|
RPL11
60S ribosomal protein L11 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''RPL11'' gene. Function Ribosomes, the organelles that catalyze protein synthesis, consist of a small 40S subunit and a large 60S subunit. Together these subunits are composed of 4 RNA species and approximately 80 structurally distinct proteins. This gene encodes a ribosomal protein that is a component of the 60S subunit. The protein belongs to the L5P family of ribosomal proteins. It is located in the cytoplasm. The protein probably associates with the 5S rRNA. Alternative splice variants encoding different isoforms may exist, but they have not been fully characterized. As is typical for genes encoding ribosomal proteins, there are multiple processed pseudogenes of this gene dispersed through the genome. Interactions RPL11 has been shown to interact with: * BLMH, * Mdm2, * NOP53, * P16, * P53, and * Promyelocytic leukemia protein Promyelocytic leukemia protein (PML) (also known as MYL, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ribosomal Protein
A ribosomal protein (r-protein or rProtein) is any of the proteins that, in conjunction with rRNA, make up the ribosomal subunits involved in the cellular process of translation. ''E. coli'', other bacteria and Archaea have a 30S small subunit and a 50S large subunit, whereas humans and yeasts have a 40S small subunit and a 60S large subunit. Equivalent subunits are frequently numbered differently between bacteria, Archaea, yeasts and humans. A large part of the knowledge about these organic molecules has come from the study of '' E. coli'' ribosomes. All ribosomal proteins have been isolated and many specific antibodies have been produced. These, together with electronic microscopy and the use of certain reactives, have allowed for the determination of the topography of the proteins in the ribosome. More recently, a near-complete (near)atomic picture of the ribosomal proteins is emerging from the latest high-resolution cryo-EM data (including ). Conservation Ribosomal p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BLMH
Bleomycin hydrolase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''BLMH'' gene. Bleomycin hydrolase (BMH) is a cytoplasmic cysteine peptidase that is highly conserved through evolution. Its biological function is hydrolysis of the reactive electrophile homocysteine thiolactone. Another of its activities is metabolic inactivation of the glycopeptide bleomycin (BLM), an essential component of combination chemotherapy regimens for cancer. The protein contains the signature active site residues of the cysteine protease papain superfamily. Interactions BLMH has been shown to Protein-protein interaction, interact with RPL29, RPL11, UBE2I and Amyloid precursor protein Amyloid-beta precursor protein (APP) is an integral membrane protein expressed in many biological tissue, tissues and concentrated in the synapses of neurons. It functions as a cell surface receptor and has been implicated as a regulator of s .... References External links * * Further reading * * * * * * * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P16 (gene)
p16 (also known as p16INK4a, cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A, CDKN2A, multiple tumor suppressor 1 and numerous other synonyms), is a protein that slows cell division by slowing the progression of the cell cycle from the G1 phase to the S phase, thereby acting as a tumor suppressor. It is encoded by the ''CDKN2A'' gene. A deletion (the omission of a part of the DNA sequence during replication) in this gene can result in insufficient or non-functional p16, accelerating the cell cycle and resulting in many types of cancer. p16 can be used as a biomarker to improve the histological diagnostic accuracy of grade 3 cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN). p16 is also implicated in the prevention of melanoma, oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma, cervical cancer, vulvar cancer and esophageal cancer. p16 was discovered in 1993. It is a protein with 148 amino acids and a molecular weight of 16 kDa that comprises four ankyrin repeats. The name of p16 is derived from its molec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Promyelocytic Leukemia Protein
Promyelocytic leukemia protein (PML) (also known as MYL, RNF71, PP8675 or TRIM19) is the protein product of the ''PML'' gene. PML protein is a tumor suppressor protein required for the assembly of a number of nuclear structures, called PML-nuclear bodies, which form amongst the chromatin of the cell nucleus. These nuclear bodies are present in mammalian nuclei, at about 1 to 30 per cell nucleus. PML-NBs are known to have a number of regulatory cellular functions, including involvement in programmed cell death, genome stability, antiviral effects and controlling cell division. PML mutation or loss, and the subsequent dysregulation of these processes, has been implicated in a variety of cancers. History PML was poorly understood until described in the findings of Grignani ''et al'' in their 1996 study of patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL). It was found that the karyotype of 90% of APL patients included a reciprocal translocation, resulting in the fusion of the gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and non-coding genes. During gene expression (the synthesis of Gene product, RNA or protein from a gene), DNA is first transcription (biology), copied into RNA. RNA can be non-coding RNA, directly functional or be the intermediate protein biosynthesis, template for the synthesis of a protein. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring, is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits from one generation to the next. These genes make up different DNA sequences, together called a genotype, that is specific to every given individual, within the gene pool of the population (biology), population of a given species. The genotype, along with environmental and developmental factors, ultimately determines the phenotype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ribosome
Ribosomes () are molecular machine, macromolecular machines, found within all cell (biology), cells, that perform Translation (biology), biological protein synthesis (messenger RNA translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by the codons of messenger RNA molecules to form polypeptide chains. Ribosomes consist of two major components: the small and large ribosomal subunits. Each subunit consists of one or more ribosomal RNA molecules and many ribosomal proteins (). The ribosomes and associated molecules are also known as the ''translational apparatus''. Overview The sequence of DNA that encodes the sequence of the amino acids in a protein is transcribed into a messenger RNA (mRNA) chain. Ribosomes bind to the messenger RNA molecules and use the RNA's sequence of nucleotides to determine the sequence of amino acids needed to generate a protein. Amino acids are selected and carried to the ribosome by transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules, which enter the riboso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organelle
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit, usually within a cell (biology), cell, that has a specific function. The name ''organelle'' comes from the idea that these structures are parts of cells, as Organ (anatomy), organs are to the Human body, body, hence ''organelle,'' the suffix ''-elle'' being a diminutive. Organelles are either separately enclosed within their own lipid bilayers (also called membrane-bounded organelles) or are spatially distinct functional units without a surrounding lipid bilayer (non-membrane bounded organelles). Although most organelles are functional units within cells, some functional units that extend outside of cells are often termed organelles, such as cilia, the flagellum and archaellum, and the trichocyst (these could be referred to as membrane bound in the sense that they are attached to (or bound to) the membrane). Organelles are identified by microscopy, and can also be purified by cell fractionation. There are many types of organe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Synthesis
Protein biosynthesis, or protein synthesis, is a core biological process, occurring inside cells, balancing the loss of cellular proteins (via degradation or export) through the production of new proteins. Proteins perform a number of critical functions as enzymes, structural proteins or hormones. Protein synthesis is a very similar process for both prokaryotes and eukaryotes but there are some distinct differences. Protein synthesis can be divided broadly into two phases: transcription and translation. During transcription, a section of DNA encoding a protein, known as a gene, is converted into a molecule called messenger RNA (mRNA). This conversion is carried out by enzymes, known as RNA polymerases, in the nucleus of the cell. In eukaryotes, this mRNA is initially produced in a premature form (pre-mRNA) which undergoes post-transcriptional modifications to produce mature mRNA. The mature mRNA is exported from the cell nucleus via nuclear pores to the cytoplasm of the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm describes all the material within a eukaryotic or prokaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, including the organelles and excluding the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. The material inside the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. The main components of the cytoplasm are the cytosol (a gel-like substance), the cell's internal sub-structures, and various cytoplasmic inclusions. In eukaryotes the cytoplasm also includes the nucleus, and other membrane-bound organelles.The cytoplasm is about 80% water and is usually colorless. The submicroscopic ground cell substance, or cytoplasmic matrix, that remains after the exclusion of the cell organelles and particles is groundplasm. It is the hyaloplasm of light microscopy, a highly complex, polyphasic system in which all resolvable cytoplasmic elements are suspended, including the larger organelles such as the ribosomes, mitochondria, plant plasti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
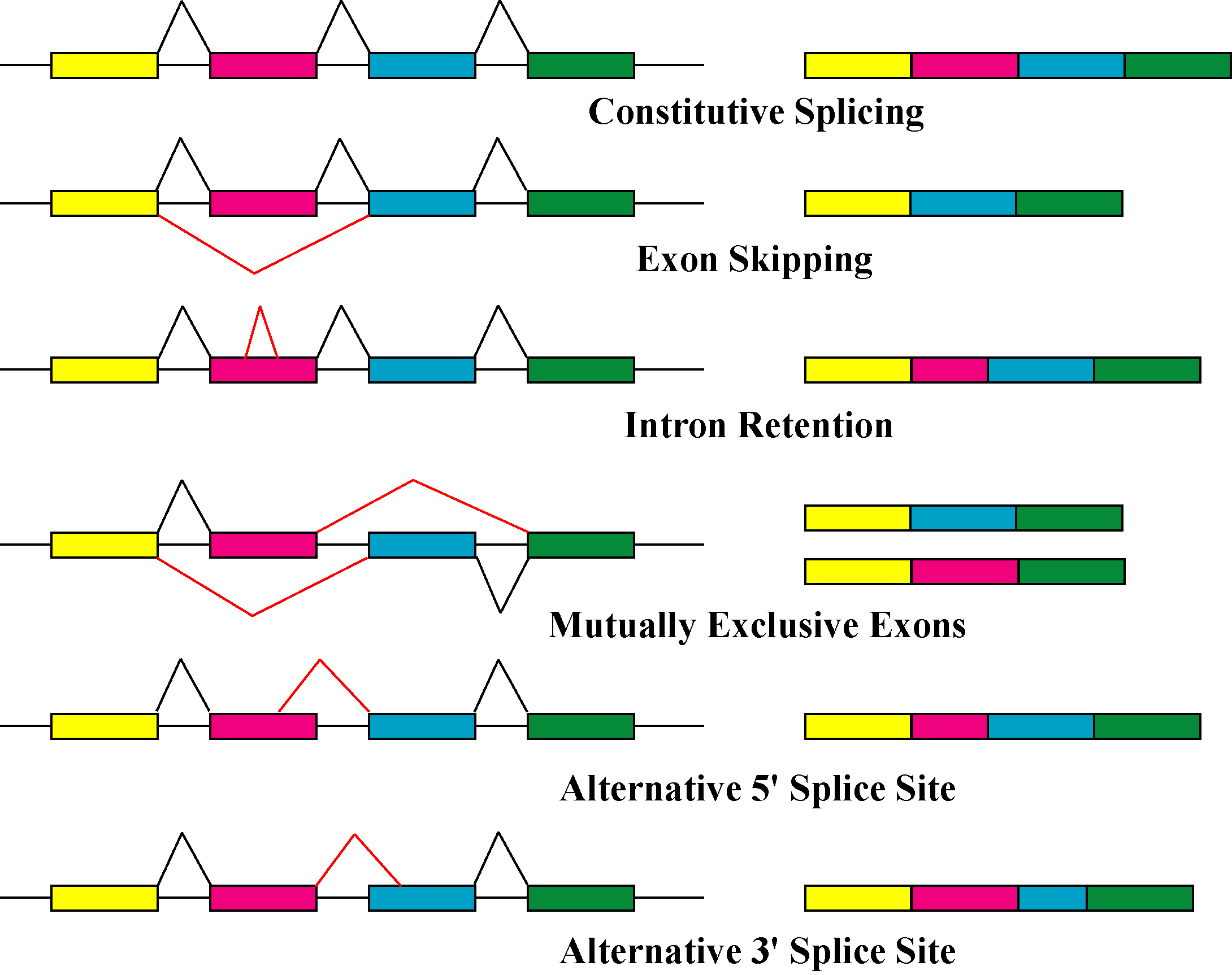
Alternative Splicing
Alternative splicing, alternative RNA splicing, or differential splicing, is an alternative RNA splicing, splicing process during gene expression that allows a single gene to produce different splice variants. For example, some exons of a gene may be included within or excluded from the final RNA product of the gene. This means the exons are joined in different combinations, leading to different splice variants. In the case of protein-coding genes, the proteins translated from these splice variants may contain differences in their amino acid sequence and in their biological functions (see Figure). Biologically relevant alternative splicing occurs as a normal phenomenon in eukaryotes, where it increases the number of proteins that can be encoded by the genome. In humans, it is widely believed that ~95% of multi-exonic genes are alternatively spliced to produce functional alternative products from the same gene but many scientists believe that most of the observed splice variants ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isoform
A protein isoform, or "protein variant", is a member of a set of highly similar proteins that originate from a single gene and are the result of genetic differences. While many perform the same or similar biological roles, some isoforms have unique functions. A set of protein isoforms may be formed from alternative splicings, variable promoter usage, or other post-transcriptional modifications of a single gene; post-translational modifications are generally not considered. (For that, see Proteoforms.) Through RNA splicing mechanisms, mRNA has the ability to select different protein-coding segments ( exons) of a gene, or even different parts of exons from RNA to form different mRNA sequences. Each unique sequence produces a specific form of a protein. The discovery of isoforms could explain the discrepancy between the small number of protein coding regions of genes revealed by the human genome project and the large diversity of proteins seen in an organism: different proteins e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |