|
Railway Electrification In Great Britain
Railway electrification in Great Britain began in the late 19th century. A range of voltages has been used, employing both overhead lines and conductor rails. The two most common systems are using overhead lines, and the third rail system used in Southeast England and on Merseyrail. As of October 2023, (38%) of the British rail network was electrified. According to Network Rail, as at 2003, 64% of the electrified network used the 25kVAC overhead system, and 36% used the 660/750VDC third-rail system.Network Rail, 2003 Technical Plan, Chapter 11 "Network Capability", page 7 "Electrification". "Approximately 40% of the rail network is currently equipped with electrification." From page 1, total network is 30764 km, 7587 km of 25 kV AC, 4285 km of 650/750 V DC and 28 km of 1500 V DC. Excludes CTRL, LUL, Old Danby test track, bulk of Tyne and Wear Metro, etc. NB it does not state what method of counting length of network is used - i.e. sidings, loops, double track etc. produce di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acton Central Station - Geograph
Acton may refer to: Places Antarctica * Mount Acton Australia * Acton, Australian Capital Territory, a suburb of Canberra * Acton, Tasmania, a suburb of Burnie * Acton Park, Tasmania, a suburb of Hobart, Tasmania, formerly known as Acton Canada * Acton, Ontario, a community * Acton Island, District of Muskoka, Ontario * Acton, New Brunswick * Acton Regional County Municipality, Quebec New Zealand * Acton, New Zealand, a rural community United Kingdom * Acton, County Armagh, Northern Ireland, a hamlet and townland * Acton, Cheshire, a village and civil parish * Acton, Cheshire (ancient parish) * Acton, Dorset, a hamlet * Acton, London, an area of west London ** Acton Green, London, between Acton and Chiswick ** East Acton ** North Acton ** South Acton, London ** West Acton ** Municipal Borough of Acton, former local government district ** Acton (UK Parliament constituency) * Acton, Northumberland, a hamlet * Acton, Shropshire, a village * Acton, Staffordshire, a hamlet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London Underground
The London Underground (also known simply as the Underground or as the Tube) is a rapid transit system serving Greater London and some parts of the adjacent home counties of Buckinghamshire, Essex and Hertfordshire in England. The Underground has its origins in the Metropolitan Railway, opening on 10 January 1863 as the world's first underground passenger railway. The Metropolitan is now part of the Circle line (London Underground), Circle, District line, District, Hammersmith & City line, Hammersmith & City and Metropolitan lines. The first line to operate underground electric locomotive, electric traction trains, the City & South London Railway in 1890, is now part of the Northern line. The network has expanded to 11 lines with of track. However, the Underground does not cover most southern parts of Greater London; there are only 33 Underground stations south of the River Thames. The system's List of London Underground stations, 272 stations collectively accommodate up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London, Brighton And South Coast Railway
The London, Brighton and South Coast Railway (LB&SCR (known also as the Brighton line, the Brighton Railway or the Brighton)) was a railway company in the United Kingdom from 1846 to 1922. Its territory formed a rough triangle, with London at its apex, practically the whole coastline of Sussex as its base, covering a large part of Surrey. It was bounded on its western side by the London and South Western Railway (L&SWR), which provided an alternative route to Portsmouth. On its eastern side the LB&SCR was bounded by the South Eastern Railway (England), South Eastern Railway (SER)—later one component of the South Eastern and Chatham Railway (SE&CR)—which provided an alternative route to Bexhill-on-Sea, Bexhill, St Leonards-on-Sea, and Hastings. The LB&SCR had the most direct routes from London to the south coast seaside resorts of Brighton, Eastbourne, Worthing, Littlehampton and Bognor Regis, and to the ports of Newhaven, East Sussex, Newhaven and Shoreham-by-Sea. It served ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midland Railway
The Midland Railway (MR) was a railway company in the United Kingdom from 1844 in rail transport, 1844. The Midland was one of the largest railway companies in Britain in the early 20th century, and the largest employer in Derby, where it had its headquarters. It amalgamated with several other railways to create the London, Midland and Scottish Railway at Railways Act 1921, grouping in 1923. The Midland had a large network of lines emanating from Derby, stretching to St Pancras railway station, London St Pancras, Manchester Central railway station, Manchester, Carlisle railway station, Carlisle, Birmingham Curzon Street railway station (1838–1966), Birmingham, and Bristol Temple Meads railway station, Bristol. It expanded as much through acquisitions as by building its own lines. It also operated ships from Heysham in Lancashire to Douglas, Isle of Man, Douglas and Belfast. A large amount of the Midland's infrastructure remains in use and visible, such as the Midland Main Lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
15 KV AC Railway Electrification
Railway electrification using at are used on transport railways in Rail transport in Germany, Germany, Rail transport in Austria, Austria, Rail transport in Switzerland, Switzerland, Rail transport in Sweden, Sweden, and Rail transport in Norway, Norway. The high voltage enables high power transmission with the lower frequency reducing the losses of the traction motors that were available at the beginning of the 20th century. Globally, railway electrification in late 20th century tends to use 25 kV AC railway electrification, AC systems which has become the preferred standard for new railway electrifications. Nevertheless, local extensions of the existing network is commonplace. In particular, the Gotthard Base Tunnel (opened on 1 June 2016) uses 15 kV, 16.7 Hz electrification. Due to high conversion costs, it is unlikely that existing systems will be converted to despite the fact that this would reduce the weight of the on-board step-down transformers to one t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crossens Railway Station
Crossens railway station was a railway station serving Crossens, a suburb of Southport, Sefton, Merseyside, England. History Located on the Lancashire and Yorkshire Railway main line between and , it was opened to passengers by the West Lancashire Railwayin 1878. In April 1904, it became the last electrified station on the Lancashire and Yorkshire Railway's suburban lines from Liverpool Exchange railway station Liverpool Exchange railway station was a railway station located in the city centre of Liverpool, England. Of the four terminal stations in Liverpool's city centre, Exchange station was the only station not accessed via a tunnel. The station w ..., forming a terminus of the Southport - Crossens electric branch. Services ended on 6 September 1964 with the closure of the Southport to Preston line.Cadwallader, Jonathan and Jenkins, Martin (2010) ''Merseyside Electrics'', Ian Allan Publishing, (p34 has colour photo of Crossens station looking north, with electric tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southport Railway Station
Southport railway station serves the town of Southport, Merseyside, England. The station is the terminal of the electricified Southport branch of the Northern Line (Merseyrail), Northern Line of the electric Merseyrail network and the diesel-operated Manchester-Southport Line. It is the fourth busiest station on the Merseyrail network. The station and services to are operated by Merseyrail, with Manchester services operated by Northern Trains. History The Liverpool, Crosby and Southport Railway (LC&SR) opened a line on 24 July 1848 from Liverpool to a temporary station at Southport Eastbank Street railway station, Eastbank Street, about half a mile short of the current terminus. The LC&SR line was extended on 5 August 1851 to the current station which opened as Southport Chapel Street. The LC&SR refused to allow the Manchester and Southport Railway (M&SR) to use its station and therefore the East Lancashire Railway (ELR) (one of the co-owners of the M&SR) built station next ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liverpool Exchange Railway Station
Liverpool Exchange railway station was a railway station located in the city centre of Liverpool, England. Of the four terminal stations in Liverpool's city centre, Exchange station was the only station not accessed via a tunnel. The station was damaged during World War II and lost a proportion of the trainshed roof, which was never rebuilt. The station's long-distance services were switched to in the 1960s, and, as a terminus, the station became redundant in the late 1970s, when its remaining local services switched to the newly opened Merseyrail tunnels under Liverpool city centre. It was closed in 1977, being replaced by the new underground station nearby. First station The grandly-appointed station was jointly owned and operated by the Lancashire and Yorkshire Railway (L&YR) and East Lancashire Railway 1844-1859, East Lancashire Railway (ELR), it opened on 13 May 1850, replacing an earlier temporary terminus at a half-mile (0.8 km) further out of Liverpool. On ope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lancashire & Yorkshire Railway
The Lancashire and Yorkshire Railway (L&YR) was a major History of rail transport in Great Britain, British railway company before the Railways Act 1921, 1923 Grouping. It was Incorporation (business)#Incorporation in the United Kingdom, incorporated in 1847 from an amalgamation of several existing railways. It was the third-largest railway system based in northern England (after the Midland Railway, Midland and North Eastern Railway (United Kingdom), North Eastern Railways). The intensity of its service was reflected in the 1,650 steam locomotive, locomotives it owned – it was by far the most densely-trafficked system in the British Isles with more locomotives per mile than any other company – and that one third of its 738 signal boxes controlled junctions averaging one every . No two adjacent stations were more than apart and its 1,904 passenger services occupied 57 pages in ''George Bradshaw#Bradshaw.27s railway timetables, Bradshaw'', a number exceed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mersey Railway
The Mersey Railway was the passenger railway connecting the communities of Liverpool and Birkenhead, England. It is currently a part of the Merseyrail network. It was extended further into the Wirral Peninsula, which lies on the opposite bank of the River Mersey to Liverpool. Both sides of the river were connected via the Mersey Railway Tunnel. The railway opened in 1886 with four stations using steam locomotives hauling unheated wooden carriages; in the next six years the line was extended with the opening of three more stations. Using the first tunnel under the Mersey, the line is the world's oldest underground railway outside London. Because the steam locomotives created a polluted atmosphere in the tunnel despite the forced ventilation system, many passengers reverted back to using the river ferries making the railway bankrupt by 1900. Recovery came after the railway adopted electric traction in 1903. The Mersey Railway remained independent after the Railways Act 1921, rail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
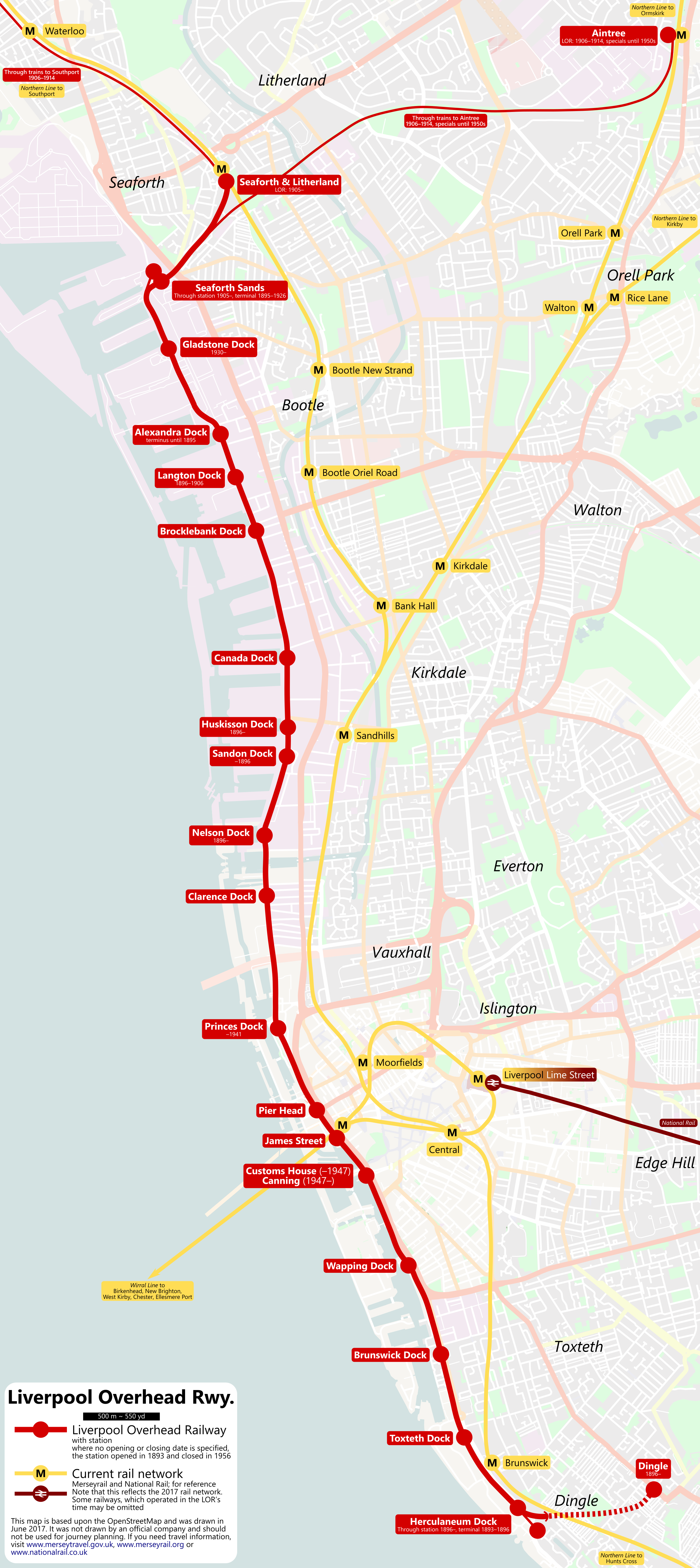
Liverpool Overhead Railway
The Liverpool Overhead Railway (known locally as the Dockers' Umbrella or Ovee) was an overhead railway in Liverpool that operated along the Liverpool Docks and opened in 1893 with lightweight electric multiple units. The railway had a number of world firsts: it was the first electric elevated railway, the first to use automatic signalling, electric colour light signals and Liverpool Overhead Railway electric units, electric multiple units, and was home to one of the first passenger escalators at a railway station. It was the second-oldest electric metro in the world, being preceded by the 1890 City and South London Railway. Originally spanning from Alexandra Dock, Liverpool, Alexandra Dock to Herculaneum Dock, the railway was extended at both ends over the years of operation, as far south as Dingle railway station, Dingle and north to Seaforth & Litherland railway station, Seaforth & Litherland. A number of stations opened and closed during the railway's operation owing to rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |