|
Range Ambiguity Resolution
Range ambiguity resolution is a technique used with medium pulse-repetition frequency (PRF) radar to obtain range information for distances that exceed the distance between transmit pulses. This signal processing technique is required with pulse-Doppler radar. The raw return signal from a reflection will appear to be arriving from a distance less than the true range of the reflection when the wavelength of the pulse repetition frequency (PRF) is less than the range of the reflection. This causes reflected signals to be folded, so that the apparent range is a modulo function of true range. Definition Range aliasing occurs when reflections arrive from distances that exceed the distance between transmit pulses at a specific pulse repetition frequency (PRF). Range ambiguity resolution is required to obtain the true range when the measurements are made using a system where the following inequality is true. :\text > \left (\frac \right) Here ''c'' is the signal speed, which fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulse-repetition Frequency
The pulse-repetition frequency (PRF) is the number of pulses of a repeating signal in a specific time unit. The term is used within a number of technical disciplines, notably radar. In radar, a radio signal of a particular carrier frequency is turned on and off; the term "frequency" refers to the carrier, while the PRF refers to the number of switches. Both are measured in terms of cycle per second, or hertz. The PRF is normally much lower than the frequency. For instance, a typical World War II radar like the Type 7 AMES Type 7, GCI radar had a basic carrier frequency of 209 MHz (209 million cycles per second) and a PRF of 300 or 500 pulses per second. A related measure is the Radar signal characteristics#pulse width, pulse width, the amount of time the transmitter is turned on during each pulse. After producing a brief pulse of radio signal, the transmitter is turned off in order for the receiver units to detect the reflections of that signal off distant targets. Since the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
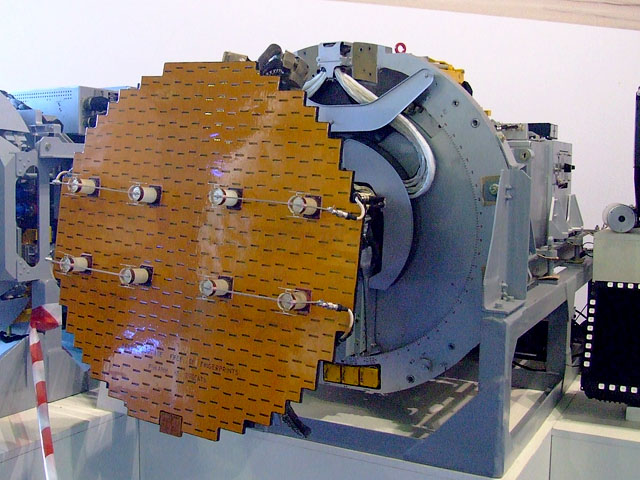
Pulse-Doppler Radar
A pulse-Doppler radar is a radar system that determines the range to a target using pulse-timing techniques, and uses the Doppler effect of the returned signal to determine the target object's velocity. It combines the features of pulse radars and continuous-wave radars, which were formerly separate due to the complexity of the electronics. The first operational pulse-Doppler radar was in the CIM-10 Bomarc, an American long range supersonic missile powered by ramjet engines, and which was armed with a W40 nuclear weapon to destroy entire formations of attacking enemy aircraft. Pulse-Doppler systems were first widely used on fighter aircraft starting in the 1960s. Earlier radars had used pulse-timing in order to determine range and the angle of the antenna (or similar means) to determine the bearing. However, this only worked when the radar antenna was not pointed down; in that case the reflection off the ground overwhelmed any returns from other objects. As the ground moves at th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modular Arithmetic
In mathematics, modular arithmetic is a system of arithmetic operations for integers, other than the usual ones from elementary arithmetic, where numbers "wrap around" when reaching a certain value, called the modulus. The modern approach to modular arithmetic was developed by Carl Friedrich Gauss in his book '' Disquisitiones Arithmeticae'', published in 1801. A familiar example of modular arithmetic is the hour hand on a 12-hour clock. If the hour hand points to 7 now, then 8 hours later it will point to 3. Ordinary addition would result in , but 15 reads as 3 on the clock face. This is because the hour hand makes one rotation every 12 hours and the hour number starts over when the hour hand passes 12. We say that 15 is ''congruent'' to 3 modulo 12, written 15 ≡ 3 (mod 12), so that 7 + 8 ≡ 3 (mod 12). Similarly, if one starts at 12 and waits 8 hours, the hour hand will be at 8. If one instead waited twice as long, 16 hours, the hour hand would be on 4. This ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulse Repetition Frequency
The pulse-repetition frequency (PRF) is the number of pulses of a repeating signal in a specific time unit. The term is used within a number of technical disciplines, notably radar. In radar, a radio signal of a particular carrier frequency is turned on and off; the term "frequency" refers to the carrier, while the PRF refers to the number of switches. Both are measured in terms of cycle per second, or hertz. The PRF is normally much lower than the frequency. For instance, a typical World War II radar like the Type 7 GCI radar had a basic carrier frequency of 209 MHz (209 million cycles per second) and a PRF of 300 or 500 pulses per second. A related measure is the pulse width, the amount of time the transmitter is turned on during each pulse. After producing a brief pulse of radio signal, the transmitter is turned off in order for the receiver units to detect the reflections of that signal off distant targets. Since the radio signal has to travel out to the target and back ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speed Of Light
The speed of light in vacuum, commonly denoted , is a universal physical constant exactly equal to ). It is exact because, by international agreement, a metre is defined as the length of the path travelled by light in vacuum during a time interval of second. The speed of light is invariant (physics), the same for all observers, no matter their relative velocity. It is the upper limit for the speed at which Information#Physics_and_determinacy, information, matter, or energy can travel through Space#Relativity, space. All forms of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, travel at the speed of light. For many practical purposes, light and other electromagnetic waves will appear to propagate instantaneously, but for long distances and sensitive measurements, their finite speed has noticeable effects. Much starlight viewed on Earth is from the distant past, allowing humans to study the history of the universe by viewing distant objects. When Data communication, comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modular Arithmetic
In mathematics, modular arithmetic is a system of arithmetic operations for integers, other than the usual ones from elementary arithmetic, where numbers "wrap around" when reaching a certain value, called the modulus. The modern approach to modular arithmetic was developed by Carl Friedrich Gauss in his book '' Disquisitiones Arithmeticae'', published in 1801. A familiar example of modular arithmetic is the hour hand on a 12-hour clock. If the hour hand points to 7 now, then 8 hours later it will point to 3. Ordinary addition would result in , but 15 reads as 3 on the clock face. This is because the hour hand makes one rotation every 12 hours and the hour number starts over when the hour hand passes 12. We say that 15 is ''congruent'' to 3 modulo 12, written 15 ≡ 3 (mod 12), so that 7 + 8 ≡ 3 (mod 12). Similarly, if one starts at 12 and waits 8 hours, the hour hand will be at 8. If one instead waited twice as long, 16 hours, the hour hand would be on 4. This ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
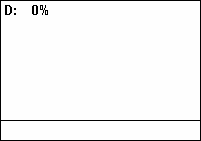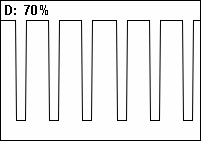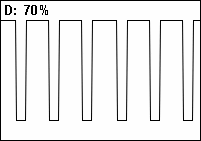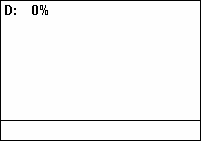
Duty Cycle
A duty cycle or power cycle is the fraction of one period in which a signal or system is active. Duty cycle is commonly expressed as a percentage or a ratio. A period is the time it takes for a signal to complete an on-and-off cycle. As a formula, a duty cycle (%) may be expressed as: :D = \frac \times 100\% Equally, a duty cycle (ratio) may be expressed as: :D = \frac where D is the duty cycle, PW is the pulse width (pulse active time), and T is the total period of the signal. Thus, a 60% duty cycle means the signal is on 60% of the time and off 40% of the time. The "on time" for a 60% duty cycle could be a fraction of a second, a day, or even a week, depending on the length of the period. Duty cycles can be used to describe the percent time of an active signal in an electrical device such as the power switch in a switching power supply or the firing of action potentials by a living system such as a neuron. Some publications use \alpha as the symbol for duty cycle. As a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Remainder Theorem
In mathematics, the Chinese remainder theorem states that if one knows the remainders of the Euclidean division of an integer ''n'' by several integers, then one can determine uniquely the remainder of the division of ''n'' by the product of these integers, under the condition that the divisors are pairwise coprime (no two divisors share a common factor other than 1). The theorem is sometimes called Sunzi's theorem. Both names of the theorem refer to its earliest known statement that appeared in '' Sunzi Suanjing'', a Chinese manuscript written during the 3rd to 5th century CE. This first statement was restricted to the following example: If one knows that the remainder of ''n'' divided by 3 is 2, the remainder of ''n'' divided by 5 is 3, and the remainder of ''n'' divided by 7 is 2, then with no other information, one can determine the remainder of ''n'' divided by 105 (the product of 3, 5, and 7) without knowing the value of ''n''. In this example, the remainder is 23. More ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convolution
In mathematics (in particular, functional analysis), convolution is a operation (mathematics), mathematical operation on two function (mathematics), functions f and g that produces a third function f*g, as the integral of the product of the two functions after one is reflected about the y-axis and shifted. The term ''convolution'' refers to both the resulting function and to the process of computing it. The integral is evaluated for all values of shift, producing the convolution function. The choice of which function is reflected and shifted before the integral does not change the integral result (see #Properties, commutativity). Graphically, it expresses how the 'shape' of one function is modified by the other. Some features of convolution are similar to cross-correlation: for real-valued functions, of a continuous or discrete variable, convolution f*g differs from cross-correlation f \star g only in that either f(x) or g(x) is reflected about the y-axis in convolution; thus i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radar Scalloping
Scalloping is a radar phenomenon that reduces sensitivity for certain distance and velocity combinations. The name is derived from the appearance of areas that are scooped out of graphs that indicate radar sensitivity. Moving objects cause a phase-shift within the transmit pulse that produces signal cancellation. This phenomenon also has detrimental effects on moving target indicator systems, where the detection scheme subtracts signals received from two or more transmit pulses. Definition There are two different types of radar scalloping. * Intra-pulse * Inter-pulse Intra-pulse Scalloping This occurs when the radial velocity of the target induces a phase shift near 360 degrees within the reflected pulse, which induces signal cancellation in the receiver. Intra-pulse radar scalloping begins to become a concern above the following velocity. :Velocity > \left (\frac \right) Scalloping occurs at 150 km/s for an L-band radar with a 1 microsecond pulse. Inter-pulse Scallop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Degrees Of Freedom (physics And Chemistry)
In physics and chemistry, a degree of freedom is an independent physical parameter in the chosen parameterization of a physical system. More formally, given a parameterization of a physical system, the number of degrees of freedom is the smallest number n of parameters whose values need to be known in order to always be possible to determine the values of ''all'' parameters in the chosen parameterization. In this case, any set of n such parameters are called degrees of freedom. The location of a particle in three-dimensional space requires three Coordinate system, position coordinates. Similarly, the direction and speed at which a particle moves can be described in terms of three velocity components, each in reference to the three dimensions of space. So, if the time evolution of the system is Deterministic system, deterministic (where the state at one instant uniquely determines its past and future position and velocity as a function of time), such a system has six degrees of f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |