safe, object-oriented programming, object-oriented programming language. It is intended to let programmers ''write once, run anywhere'' (Write once, run anywhere, WORA), meaning that compiler, compiled Java code can run on all platforms that support Java without the need to recompile. Java applications are typically compiled to Java bytecode, bytecode that can run on any Java virtual machine (JVM) regardless of the underlying computer architecture. The syntax (programming languages), syntax of Java is similar to C (programming language), C and C++, but has fewer low-level programming language, low-level facilities than either of them. The Java runtime provides dynamic capabilities (such as Reflective programming, reflection and runtime code modification) that are typically not available in traditional compiled languages. Java gained popularity sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross-platform
Within computing, cross-platform software (also called multi-platform software, platform-agnostic software, or platform-independent software) is computer software that is designed to work in several Computing platform, computing platforms. Some cross-platform software requires a separate build for each platform, but some can be directly run on any platform without special preparation, being written in an interpreted language or compiled to portable bytecode for which the Interpreter (computing), interpreters or run-time packages are common or standard components of all supported platforms. For example, a cross-platform application software, application may run on Linux, macOS and Microsoft Windows. Cross-platform software may run on many platforms, or as few as two. Some frameworks for cross-platform development are Codename One, ArkUI-X, Kivy (framework), Kivy, Qt (software), Qt, GTK, Flutter (software), Flutter, NativeScript, Xamarin, Apache Cordova, Ionic (mobile app framework ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Media Server
A media server is a computer appliance or an application software that stores digital media (video, audio or images) and makes it available over a network. Media servers range from servers that provide video on demand to smaller personal computers or NAS (Network Attached Storage) for the home. Purpose By definition, a media server is a device that simply stores and shares media. This definition is vague, and can allow several different devices to be called media servers. It may be a NAS drive, a home theater PC running Windows XP Media Center Edition, MediaPortal or MythTV, or a commercial web server that hosts media for a large web site. In a home setting, a media server acts as an aggregator of information: video, audio, photos, books, etc. These different types of media (whether they originated on DVD, CD, digital camera, or in physical form) are stored on the media server's hard drive. Access to these is then available from a central location. It may also be used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apache License
The Apache License is a permissive free software license written by the Apache Software Foundation (ASF). It allows users to use the software for any purpose, to distribute it, to modify it, and to distribute modified versions of the software under the terms of the license, without concern for royalties. The ASF and its projects release their software products under the Apache License. The license is also used by many non-ASF projects. History Beginning in 1995, the Apache Group (later the Apache Software Foundation) released successive versions of the Apache HTTP Server. Its initial license was essentially the same as the original 4-clause BSD license, with only the names of the organizations changed, and with an additional clause forbidding derivative works from bearing the Apache name. In July 1999, the Berkeley Software Distribution accepted the argument put to it by the Free Software Foundation and retired their ''advertising clause'' (clause 3) to form the new 3-clau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Software
Free software, libre software, libreware sometimes known as freedom-respecting software is computer software distributed open-source license, under terms that allow users to run the software for any purpose as well as to study, change, distribute it and any adapted versions. Free software is a matter of liberty, not price; all users are legally free to do what they want with their copies of a free software (including profiting from them) regardless of how much is paid to obtain the program.Selling Free Software (GNU) Computer programs are deemed "free" if they give end-users (not just the developer) ultimate control over the software and, subsequently, over their devices. The right to study and modify a computer program entails that the source code—the preferred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adobe Flash Media Server
Adobe Media Server (AMS) is a proprietary data and media server from Adobe Systems (originally a Macromedia product). This server works with the Flash Player and HTML5 runtime to create media driven, multiuser RIAs ( Rich Internet Applications). The server uses ActionScript 1, an ECMAScript based scripting language, for server-side logic. Prior to version 2, it was known as Flash Communication Server. Prior to version 5, it was known as Flash Media Server. In February 2019, Adobe Systems Incorporated granteVeriskope Incrights to further develop, resell, and extend distribution of the software product. History On March 16, 2002, Macromedia released Flash Player 6. This version included all the functionality for a yet to be released server called Flash Communication Server MX. Version 1.0 was released on 9 July 2002 and included all the basic features that make up the product, including the NetConnection, SharedObject and NetStream objects. Version 1.5 was released on 27 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wowza Streaming Engine
Wowza Streaming Engine (known as Wowza Media Server prior to version 4) is a unified streaming media server software developed by Wowza. The server is used for streaming of live and on-demand video, audio, and rich Internet applications over IP networks to desktop, laptop, and tablet computers, mobile devices, IPTV set-top boxes, internet-connected TV sets, game consoles, and other network-connected devices. The server is a Java application deployable on most operating systems. History Version 1.0.x was released on February 19, 2007.(Press Release) This version was originally offered as an alternative to the Adobe Flash Media Server, and supported streamed video, audio and RIA’s for the Flash Player client playback and interaction based on the Real Time Messaging Protocol (RTMP) using content encoded with Spark and VP6 codecs. The original product name was Wowza Media Server Pro. Version 1.5.x was released on May 15, 2008(Press Release) and added support for H.264 video ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
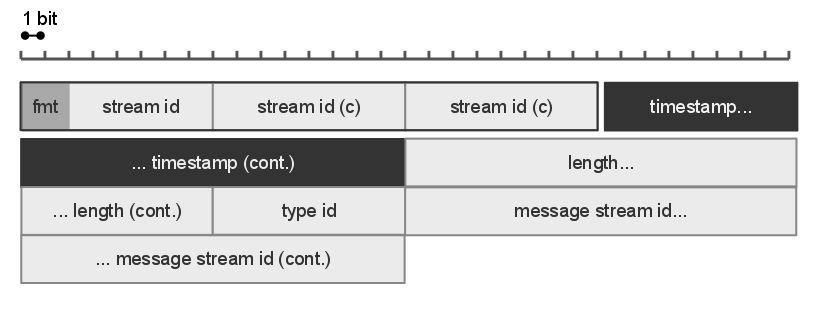
Action Message Format
Action Message Format (AMF) is a binary format used to serialize object graphs such as ActionScript objects and XML, or send messages between an Adobe Flash client and a remote service, usually a Flash Media Server or third party alternatives. The Actionscript 3 language provides classes for encoding and decoding from the AMF format. The format is often used in conjunction with Adobe's RTMP to establish connections and control commands for the delivery of streaming media. In this case, the AMF data is encapsulated in a ''chunk'' which has a header which defines things such as the message length and type (whether it is a "ping", "command" or media data). Format analysis AMF was introduced with Flash Player 6, and this version is referred to as AMF0. It was unchanged until the release of Flash Player 9 and ActionScript 3.0, when new data types and language features prompted an update, called AMF3. Flash Player 10 added vector and dictionary data types documented in a revised spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
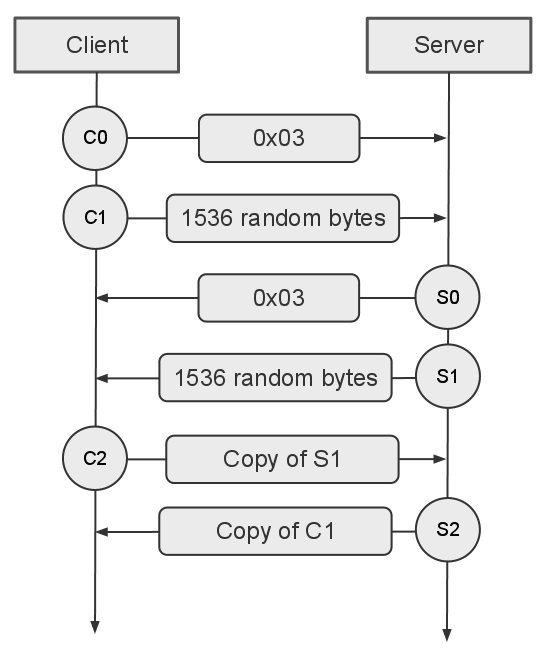
Real Time Messaging Protocol
Real-Time Messaging Protocol (RTMP) is a communication protocol for streaming media, streaming audio, video, and data over the Internet. Originally developed as a proprietary protocol by Macromedia for streaming between Flash Player and the Flash Communication Server, Adobe Systems, Adobe (which acquired Macromedia) has released an incomplete version of the specification of the protocol for public use. The RTMP protocol has multiple variations: # RTMP proper, the "plain" protocol which works on top of Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and uses port number 1935 by default. # RTMPS, which is RTMP over a Transport Layer Security (TLS/SSL) connection. # RTMPE, which is RTMP encrypted using Adobe's own security mechanism. While the details of the implementation are proprietary, the mechanism uses industry standard cryptographic primitives. # RTMPT, which is encapsulation (networking), encapsulated within HTTP requests to traverse firewall (computing), firewalls. RTMPT is frequently f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Real-Time Messaging Protocol
Real-Time Messaging Protocol (RTMP) is a communication protocol for streaming audio, video, and data over the Internet. Originally developed as a proprietary protocol by Macromedia for streaming between Flash Player and the Flash Communication Server, Adobe (which acquired Macromedia) has released an incomplete version of the specification of the protocol for public use. The RTMP protocol has multiple variations: # RTMP proper, the "plain" protocol which works on top of Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and uses port number 1935 by default. # RTMPS, which is RTMP over a Transport Layer Security (TLS/SSL) connection. # RTMPE, which is RTMP encrypted using Adobe's own security mechanism. While the details of the implementation are proprietary, the mechanism uses industry standard cryptographic primitives. # RTMPT, which is encapsulated within HTTP requests to traverse firewalls. RTMPT is frequently found utilizing cleartext requests on TCP ports 80 and 443 to bypass most corpora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GitHub
GitHub () is a Proprietary software, proprietary developer platform that allows developers to create, store, manage, and share their code. It uses Git to provide distributed version control and GitHub itself provides access control, bug tracking system, bug tracking, software feature requests, task management, continuous integration, and wikis for every project. Headquartered in California, GitHub, Inc. has been a subsidiary of Microsoft since 2018. It is commonly used to host open source software development projects. GitHub reported having over 100 million developers and more than 420 million Repository (version control), repositories, including at least 28 million public repositories. It is the world's largest source code host Over five billion developer contributions were made to more than 500 million open source projects in 2024. About Founding The development of the GitHub platform began on October 19, 2005. The site was launched in April 2008 by Tom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WebRTC
WebRTC (Web Real-Time Communication) is a free and open-source project providing web browsers and mobile applications with real-time communication (RTC) via application programming interfaces (APIs). It allows audio and video communication and streaming to work inside web pages by allowing direct peer-to-peer communication, eliminating the need to install plugins or download native apps. Supported by Apple, Google, Microsoft, Mozilla, and Opera, WebRTC specifications have been published by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) and the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). History In May 2010, Google bought Global IP Solutions or GIPS, a VoIP and videoconferencing software company that had developed many components required for RTC, such as codecs and echo cancellation techniques. Google open-sourced the GIPS technology and engaged with relevant standards bodies at the IETF and W3C to ensure industry consensus. In May 2011, Google released an open-source project for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |