|
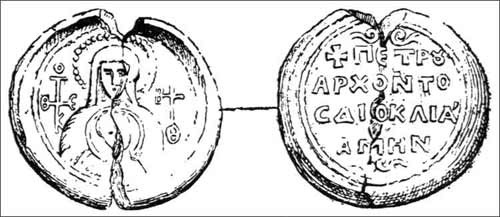
Radoslav Of Duklja
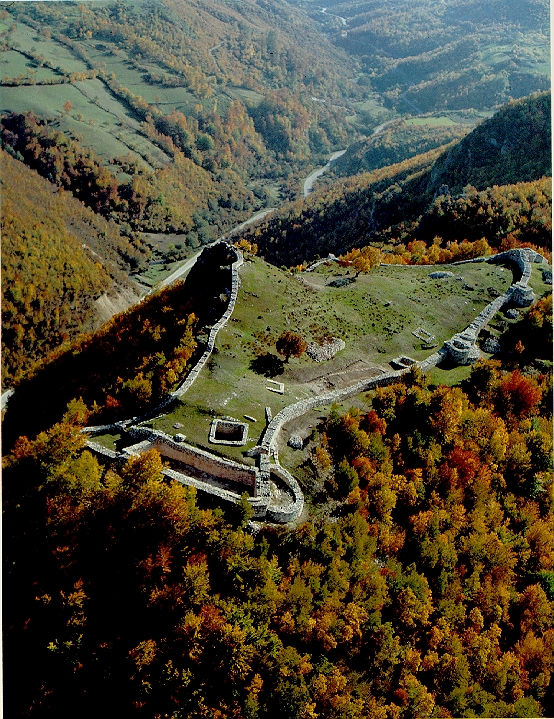
Radoslav ( sr-cyr, Радослав) was the Prince of Duklja from 1146 to 1149. As the oldest son, he succeeded as ruler of Duklja after the death of his father, Gradinja in 1146. He was installed by Manuel I Komnenos upon a visit to Constantinople to pay homage to the Emperor. Unlike his father who was a titular king, Radoslav had the title of Prince (''knez''). Radoslav began his rule at a time when the Serbs of Raška (the Vukanovići) had ambitions towards Duklja. In ca. 1148, the political situation in the Balkans was divided by two sides, one being the alliance of the Byzantines and Venice, the other the Normans and Hungarians. The Normans were sure of the danger that the battlefield would bring from the Balkans to their area in Italy. Manuel also allied himself with the Germans after defeating the Cumans in 1148. The Serbs, Hungarians and Normans exchanged envoys, being in the interest of the Normans to stop Manuel's plans to recover Italy. The Serbs under brothers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
List Of Rulers Of Duklja
This is a list of monarchs of Duklja. List of monarchs Duklja continues as a crownland of Grand Principality of Serbia, under Vukan Nemanjić and Đorđe Nemanjić. Monarchs according to the ''Chronicle of the Priest of Duklja'' The following monarchs are mentioned only in the ''Chronicle of the Priest of Duklja'' (CPD), written by a Catholic monk of the Cistercian order by the name of Roger (Rudger) at the request of Croatian Ban Paul Šubić. It was written in two versions – the first one in Split in 1298 while Roger was handling the Archbishop of Split's finances, and the second ca. 1300, while he was the Archbishop of Antivari (Bar). The chronicle, built round a core written in Slavonic, but added to by a bishop of Bar intent on demonstrating his diocese' superiority over that of Split, is one of the oldest known written sources, but only Latin redactions from the 16th and 17th centuries have been preserved. Historians have largely discounted it, though it contains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Chronicle Of The Priest Of Duklja
The ''Chronicle of the Priest of Dioclea or Duklja'' ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, Ljetopis popa Dukljanina, Љетопис попа Дукљанина; ) is the usual name given to a medieval chronicle written in two versions between 1295 and 1301 by an ecclesiastic from Duklja, recently identified as Rudger, Archbishop of Bar. Its oldest preserved copy is in Latin from the 17th century, and modern historians have debated the text's date of composition (mid-12th to late 16th century) and authenticity. It contains some semi-mythical material on the early history of the Western South Slavs. Historians have yet to discount the work as based on inaccuracies and fiction. The postulates are there that Slavs lived in the Balkans from the 5th- to the 12th-century. It recounts the history of Dalmatia and nearby regions from the 5th to the mid-12th century. The section "Life of St. Jovan Vladimir", is believed to be one of the local traditions integrated into the narrative. Authorship and date The wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
People From The Grand Principality Of Serbia
The term "the people" refers to the public or common mass of people of a polity. As such it is a concept of human rights law, international law as well as constitutional law, particularly used for claims of popular sovereignty. In contrast, a people is any plurality of persons considered as a whole. Used in politics and law, the term "a people" refers to the collective or community of an ethnic group or nation. Concepts Legal Chapter One, Article One of the Charter of the United Nations states that "peoples" have the right to self-determination. Though the mere status as peoples and the right to self-determination, as for example in the case of Indigenous peoples (''peoples'', as in all groups of indigenous people, not merely all indigenous persons as in ''indigenous people''), does not automatically provide for independent sovereignty and therefore secession. Indeed, judge Ivor Jennings identified the inherent problems in the right of "peoples" to self-determination, as i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Monarchs Of Duklja
A monarch () is a head of stateWebster's II New College Dictionary. "Monarch". Houghton Mifflin. Boston. 2001. p. 707. Life tenure, for life or until abdication, and therefore the head of state of a monarchy. A monarch may exercise the highest authority and power in the Sovereign state, state, or others may wield that power on behalf of the monarch. Usually, a monarch either personally inheritance, inherits the lawful right to exercise the state's sovereign rights (often referred to as ''the throne'' or ''the Crown, the crown'') or is elective monarchy, selected by an established process from a family or cohort eligible to provide the nation's monarch. Alternatively, an individual may self-proclaimed monarchy, proclaim oneself monarch, which may be backed and Legitimacy (political), legitimated through acclamation, right of conquest or a combination of means. If a young child is crowned the monarch, then a regent is often appointed to govern until the monarch reaches the requisi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
12th-century Serbian Royalty
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number, numeral, and glyph. It is the first and smallest positive integer of the infinite sequence of natural numbers. This fundamental property has led to its unique uses in other fields, ranging from science to sports, where it commonly denotes the first, leading, or top thing in a group. 1 is the unit of counting or measurement, a determiner for singular nouns, and a gender-neutral pronoun. Historically, the representation of 1 evolved from ancient Sumerian and Babylonian symbols to the modern Arabic numeral. In mathematics, 1 is the multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number. In digital technology, 1 represents the "on" state in binary code, the foundation of computing. Philosophically, 1 symbolizes the ultimate reality or source of existence in various traditions. In mathematics The number 1 is the first natural number after 0. Each natural number, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Desa, Grand Prince Of Serbia
Desa ( sr-cyr, Деса)He is also known as Desa Vukanović. was the Grand Prince of Serbia from ca. 1162 to ca. 1165. He was one of several sons of grand prince Uroš I (d. 1145). Sometime between 1153 and 1155, Desa tried to depose his brother, the ruling grand prince Uroš II, but failed to establish himself as a new ruler. Only later, after the abdication of their other brother, the next grand prince Beloš ca. 1162, Desa became the new ruler of Serbia. He tried to challenge the Byzantine suzerainty over Serbia, but was deposed by emperor Manuel I Komnenos. Before he became the grand prince, Desa ruled as prince of Duklja, Travunija and Zahumlje, ca. from 1149 to 1162. Biography Desa was the youngest of three sons of Uroš I, the Grand Prince of Serbia from 1112 to 1145. His mother was Anna, a Byzantine noblewoman. The eldest son Uroš II succeeded their father in 1145. Their sister, Helena, married Béla II of Hungary (r. 1131–41). Upon the death of Béla II, Helena an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Grand Principality Of Serbia
The Grand Principality of Serbia ( sr-Cyrl-Latn, Великожупанска Србија, Velikožupanska Srbija, separator=" / "), also known by the anachronistic exonym Raška (region), Rascia ( sr-Cyrl-Latn, Рашка, Raška, separator=" / ", link=no), was a medieval Serbs, Serbian state that existed from the second half of the 11th century up until 1217, when it was transformed into the Kingdom of Serbia (1217–1346), Kingdom of Serbia. After the Grand Principality of Serbia emerged, it gradually expanded during the 12th century, encompassing various neighbouring regions, including territories of Raška (region), Raška ( sr-Cyrl, Рашка; ), modern Montenegro, Herzegovina, and southern Dalmatia. It was founded by Grand Prince Vukan, Grand Prince of Serbia, Vukan, who initially served as the regional governor of the principality ( 1082), appointed by King Constantine Bodin. During the Byzantine–Serbian wars ( 1090), Vukan gained prominence and became a self-governing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Patronymic
A patronymic, or patronym, is a component of a personal name based on the given name of one's father, grandfather (more specifically an avonymic), or an earlier male ancestor. It is the male equivalent of a matronymic. Patronymics are used, by custom or official policy, in many countries worldwide, although elsewhere their use has been replaced by or transformed into patronymic surnames. Examples of such transformations include common English surnames such as Johnson (surname), Johnson (son of John). Origins of terms The usual noun and adjective in English is ''patronymic'', but as a noun this exists in free variation alongside ''patronym''. The first part of the word ''patronym'' comes from Greek language, Greek πατήρ ''patēr'' 'father' (Genitive case, GEN πατρός ''patros'' whence the combining form πατρο- ''patro''-); the second part comes from Greek ὄνυμα ''onyma'', a variant form of ὄνομα ''onoma'' 'name'. In the form ''patronymic'', this stand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Slavic Name
Given names originating from the Slavic languages are most common in Slavic countries. The main types of Slavic names: * Two-base names, often ending in mir/měr (''Ostromir/měr'', ''Tihomir/měr'', '' Němir/měr''), *voldъ (''Vsevolod'', ''Rogvolod''), *pъlkъ (''Svetopolk'', ''Yaropolk''), *slavъ (''Vladislav'', ''Dobroslav'', ''Vseslav'') and their derivatives (''Dobrynya, Tishila, Ratisha, Putyata'', etc.) * Names from flora and fauna (''Shchuka'' - pike, ''Yersh'' - ruffe, ''Zayac'' - hare, ''Wolk''/'' Vuk'' - wolf, ''Orel'' - eagle) * Names in order of birth (''Pervusha'' - born first, ''Vtorusha''/''Vtorak'' - born second, ''Tretiusha''/''Tretyak'' - born third) * Names according to human qualities (''Hrabr'' - brave, ''Milana/Milena'' - beautiful, ''Milosh'' - beloved, ''Nadezhda -'' hope) * Names containing the root of the name of a Slavic deity (''Troyan'', ''Perunek/Peruvit'', ''Yarovit'', ''Stribor'', ''Šventaragis'', ''Veleslava'') History In pre-Christi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Radoslav
Radoslav () is a common Slavic masculine given name, derived from ''rad-'' ("happy, eager, to care") and ''slava'' ("glory, fame"), both very common in Slavic dithematic names. It roughly means "eager glory". It is known since the Middle Ages. The earliest known Radoslav was a 9th-century Serbian ruler. Notable people with the name Royalty and nobility * Radoslav of Serbia, Prince of Serbia (r. 800–822) * Radoslav of Duklja, Prince of Duklja (r. 1146–48) * Radoslav, Lord of Hum ( 12th century) * Stefan Radoslav (c. 1192 – c. 1234), king of Serbia from 1228 to 1233 * Radoslav Babonić ( 1264–95), Croatian–Hungarian magnate * Radoslav Hlapen ( 1350–71), Serbian magnate * Radoslav, 13th–14th-century Bulgarian ''sebastokrator'' * Radoslav Pavlović Radinović (died 1441), Bosnian nobleman * Radoslav Čelnik, 16th-century duke (voivode) of Srem Other * Radoslav (painter), Serbian 15th-century painter * Radoslav Anev (born 1985), Bulgarian footballer * Radosla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Charles Du Fresne, Sieur Du Cange
Charles du Fresne, sieur du Cange (; December 18, 1610 in Amiens – October 23, 1688 in Paris, aged 77), also known simply as Charles Dufresne, was a distinguished French philologist and historian of the Middle Ages and Byzantium. Life Educated by Jesuits, du Cange studied law and practiced for several years before assuming the office of Treasurer of France. Du Cange was a busy, energetic man who pursued historical scholarship alongside his demanding official duties and his role as head of a large family. Du Cange's most important work is his ''Glossarium ad scriptores mediae et infimae Latinitatis'' (Glossary of writers in medieval and late Latin, Paris, 1678, 3 vol.), revised and expanded under various titles, for example, ''Glossarium manuale ad scriptores mediae et infimae Latinitatis'' (Halae, 1772–1784) or from 1840 onward, ''Glossarium mediae et infimae Latinitatis'' (Glossary of medieval and late Latin). This work, together with a glossary of medieval and late Gree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |