|
Raja Ampat–South Halmahera Languages
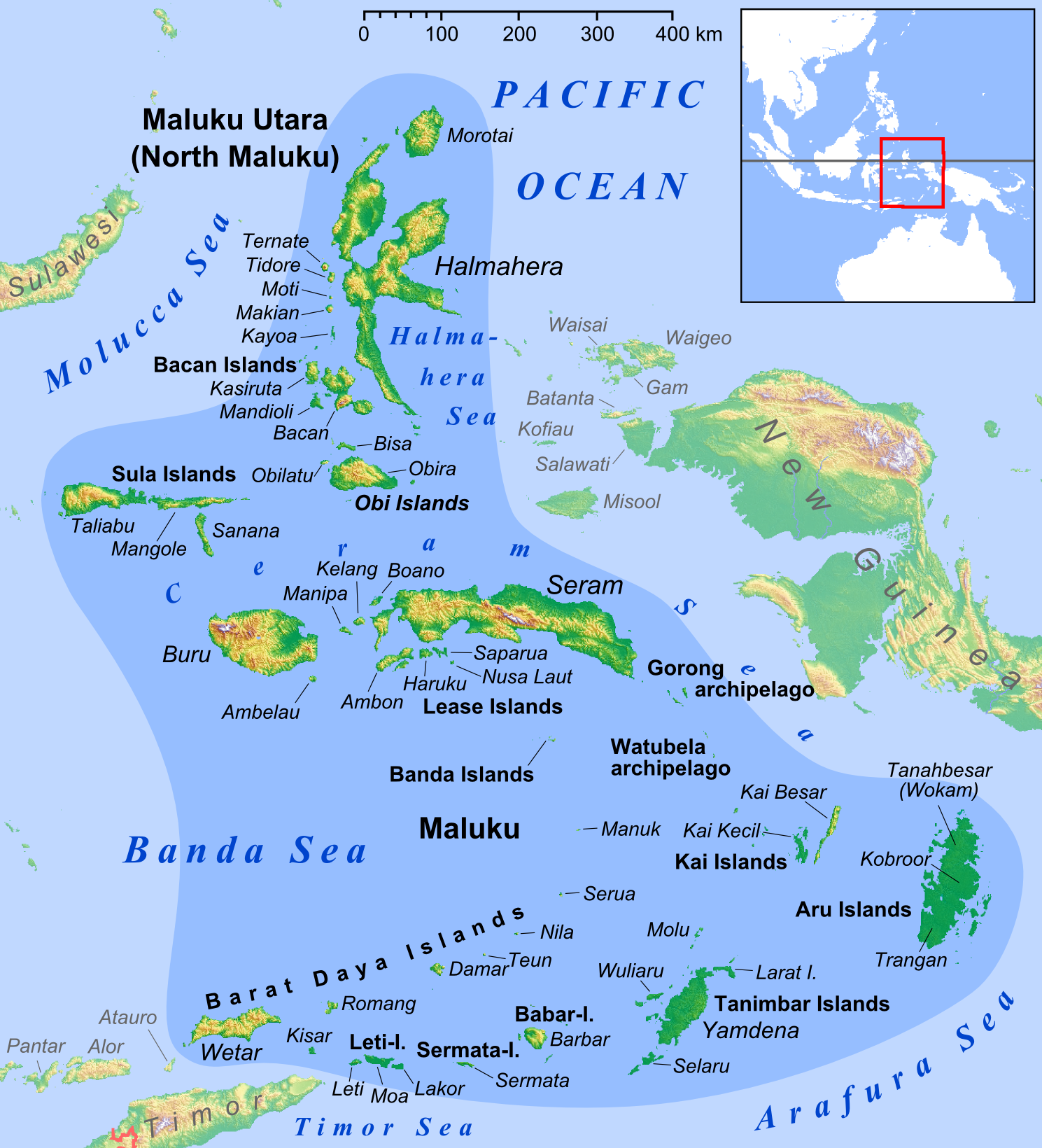
The Raja Ampat–South Halmahera languages are a branch of Malayo-Polynesian languages of eastern Indonesia. They are spoken on islands in the Halmahera Sea, and on its margins from the south-eastern coast of Halmahera to the Raja Ampat Islands off the western tip of New Guinea. The languages of the Raja Ampat Islands show a strong Papuan substratum influence; it is not clear that they are actually Austronesian as opposed to relexified Papuan languages.* Remijsen (2001) and Blust (1978) linked the languages of Raja Ampat to the South Halmahera languages. Historical morphology Reconstructions of subject markers and inalienable possessive markers for Raja Ampat–South Halmahera proto-languages according to Kamholz (2015). Note that V = vocalic conjugation, C = consonantal conjugation: Proto-Raja Ampat–South Halmahera: : : Proto-Ma'ya-Matbat: : : Subject markers and personal pronouns of Proto-Raja Ampat–South Halmahera according to Arnold (2023): : : Languages From Kamh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halmahera Sea
The Halmahera Sea is a regional sea located in the central eastern part of the Australasian Mediterranean Sea. It is centered at about 1°S and 129°E and is bordered by the Pacific Ocean to the north, Halmahera to the west, Waigeo and West Papua to the east, and the Seram Sea to the south. It covers about and its topography comprises a number of separate basins and ridges, the chief of which is the Halmahera Basin reaching a depth of 2039 m. Extent The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) defines the Halmahera Sea as being one of the waters of the East Indian Archipelago. The IHO defines its limits as follows: ''On the North'' A line from Wajaboela ( Morotai) to Tg. Djodjefa, the Northern point of Halmahera. ''On the East.'' A line from Tg. Gorango, the Northeastern point of Morotai Island, through Sajang and Kawé Islands to the Western extremes of Waigeo and Batanta Islands across to the Northwest point of Samawati Island, down the coast to Tg. Menon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; , fossilized , also known as Papua or historically ) is the List of islands by area, world's second-largest island, with an area of . Located in Melanesia in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Mainland Australia, Australia by the wide Torres Strait, though both landmasses lie on the same continental shelf, and were united during episodes of low sea level in the Pleistocene glaciations as the combined landmass of Sahul. Numerous smaller islands are located to the west and east. The island's name was given by Spanish explorer Yñigo Ortiz de Retez during his maritime expedition of 1545 due to the perceived resemblance of the indigenous peoples of the island to those in the Guinea (region), African region of Guinea. The eastern half of the island is the major land mass of the nation of Papua New Guinea. The western half, known as Western New Guinea, forms a part of Indonesia and is organized as the provinces of Pap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambel Language
Ambel (Amber), also known as Waigeo after the island where it is primarily spoken, is a heavily Papuan-influenced Austronesian language spoken on the island of Waigeo in the Raja Ampat archipelago near the northwestern tip of West Papua, Indonesia. It is spoken by approximately 1,600 people. It is endangered, as the population is shifting to Papuan Malay and few people born after the year 2000 have any knowledge of the language. Name The name ''Ambel'' is probably derived from the Biak word ''amber'', meaning "foreigner" or "stranger". It was adapted into the language itself, where the designation is ''galí Ambél''. The alternative name ''Waigeo'' is named after the island. Speakers of ''Ambel'' consider themselves to be part of the Ma'ya tribe, hence the alternative designation ''galí Mayá'', despite Ambel only being remotely related to Ma'ya via descent from Proto-Raja Ampat–South Halmahera. Dialects Ambel is spoken by approximately 1,600 people on Waigeo, an island ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matbat Language
Matbat is a heavily Papuan-influenced Austronesian language spoken in West Papua, Indonesia, on the island of Misool, Raja Ampat islands Raja Ampat (), or the Four Kings, is an archipelago located off of the northwest tip of Bird's Head Peninsula (on the island of New Guinea), Southwest Papua , Southwest Papua province, Indonesia. It comprises over 1,500 small islands, cays, and sh .... Its dialects are ''Magey'' and ''Tomolol''. Similar to the neighboring Ma'ya language, Matbat is one of a handful of Austronesian languages with true lexical tone rather than a pitch-accent system or complete lack of phonemic tonal contrasts as with most other Austronesian languages. Distribution Matbat is spoken in the following locations within Raja Ampat Regency: *Misool Timur District: Tumolol, Lenmalas, Lenmalas Timur Barat, Audam, Foley, and Eduai villages *Misool Utara District: Atkari and Salafen villages *Misool Barat District: Magei village Phonology The phonology of the Matbat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salawati Language
Salawati is an Austronesian language spoken on Salawati Island, in the Raja Ampat Islands Raja Ampat (), or the Four Kings, is an archipelago located off of the northwest tip of Bird's Head Peninsula (on the island of New Guinea), Southwest Papua , Southwest Papua province, Indonesia. It comprises over 1,500 small islands, cays, and sh ... in Indonesian New Guinea. There is some uncertainty as to whether the dialects comprise a single language or two separate ones (divided geographically between the west and east sides of the island). Salawati is a vulnerable-to-endangered language (6b-7 on the EGIDS scale), with younger community members having only a passive command of the language. Anecdotal reports suggest that younger speakers may be learning the language in some Tepin-dialect villages, but these reports are unconfirmed. Like its related languages of the Raja Ampat Islands, Salawati has approximately 15 consonants and 5-6 vowels and lexical tone. It is mainly head-initi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Batta Language
Batta is an Austronesian language spoken in Batanta Island, one of the Raja Ampat Islands Raja Ampat (), or the Four Kings, is an archipelago located off of the northwest tip of Bird's Head Peninsula (on the island of New Guinea), Southwest Papua , Southwest Papua province, Indonesia. It comprises over 1,500 small islands, cays, and sh .... References South Halmahera–West New Guinea languages Languages of Western New Guinea {{indonesia-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biga Language
Biga is a heavily Papuan-influenced Austronesian language spoken in Southwest Papua, Indonesia in the south of the island of Misool. It is the predominant spoken language in the single village of Biga in Misol Timur Selatan District. Its status is slightly less precarious than other Raja Ampat–South Halmahera languages, as children of the village still learn the Biga language. However, its use by the younger generation is limited to speech to elders, and Papuan Malay Papuan Malay or Irian Malay is a Malay-based creole, Malay-based creole language spoken in the Papua (Indonesia), Indonesian part of New Guinea. It emerged as a contact language among tribes in Indonesian New Guinea (now Papua (Indonesian provin ... dominates child-to-child speech. Laura Arnold classifies Biga as a divergent dialect of the Ma'ya language.Arnold, Laura (2025). The Diachrony of Word Prosody in the Maˈya-Salawati Languages of Raja Ampat. Oceanic Linguistics: University of Hawai'i Press. Refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substrata (linguistics)
In linguistics, a stratum (Latin for 'layer') or strate is a historical layer of language that influences or is influenced by another language through contact. The notion of "strata" was first developed by the Italian linguist Graziadio Isaia Ascoli, and became known in the English-speaking world through the work of two different authors in 1932. Both concepts apply to a situation where an intrusive language establishes itself in the territory of another, typically as the result of migration. Whether the superstratum case (the local language persists and the intrusive language disappears) or the substratum one (the local language disappears and the intrusive language persists) applies will normally only be evident after several generations, during which the intrusive language exists within a diaspora culture. In order for the intrusive language to persist, the ''substratum'' case, the immigrant population will either need to take the position of a political elite or immigrate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papuan Languages
The Papuan languages are the non- Austronesian languages spoken on the western Pacific island of New Guinea, as well as neighbouring islands in Indonesia, Solomon Islands, and East Timor. It is a strictly geographical grouping, and does not imply a genetic relationship. New Guinea is the most linguistically diverse region in the world. Besides the Austronesian languages, there arguably are some 800 languages divided into perhaps sixty small language families, with unclear relationships to each other or to any other languages, plus many language isolates. The majority of the Papuan languages are spoken on the island of New Guinea, with a number spoken in the Bismarck Archipelago, Bougainville Island and the Solomon Islands to the east, and in Halmahera, Timor and the Alor archipelago to the west. The westernmost language, Tambora in Sumbawa, is extinct. One Papuan language, Meriam, is spoken within the national borders of Australia, in the eastern Torres Strait. Several ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halmahera
Halmahera, formerly known as Jilolo, Gilolo, or Jailolo, is the largest island in the Maluku Islands. It is part of the North Maluku Provinces of Indonesia, province of Indonesia, and Sofifi, the capital of the province, is located on the west coast of the island. Halmahera has a land area of . It is the largest island of Indonesia outside the five main islands. It had a population of 162,728 in 1995; by 2010, it had increased to 449,938 for the island itself (excluding the tip which is considered part of the Joronga Islands, but including Gebe and Ju islands) and 667,161 for the island group (including all of South Halmahera and Tidore, but not Ternate). Approximately half of the island's inhabitants are Islam in Indonesia, Muslim and half are Christianity in Indonesia, Christian. History Sparsely-populated Halmahera's fortunes have long been closely tied to those of the smaller islands of Ternate and Tidore, both off its west coast. This island was the site of Sultanate of Jai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raja Ampat Islands
Raja Ampat (), or the Four Kings, is an archipelago located off of the northwest tip of Bird's Head Peninsula (on the island of New Guinea), Southwest Papua , Southwest Papua province, Indonesia. It comprises over 1,500 small islands, cays, and shoals around the four main islands of Misool, Salawati, Batanta, and Waigeo, and the smaller island of Kofiau. The Raja Ampat archipelago straddles the equator and forms part of Coral Triangle, the Coral Triangle, an area of Southeast Asian seas containing the richest marine biodiversity on earth. The Coral Triangle itself is an approximate area west-southwest of the Philippines, east-northeast and southeast of the island of Borneo, and north, east and west of the island of New Guinea, including the seas in between. Thousands of species of marine organisms, from the tiniest cleaner shrimp and camouflaged pygmy seahorses to the majestic cetaceans and whale sharks, thrive in these waters. Administratively, the archipelago is part of the prov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |